Abstract
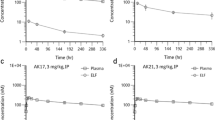
Extracorporeal immunoadsorption is a new technique for removal of circulating radiolabeled antibody from the peripheral blood (1) to reduce background activity for improved tumor imaging, and (2) to reduce whole-body and marrow toxicity when high doses of radiolabeled antibodies are used for antitumor therapy. A pharmacokinetic model was developed to describe plasma disappearance of111In -KC-4G3 prior to, during, and after immunoadsorption in humans. The model is developed based on a two-compartment open model, and during immunoadsorption a third compartment is added for removed radioactivity by the immunoadsorption column. Goodness-of-fit statistics indicate a good fit of the model to the data. The resulting pharmacokinetic parameters for a selected patient are V1=2.64L, Vss=3.64 L, t1/2α=3.77hr, and t1/2β hr. The immunoadsorption clearance (CL1A=19.3 ml/min) was 21-fold greater than the patient's plasma clearance (CL10=0.899 ml/min), indicating a very effective immunoadsorption process. The model predicts an increase in plasma radioactivity upon termination of immunoadsorption, probably due to redistribution of radioactivity from the extravascular compartment to the plasma in response to the rapid decline in plasma radioactivity during immunoadsorption. Two series of simulations were performed to examine the influence of onset time and duration of immunoadsorption. In series one the onset time was varied and in series two immunoadsorption duration was varied. In series one, the predicted radioactivity amounts adsorbed by the immunoadsorption column ranged from 75% of the injected dose (4-hr onset) to 52% of the injected dose (24-hr onset). In series two, immunoadsorbed radioactivity ranged from 32% (2-hr duration) to 64% of the injected dose (12-hr duration). When instituted as early as 4 hr, the predictions suggest that earlier immmoadsorption onset improves the effectiveness of radioactivity removal, relating to higher early circulation concentrations, and longer immunoadsorption periods remove more radioactivity, but also result in larger predicted radioactivity redistribution from tissue to plasma. To employ the immunoadsorption procedure for tumor imaging and therapy optimally, the data and our predictions indicate that a compromise must be made that will balance immunoadsorption onset and duration against tumor radioactivity uptake and subsequent radioactivity redistribution from tissues back to plasma. Together with biologic considerations providing sufficient antigenantibody interaction and dependent on the utilized radioisotope, these data support the utility of extracorporeal immunoadsorption during the radioimmunodetection of cancer and for future therapeutic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Schlom. Basic principles in applications of monoclonal antibodies in the management of carcinomas: The Richard and Hinda Rosenthal Foundation Award Lecture.Cancer Res. 46:3225–3238 (1986).
R. K. Oldham. Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy.J. Clin. Oncol. 1(9):582–590 (1983).
S. M. Larson. Radiolabeled monoclonal antitumor antibodies in diagnosis and therapy.J. Nucl. Med. 26:538–545 (1985).
D. Hofheinz, D. G. Dienhart, G. Miller, S. Healy, P. Furmanski, S. Sedlacek, C. Longley, P. A. Bunn, Jr., and K. Kortright. Monoclonal antibody, KC-4G3, recognizes a novel widely expressed antigen on human epithelial cancers.Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 28:391 (1987).
C. Longley, P. Furmanski, D. G. Dienhart, J. Lear, D. Bloedow, R. Kasliwal, and P. A. Bunn. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and gamma camera imaging of111In-KC-4G3 murine monoclonal antibody in athymic nude mice with or without human tumor xenografts.Cancer Res. 50:5954–5961 (1990).
D. G. Dienhart, R. F. Schmelter, J. L. Lear, G. J. Miller, S. D. Glenn, D. C. Bloedow, R. Kasliwal, P. Moran, P. Seligman, J. R. Murphy, K. Kortright, and P. A. Bunn. Imaging of non-small cell lung cancers with a monoclonal antibody, KC-4G3, which recognizes a human milk fat globule antigen.Cancer Res. 50:7068–7076 (1990).
J. L. Murray, L. M. Lamki, L. J. Shanken, M. E. Blake, C. E. Plager, R. S. Benjamin, S. Schweighardt, M. W. Unger, and M. G. Rosenblum. Immunospecific saturable clearance mechanisms for indium-111-labeled anti-melanoma monoclonal antibody 96.5 in humans.Cancer Res. 48:4417–4422 (1988).
T. W. Griffin, F. Bokhari, J. Collins, M. Stochl, M. Bernier, M. Gionet, D. Siebecker, M. Wertheimer, E. S. Giroves, L. Greenfield, L. L. Houston, P. W. Doherty, and J. Wilson. A preliminary pharmacokinetic study of 111-In-labeled 260F9 anti-(breast cancer) antibody in patients.Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 29:43–50 (1989).
P. H. Brown, G. T. Krishnamurthy, F. E. Turner, R. K. Denney, S. A. Gilbert, and M. E. Slauson. Primary lung cancer: Biodistribution and dosimetry of two In-111-labeled monoclonal antibodies.Radiology 173:701–705 (1989).
H. Kalofonos, G. Rowlinson, and A. A. Epenetos. Enhancement of monoclonal antibody uptake in human colon tumor xenografts following irradiation.Cancer Res. 50:159–163 (1990).
B. A. Brown, R. D. Comecin, P. L. Jones, F. A. Liberatore, W. P. Neacy, H. Sands, and B. M. Gallagher. Pharmacokinetics of the monoclonal antibody B72.3 and its fragments labeled with either125I or111In.Cancer Res. 47:1149–1154 (1987).
R. R. Eger, D. G. Covell, J. A. Carrasquillo, P. G. Abrams, K. A. Foon, J. C. Reynolds, R. W. Schroff, A. C. Morgan, S. M. Larson, and J. N. Weinstein. Kinetic model for the biodistribution of an 111 -In-labeled monoclonal antibody in humans.Cancer Res. 47:3328–3336 (1987).
M. G. Rosenblum, J. L. Murray, T. P. Haynie, H. J. Glenn, M. F. Jahns, R. S. Benjamin, J. M. Frincke, D. J. Carlo, and E. M. Hersh. Pharmacokinetics of 111-In-labeled Anti-p97 monoclonal antibody in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma.Cancer Res. 45:2382–2386 (1985).
D. J. Hnatowich, T. W. Griffin, C. Koscincyk, M. Rusckowski, R. L. Childs, J. A. Mattis, D. Shealy, and P. W. Doherty. Pharmacokinetics of an indium-111-labeled monoclonal antibody in cancer patients.J. Nucl. Med. 26:849–858 (1985).
D. J. Hnatowich, M. Gionet, M. Rusckowski, D. A. Siebecker, J. Roche, D. Shealy, J. A. Mattis, J. Wilson, J. McGann, R. E. Hunter, T. Griffin, and P. W. Doherty. Pharmacokinetics of 111-In-labeled OC-125 antibody in cancer patients compared with the 19-9 antibody.Cancer Res. 47:6111–6117 (1987).
S. E. Halpern, P. L. Hagan, P. R. Garver, J. A. Koziol, A. W. N. Chen, J. M. Frincke, R. M. Bartholomew, G. S. David, and T. H. Adams. Stability, characterization, and kinetics of 111-In-labeled monoclonal antitumor antibodies in normal animals and nude mousehuman tumor models.Cancer Res. 43:5347–5355 (1983).
D. G. Dienhart, R. Kasliwal, J. L. Lear, T. K. Johnson, D. C. Bloedow, C. Hartmann, P. A. Seligman, G. J. Miller, S. D. Glenn, M. J. McAteer, D. Thickman, A. Feyerabend, E. N. Maddock, S. W. Maddock, and P. A. Bunn, Jr. Extracorporeal immunoadsorption of radiolabeled monoclonal antibody: A method for reduction of background radioactivity and its potential role during the radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy of cancer (submitted for publication).
O. W. Press, J. F. Eary, C. C. Badger, P. J. Martin, F. R. Appelbaum, R. Levy, R. Miller, S. Brown, W. B. Nelp, K. A. Krohn, D. Fisher, K. DeSantes, B. Porter, P. Kidd, E. D. Thomas, and I. D. Bernstein. Treatment of refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with radiolabeled MB-1 (anti-CD37) antibody.J. Clin. Oncol. 7:1027–1038 (1989).
T. K. Johnson, S. Maddock, R. Kasliwal, D. Bloedow, C. Hartmann, A. Feyerabend, D. Dienhart, S. Glenn, R. Gonzalez, J. Lear, and P. Bunn. Radioimmunoadsorption of KC-4G3 antibody in peripheral blood: Implications for radioimmunotherapy.J. Antibody. Immunoconj. Radiopharm. 4:24 (1991).
Micromath Scientific Software, Salt Lake City, Utah.
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982.
H. Akaike. An information criterion (AIC).Math. Sci. 14:5–9 (1976).
A. Mrhar, R. Karba, J. Drinovec, S. Primozic, J. Varl, A. F. Bren, and F. Zozjek. Computer simulation of ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics in patients on CAPD.Int. J. Artif. Organs 13:169–175 (1990).
E. Sanchez, C. M. Evora, A. Torres, and M. Llabres. A new approach to pharmacokinetic parameters: Estimation of cefuroxime during haemodialysis.Biopharm. Drug. Dispos. 11:107–120 (1990).
J. E. Svirbely, A. J. Pesce, S. Singh, and E. J. O'Flaherty. Cotrimoxazole (sulphamethoxazole plus trimethoprim) peritoneal barrier transfer pharmacokinetics.Clin. Pharmacokinet. 16:317–325 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health Clinical Research Center (Grant RR-51), National Cancer Institute (Grant PO1 CA42767-01A2), National Institute of General Medical Science (Grant GM29543), and Cancer Center (Grant 1P30 CA46934-02), The Cancer League of Colorado and Coulter Immunology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, C., Bloedow, D.C., Dienhart, D.G. et al. A pharmacokinetic model describing the removal of circulating radiolabeled antibody by extracorporeal immunoadsorption. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 19, 385–403 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061663
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061663