Abstract
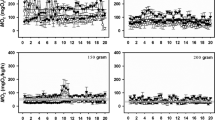
Both oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion ofPenaeus chinensis had a negative power regression with body weight. WhenP. chinensis juveniles (0.079+-0.004 g) were subjected to increased ambient ammonia-N (un-ionized plus ionized ammonia as nitrogen) in the range of 0.015–5.529 mg/L at 25°C and pH 7.93–8.24, oxygen consumption (O2 mg/g/h) and ammonia-N excretion (mg/g/h) increased. Oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion of the shrimps exposed to control (0.015 mg/L) and 5.529 mg/L ammonia-N was 0.858 to 1.628, 1.159 to 2.675 O2 mg/g/h and 0.028 to 0.049 and 0.942 to 2.004 ammonia-N mg/g/h, respectively. Both oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion of the shrimp had a linear correlation after 6, 10, and 14 h; and had a power correlation after 20 h with ambient ammonia-N in the range of 0.015–5.529 mg/L. Mean cumulative amount of dissolved oxygen consumed in 20 h was 1.518, 1.786, 1.897, 2.085, 2.193, 2.322, and 2.526 mg; and a mean cumulative amount of excreted ammonia-N in 20 h was 0.059, 0.501, 0.671, 0.792, 1.527, 1.780, and 1.964 mg for individualP. chinensis exposed to 0.015, 0.618, 1.182, 2.112, 2.876, 4.381, and 5.529 mg/L ammonia-N, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron J (1986) Response to reversed NH3 and NH4 + gradients in a teleost (Ictalurus punctatus), an elasmobranch (Raja erinacea), and a crustacean (Callinectes sapidus): evidence for NH4/H+ exchange in the teleost and the elasmobranch. J Exp Zool 239:183–195
Cameron J, Heisler N (1983) Studies of ammonia in the rainbow trout: Physico-chemical parameters, acid-base behaviour and respiratory clearance. J Exp Biol 105:107–125
Chen LC (1990) Aquaculture in Taiwan. Fishing News Books, London
Chen JC, Nan FH (1991) Lethal effect of nitrite onMetapenaeus ensis larvae. J World Aquacult Soc 22(1): (in press)
Chen JC, Ting YY, Lin JN, Lin MN (1990) Lethal effects of ammonia and nitrite onPenaeus chinensis juveniles. Mar Biol 107:427–431.
Dalla Via GJ (1986) Salinity response of the juvenile penaeid shrimpPenaeus japonicus I. Oxygen consumption and estimation of productivity. Aquaculture 55:297–306
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple-range and multiple F test. Biometrics 11:1–42
Fromm PO, Gillette JR (1968) Effect of ambient ammonia on blood ammonia and nitrogen excretion of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Comp Biochem Physiol 26:887–896
Kinne O (1976) Cultivation of marine organisms: Water quality management. In: Kinne O (ed) Marine ecology. Vol. III. Part 1, Wiley-Interscience. NY, pp 79–300
Lei CH, Hsieh LY, Chen CK (1989) Effects of salinity on the oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion of young juveniles of the grass shrimp,Penaeus monodon Fabricius. Bull Inst Zool Academia Sinica 28 (4):245–256
Liao IC (1986) General introduction to the prawn pond system in Taiwan. Aquacult Engin 5:219–233
Liao IC, Huang HJ (1975) Studies on the respiration of economic prawn in Taiwan. I. Oxygen consumption and lethal dissolved oxygen of egg up to young prawn ofPenaeus monodon Fabricius. J Fish Soc Taiwan 4:33–50
Liao IC, Murai T (1986) Effects of dissolved oxygen, temperature and salinity on the oxygen consumption of the grass shrimp,Penaeus monodon. In: Maclean JL, Dizon LB, Hosilos LV (eds) The First Asian Fisheries Forum, Asian Fisheries Society, Manila, Philippines, pp 641–646
Liu RY (1983) Shrimp mariculture studies in China. In: Rogers GL, Day R, Lim A (eds) Proceedings of the First International Conference on Warm Water Aquaculture-Crustacean. Brigham Young University, Hawaii Campus, Laie, Hawaii pp 82–87
Marangos C, Alliot E, Brogren C-H, Ceccaldi HJ (1989) Nycthemeral variations of ammonia excretion inPenaeus japonicus (Crustacea, Decapoda, Penaeidae). Aquaculture 84:383–391
Randall JR, Wright PA (1987) Ammonia distribution and excretion in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 3:107–120
Solorzano L (1969) Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limno and Oceano 14:799–801
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill, NY
Ting YY (1970) Study on the oxygen consumption of grass shrimp,Penaeus monodon and sand shrimp,Metapenaeus monoceros. Bull Taiwan Fish Res Inst 16:111–118
Tzeng BS, Li CD, Ting YY, Lin MN (1990) Breeding of the fleshy prawn,Penaeus chinensis Kishinouye. Bull Taiwan Fish Res Inst 49:183–188
Wright PA, Wood CM (1985) An analysis of branchial ammonia excretion in the freshwater rainbow trout: Effects of environmental pH change and sodium uptake blockade. J Exp Biol 114:329–353
Wu S, Lou K (1965) Induced maturation, spawning and the laboratory rearing of postlarvae ofPenaeus orientalis Kishinouye. Oceanol Limno Sinica MO (1): 180–190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JC., Nan, FH. & Kuo, CM. Oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion of prawns (Penaeus chinensis) exposed to ambient ammonia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 21, 377–382 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060359
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060359