Abstract
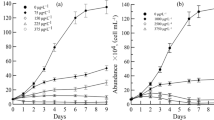
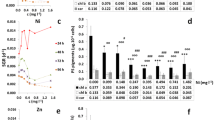
Using the growth response of the green algaChlorella vulgaris as a model system, the effects of combinations of the environmentally active cations Cd, Co, and Cu were evaluated. The 96-h static EC50 for these cations toC. vulgaris were, respectively, 0.89 μM, 9.0 μM, and 2.8 μM, yielding a toxicity series such that Cd>Cu>Co. The cation combinations of Cd+Cu, and Cu+Co acted synergistically, while Cd + Co, and the tri-metallic combination Cd + Cu + Co resulted in antagonistic interactions. Examination of these toxic combinations at 24, 48, 72, and 96 h indicate that the cellular response is not a uniform one. Failure of energy dispersive X-ray spectrophotometric analysis to demonstrate any intracellular incorporation of these cations (except for a weak cytoplasmic Cu peak at the 8.0 KEV position) suggests that the toxic actions of these cations at EC50 concentrations are exerted at the level of the plasma membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baxter M, Jensen TE (1980) A study of methods forin situ X-ray energy dispersive analysis of polyphosphate bodies inPlectonema boryanum. Arch Microbiol 126:213–215
Bold HC (1949) Morphology ofClamydomonas chlamydogama sp. nov. Bull Torr Bot Club 76:101–108
Boudou A, Ribeyre F (1989a) Aquatic ecotoxicology: Fundamental concepts and methodologies. Vol. I CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, FL
—,— (1989b) Aquatic ecotoxicology: Fundamental concepts and methodologies. Vol. II. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, FL
Ionouhe M, Inagawa A, Monta M, Tohoyama H, Joho M, Murayama T (1991) Contributions of cell wall and metal-binding peptide to Cd and Cu tolerances in suspension-culture cells of tomato. Bot Mag Tokyo 104:217–482
Jensen TE, Rachlin JW, Jani V, Warkentine B (1982) An X-ray energy dispersive study of cellular compartmentalization of lead and zinc inChlorella saccharophila (Chlorophyta),Navicula incerta andNitzschia closterium (Bacillariophyta). Environ Exp Bot 22:319–328
Majidi V, Laude DA, Holcombe JA (1990) Investigations of the metalalgae binding site with113Cd nuclear magnetic resonance. Environ Science Technol 24:1309–1312
Rachlin JW, Farran M (1974) Growth response of the green algaeChlorella vulgaris to selected concentrations of zinc. Water Res 8:575–577
Rachlin JW, Grosso A (1991) The effects of pH on the growth ofChlorella vulgaris and its interactions with cadmium toxicity. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:505–508
Rachlin JW, Jensen TE, Baxter M, Jani V (1982) Utilization of morphometric analysis in evaluating response ofPlectonema boryanum (Cyanophyceae) to exposure to eight heavy metals. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11:323–333
Rachlin JW, Jensen TE, Warkentine B (1983) The growth response of the diatomNavicula incerta to selected concentrations of the metals: cadmium, copper, lead and zinc. Bull Torr Bot Club 110:217–223
—,—,— (1984) The toxicological response of the algaAnabaena flos-aquae (Cyanophyceae) to cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 13:143–151
— (1985) Morphometric analysis of the response ofAnabaena flos-aquae andAnabaena variabilis (Cyanophyceae) to selected concentrations of zinc. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 14:395–402
Rai LC, Gaur JP, Kumar HD (1981) Phycology and heavy metal pollution. Biol Rev 56:99–151
Rai LC, Jensen TE, Rachlin JW (1990) A morphometric and X-ray energy dispersive approach to monitoring pH-altered cadmium toxicity inAnabaena flos-aquae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:479–487
Rosko JJ, Rachlin JW (1975) The effect of copper, zinc, cobalt and manganese on the growth of the marine diatomNitzschia closterium. Bull Torr Bot Club 102:100–106
—,— (1977) The effect of cadmium, copper, mercury, zinc and lead on cell division, growth, and chlorophyll a content of the chlorophyteChlorella vulgaris. Bull Torr Bot Club 104:226–233
Rothstein A (1959) Cell membrane as site of action of heavy metals. Fed Proc Fed Amer Soc Exp Biol 18:1026–1028
Simkiss K (1979) Metal ions in cells. Endeavour 3:2–6
Sunda WG (1988/89) Trace metal interactions with marine phytoplankton. Biol Oceanog 6:411–442
Taylor GJ (1989) Multiple metal stress inTriticum aestivum. Differentiation between additive, multiplicative, antagonistic, and synergistic effects. Can J Bot 67:2272–2276
Taylor GJ, Stadt KJ (1990) Interactive effects of cadmium, copper, manganese, nickel, and zinc on root growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in solution. In: Van Beusichem ML (ed) Plant nutrition—physiology and applications. Proceedings of the 11th international plant nutrition colloquium, Wageningen, The Netherlands, July 30 to August 4, 1989. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 317–322
Visviki I, Rachlin JW (1991) The toxic action and interactions of copper and cadmium to the marine algaDunaliella minuta, in both acute and chronic exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:271–275
Xue HB, Sigg L (1990) Binding of Cu(II) to algae in a metal buffer. Water Res 24:1129–1136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rachlin, J.W., Grosso, A. The growth response of the green algaChlorella vulgaris to combined divalent cation exposure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 16–20 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061084
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061084