Abstract
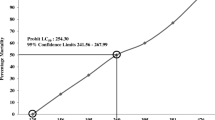
The Clean Water Act of 1971 directed the Environmental Protection Agency to establish ambient water quality criteria for several classes of elements and compounds, including phthalate esters. Multispecies acute toxicity data are required to develop these criteria. Static bioassay LC50s for butylbenzyl phthalate (BBP) for a single species of marine fish based on nominal doses range from 3 mg/L to 440 mg/L. Flow-through bioassays were used in this study of BBP with shiner perch (Cymatogaster aggregata). Using measured exposure concentrations, 96-hr LC50s averaged 0.51 mg/L. Effects on schooling behavior were found at 0.08 mg/L and coloration at 0.24 mg/L. Coupled with the behavioral changes, reduced brain levels of epinephrine found in surviving fish indicated that the mode of acute toxicity for BBP may be through its effects on the catecholamines of the central adrenergic nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, J. S., and T. J. Good: Trace enrichment of pesticides using bonded-phase sorbents. American Laboratory11, 70 (1982).
APHA, American Public Health Association: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 14 ed. Washington, DC: APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1976).
Aronson, L. R., and H. Kaplan: Function of the teleostean forebrain, In D. Ingle (ed.): The central nervous system and fish behavior. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press (1968).
ASTM, American Society for Testing and Materials: Standard practice for conducting acute toxicity tests with fishes, macroinvertebrates, and amphibians. E 729-80. Philadelphia, PA. ASTM (1980).
Belding, D. L.: The respiratory movements of fish as an indicator of toxic environment. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc.,59, 328 (1929).
Crawford, D. L., and D. K. Law: Mineral composition of Oregon pellet production formulations. Progressive Fish Culturist34, 126 (1972).
Fingerman, S. W., and L. C. Russell: Effects of the polychlorinated biphenyl Aroclor 1242® on the locomotor activity and the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain of the Gulf killifish (Fundus grandis). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.25, 682 (1980).
Finney, D. J.: Probit analysis. 3 ed. Cambridge, England, U.K.: Cambridge University Press (1971).
Gledhill, W. E., R. G. Kaley, W. J. Actams, O. Hicks, P. R. Michael, V. W. Saeger, and G. S. LeBlanc: An environmental safety assessment of butyl benzyl phthalate. Environ. Sci. Technol.14, 301 (1980).
Gray, T. J., and K. R. Butterworth: Testicular atrophy produced by phthalate esters. Arch. Toxicol.4, 452 (1980).
Healey, E. G., and D. M. Ross: The effects of drugs on the background colour response of the minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus 1. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.19, 545 (1966).
Heitmuller, P. T., T. A. Hollister, and P. R. Parrish: Acute toxicity of 54 industrial chemicals to sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.27, 596 (1981).
Maruyama, Y., T. Oshima, and E. Nakajima: Simultaneous determination of catecholamines in rat brains by reversed-phase liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci.26, 1115 (1980).
Randall, R. C., R. J. Ozretich, and B. L. Boese: The acute toxicity of butylbenzyl phthalate to the saltwater fish English sole (Paraphrys vetulus). Environ. Sci. Technol. (in press).
Sheldon, L. S., and R. A. Hites: Organic compounds in the Delaware River. Environ. Sci. Technol.12, 1188 (1978).
Smith, J. R., and R. B. Sleet: The effects of laboratory environment, holding time, and simulated intertidal conditions on dopamine and serotonin levels in ciliated and nervous tissues of the marine bivalve (Mytilus californianus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.73, 115 (1982).
Sullivan, K. F., E. L. Atlas, and C. S. Giam: Loss of phthalic acid esters and polychlorinated biphenyls from seawater samples during storage. Anal. Chem.53, 1718 (1981).
Taylor, B. F., R. W. Curry, and E. F. Corcoran: Potential for biodegradation of phthalic acid esters in marine regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.42, 590 (1981).
Thomas, P., H. W. Wofford, and J. M. Neff: Biochemical stress responses of striped mullet (Mugil cephalus L.) to fluorene analogs. Aquatic Toxicol.1, 329 (1981).
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: National Toxicology Program, Interagency Regulatory Liaison Group. Conference on Phthalates. Washington, DC (June 1981).
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Monitoring to detect previously unrecognized pollutants in surface waters. EPA-560/6-77-015A. Washington, DC: U.S. Environ. Prot. Agency, Office of Toxic Substances (1977).
—: Federal Register43, 4108 (1978).
—: Fate of priority pollutants in publicly owned treatment works. Interim Report. EPA-440/1-80-301. Washington, DC: U.S. Environ. Prot. Agency, Office of Wastewater Management (1980a).
—: Ambient water quality criteria for phthalate esters. EPA-440/5-80-067. Washington, DC: U.S. Environ. Prot. Agency, Office of Water Regulations and Standards (1980b).
—: Federal Register45, 79318 (1980c).
U.S. International Trade Commission: Synthetic organic chemicals, U.S. production and sales. Washington, DC (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozretich, R.J., Randall, R.C., Boese, B.L. et al. Acute toxicity of butylbenzyl phthalate to shiner perch (Cymatogaster aggregata). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 12, 655–660 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060747
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060747