Abstract
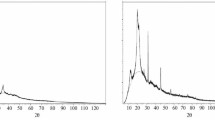
The reaction of cellulose with solid sodium hydroxide in conditions of shear in a screw mixer results in the formation of alkaline cellulose in two modifications. Dissolution of alkaline cellulose in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide produces concentrated pastes with a concentration of cellulose of up to 10 wt. % for a DP of the cellulose no lower than 300.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yamashiki, et al., Brit. Polym. J.,22, 73, 121, 201 (1990).
T. Yamashiki, M. Saiton, et al., Cell. Chem. Technol.,24, 237 (1990).
M. M. Iovleva, Khim. Volokna, No. 2, 11–14 (1996).
USSR Inventor's Certificate No. 1613445 (1988).
K. Gettse, Production of Viscose Fibres [Russian translation], Khimiya, Moscow (1972).
M. M. Iovleva, V. N. Smirnova, et al., Byull. Izobr., No. 8, 62 (1996).
Additional information
All-Union Scientific-Research Institute of Polymer Fibres, Mytishchi. Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 5, pp. 49–52, September–October, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iovleva, M.M., Smirnova, V.N., Belousova, T.A. et al. Some properties of activated mixtures of cellulose with solid sodium hydroxide. Fibre Chem 28, 347–350 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057704
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057704