Abstract
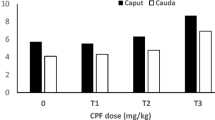
Acute and chronic effects of cadmium exposure on spermatozoan choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) were studied to investigate the mechanism of cadmium induced sterility. Cadmium at dosages of 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg given orally inhibited ChAT in all segments of spermatozoa obtained from rat epididymis. Maximum inhibition was observed about 72 hr after treatment. Decreased ChAT activity was seen in chronic experiments where animals were exposed to cadmium via drinking water; surprisingly, a greater decrease was observed at the lower dosage. Cadmium also inhibited ChAT activity of rat cauda spermatozoa, and human spermatozoa when they were incubatedin vitro at a concentration of 5 × 10−4M. Cadmium decreased human spermatozoan motility when incubated at a concentration of 5 × 10−4M. Acetyl-choline (ACh) and physostigmine (a cholinesterase inhibitor), however, increased spermatozoan motility. The results indicate that cadmium may produce sterility by inhibiting spermatozoan choline acetyltransferase, decreasing acetyl choline synthesis, and impairing spermatozoan motility, and could be a potential reproductive hazard to humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsberg, C. L., and E. W. Schwartze: Pharmacological action of cadmium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.14, 504 (1919).
Bishop, M. R., B. V. R. Sastry, D. E. Schmidt, and R. D. Harbison: Spermic cholinergic system and occurrence of acetyl-choline and other quaternary ammonium compounds in mammalian spermatozoa. Tox. Appl. Pharmacol.33, 733 (1975).
—: Occurrence of choline acetyltransferase and acetyl-choline and other quaternary ammonium compounds in mammalian spermatozoa. Biochem. Pharmacol25, 1617 (1976).
Carroll, R. E.: The relationship of cadmium in the air to cardiovascular disease death rates. J. Amer. Med. Assc.198, 267 (1966).
Cheremisinoff, P. N., and Y. A. Habib: Cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury: A plenary account of water pollution. Part 1-Occurrence, toxicity, and detection. Water Sewage Wks.7, 73 (1972).
Dwivedi, C., D. N. Singh, E. P. Crump, and R. D. Harbison: Reproductive toxicity of cadmium. Tox. Appl. Pharmacol.41, 194 (1977).
Dwivedi, C.: Proposed role of cholinergic system in regulation of spermatozoa motility. Ind. J. Biochem Biophys.18, 38 (1981a).
Dwivedi, C., D. N. Singh, and R. D. Harbison: Choline acetyl-transferase inhibitor as a male contraceptive. Proceedings of Second Congress of the Federation of Asian and Oceanian Biochemists, p. 22, En8 (1981b).
Dwivedi, C., R. Raghunathan, B. C. Joshi, and H. W. Foster, Jr.: Effect of mercury compounds on choline acetyltransferase. Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharm.30, 381 (1980).
Fassett, D. W.: Cadmium. In D. H. K. Lee (ed.): Metallic contaminants and human health. New York: Academic Press (1974).
Fowler, A. J., D. N. Singh, and C. Dwivedi: The effect of cadmium on Meiosis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. (in press) 1982.
Friberg, L.: Health hazards in the manufacture of alkaline accumulators, with special reference to chronic cadmium poisoning. Acta Med. Scand.138, 1 (1950).
Friberg, L., M. Piscator, G. F. Nordberg, and T. Kjellstorm: Cadmium in the environment. Cleveland, OH: CRC Press (1974).
Gabbiani G., D. Baic, and C. Deziel: Studies on tolerance and ionic antagonism for cadmium and mercury. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.45, 443 (1967a).
—: Toxicity of cadmium for the central nervous system. Exp. Neurol.18, 154 (1967b).
Gunn S. A., and T. C. Gould: Cadmium and other mineral elements. In the testes. In A. D. Johnson W. R. Gomes and N. L. Vandermark (eds.): p. 377. New York: Academic Press (1970).
Hagino, N., and K. Yoshioka: A study on the etiology of the so-called “Itai-Itai” disease. J. Japan Orthop. Assoc.35, 812 (1961).
Harbison, R. D., C. Dwivedi, and B. V. R. Sastry: Development of sperm cholineacetyltransferase activity. Pharmacologist,16, 306 (1974a).
Harbison, R. D., C. Dwivedi, M. C. Orgebin-Crist, and B. V. R. Sastry: Antifertility activity of trimethylphosphate: Studies on mechanism of action. Proceedings of International Union of Physiological Sciences, Vol. 11, p. 325. Twenty Sixth International Congress, New Delhi, India (1974b).
Harbison, R. D., C. Dwivedi, and M. A. Evans: A proposed mechanism for trimethyl phosphate induced sterility. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.35, 481 (1976a).
Harbison, R. D., M. C. Orgebin-Crist, C. Dwivedi, and B. V. R. Sastry: Choline acetyltransferase activity in sperm of rabbit and man: Possible involvement in trimethylphosphate induced sterility. In K. R. Laumas (ed.): New methods in contraceptive technology, p. 125. New Delhi: Ankur Publishing House (1976b).
Hrdina, P. D., D. A. V. Peters, and R. L. Singhal: Effects of chronic exposure to cadmium, lead, and mercury on brain biogenic amines in the rat. Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol.15, 483 (1976).
Joshi, B. C., C. Dwivedi, A. Powell, and M. Holscher: Immune complex nephritis in rats induced by long term oral exposure to cadmium. J. Comp. Path.91, 11 (1981).
Johnston, R. E., T. S. Miya, and R. C. Schnell: Cadmium potentiation of drug response-role of liver. Biochem. Pharmacol.24, 887 (1975).
Kotsonis, F. N., and C. D. Klassen: The relationship of metal-lothionein to the toxicity of cadmium after prolonged oral administration to rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.46, 39 (1978).
Lee, I. P., and R. L. Dixon: Effects of cadmium on spermatogenesis studied by velocity sedimentation cell separation and serial mating. Jour. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap.187, 641 (1973).
Mannervik, B., and B. Sorbo: Inhibition of choline acetyl-transferase from bovine caudate nucleus by sulfhydryl reagents and reactivation of the inhibited enzyme. Biochem. Pharmacol.19, 2509 (1970).
McCaman, R. E., and J. M. Hunt: Microdetermination of choline acetylase in nervous tissue. J. Neurochem.12, 253 (1965).
Nelson, L.: Sperm motility. In C. B. Metz and L. Nelson (eds.): Fertilization, p. 27. New York: Academic Press (1967).
Nelson, L.: Neurochemical control of Arbacia sperm motility. Exp. Cell Res.74, 269 (1972).
Norman, C.: V Congresso Internazionale PerLa Riiproduzious Animale E La Fecondazione Artificiate, Sezione 111–15, 269 (1964).
Parizek, J., and Z. Zahor: Effects of cadmium salts on testicular tissue. Nature177, 1036 (1956).
Perry, H. M., Jr., and M. L. Erlanger: Metal induced hypertension following chronic feeding of low doses of cadmium and mercury. J. Lab. Clin. Med.83, 541 (1974).
Piotrowski, J. K., B. Trojanowska, J. M. WiŚmiewska-Krypl, and W. Bolanowska: Mercury binding in the kidney and liver of rats repeatedly exposed to mercuric chloride: Induction of metallothionein by mercury and cadmium. Tox. Appl. Pharmacol.27, 11 (1974).
Piscator, M.: Proteinuria in chronic cadmium poisoning. Arch. Environ. Health.5, 55 (1962).
Powell, A. L., B. Joshi, C. Dwivedi, and L. Green: Immuno pathological changes in cadmium treated rats. Vet. Pathol.16, 116 (1979).
Rosenthal, H., and K. R. Sperling: Effects of cadmium on development and survival of herring eggs, In J. H. S. Blaxter (ed.): The early life history of fishes, New York: Springer-Verlag (1974).
Sastry, B. V. R., and C. Sadavongvivad: Cholinergic Systems in Non-nervous tissue. Pharmacol. Review30, 65 (1979).
Sastry, B. V. R., V. E. Janson, and A. K. Chaturvedi: Inhibition of human sperm motility by inhibitors of choline acetyl-transferase. J. Pharm. Exp. Therap.26, 378 (1981).
Schroeder, H. A., and J. J. Balassa: Abnormal trace metals in man: Cadmium. J. Chronic Dis.14, 236 (1961).
Schroeder, H. A., and W. H. Vinton, Jr.: Hypertension induced in rats by small doses of cadmium. Am. J. Physiol.202, 515 (1962).
Schroeder, H. A.: Cadmium, chromium, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation35, 570 (1967).
Stowe, H. D., M. D. Wilson, and R. A. Goyer: Clinical and morphological effects of oral cadmium toxicity in rabbits. J. Arch. Pathol.94, 389 (1972).
Tipton, I. H., and P. L. Stewart: Patterns of elemental excretion in long term balance studies, II. In W. S. Snyder (ed.): Internal dosimetry, p. 303. Health Physical Division Annual Progress Report ORNL 4446, (1970).
Unger, M., and J. Clausen: Liver cytochrome P-450 activity after ip. administration of cadmium salts in the mouse. Environ. Physiol. Biochem.3, 236 (1973).
Vallee, B. L., and D. D. Ulmer: Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. Ann. Rev. Biochem.41, 91 (1972).
Wagstaff, D. D.: Stimulation of liver detoxification enzymes by dietary cadmium acetate. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.10, 328 (1973).
Wilson, R. H., F. DeEds, and A. J. Cox: Effects of continued cadmium feeding. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.71, 222 (1941).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, C. Cadmium-induced sterility: Possible involvement of the cholinergic system. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 12, 151–156 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059574
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01059574