Abstract
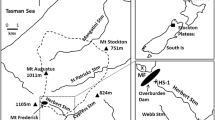
A 24-hr dosing experiment was carried out in a soft-water stream in upland Wales during which four separate zones were created by the simultaneous addition of sulphuric acid, aluminium sulphate, and citric acid. An upstream control zone (A), an acid zone pH 4.9 (B), an aluminium and acid (total filterable aluminium 0.27 mg/L, pH 4.9) zone (C) and a downstream zone (D) of aluminium complexed with citrate at low pH (total filterable aluminium 0.23 mg/L, pH 4.9). Test species exposed in all zones were the invertebratesGammarus pulex (L.),Baetis rhodani (Pict.),Ephemerella ignita (Poda) and the fishSalmo salar L.,Salmo trutta L. andCottus gobio L.
Response criteria measured were mortality, feeding, effects of pretreatment, brief-exposure, and the ability of animals to recover. Minimal effects were observed in the control and acid zones whilst large mortalities and reduced feeding were recorded in the acid and aluminium zone. These effects were significantly reduced in the acid, aluminium and citrate zone due to complexation of aluminium with citrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel PD (1980) Toxicity of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane) toGrammarm pulex: mortality in relation to concentration and duration of exposure. Freshwater Biol 10:251–259
Abel PD, Green DWJ (1981) Ecological and toxicological studies on invertebrate fauna of two rivers in the northern Pennine Orefield. In: Say PJ, Whitton BA (eds) Heavy metals in Northern England: Environmental and Biological Aspects. University of Durham. Dept of Botany, pp 109–122
Abel PD, Garner SM (1986) Comparisons of median survival times and median lethal exposure times forGammarus pulex exposed to cadmium, permethrin, and cyanide. Water Res 20:579–582
Allard M, Moreau G (1985) Short term effect on the metabolism of lotie benthic communities following experimental acidification.Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:1676–1680
— (1987) Effects of experimental acidification on a lotie macroinvertebrate community. Hydrobiologia 144:37–49
Almer B, Dickson W, Ekstrom C, Hornstrom E, Miller V (1974) Effects of acidification on Swedish lakes. Ambio 3:30–36
Baker JP, Schofield CL (1980) Aluminium toxicity to fish as related to acid precipitation and Adirondack surface water quality. In: Drabløs D, Tollan A (eds) Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.E: Oslo, pp 292–293
Beamish RJ, Harvey HH (1972) Acidification of the La Cloche mountain lakes, Ontario and resulting fish mortalities. J Fish Res Board Can 29:1131–1143
Beattie JH, Pascoe D (1978) Cadmium uptake by rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri eggs and alevins. J Fish Biol 13:631–637
Brown DJA (1983) Effect of calcium and aluminum concentrations on the survival of brown trout (Salmo trutta) at low pH. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 30:582–587
Burton TM, Allan JW (1986) Influence of pH, aluminium, and organic matter on stream invertebrates. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43:1285–1289
Driscoll CT, Baker JP, Bisogni JJ, Schofield CL (1980) Effect of aluminium speciation on fish in dilute acidified water. Nature 284:161–164
Driscoll CT (1984) A procedure for the fractionation of aqueous aluminium in dilute acidic waters. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 16:267–284
Duncan DA, Klaverkamp JF (1983) Tolerance and resistance to cadmium in white suckers (Catostomus commersoni) previously exposed to cadmium, mercury, zinc, or selenium. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 40:128–138
Edwards RW, Brown VM (1967) Pollution and fisheries: A progress report. J Inst Water Pollut Control Lond 66:63–78
Farmer GJ, Ritter JA, Ashfield D (1978) Seawater adaptation and parr-smolt transformation of juvenile Atlantic salmonSalmo salar. J Fish Res Board Can 35:93–100
Fivelstad S, Leivestad H (1984) Aluminium toxicity to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and brown trout (Salmo trutta L.): mortality and physiological response. Rep Inst Freshwater Res Drottningholm 61:69–77
Haines TA (1981) Acidic precipitation and its consequences for aquatic ecosystems. A review. Trans Am Fish Soc 110:669–707
Hall RJ, Likens GE, Fiance SB, Hendrey GE (1980) Experimental acidification of a stream in the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest, New Hampshire. Ecology 61:976–989
Hall RJ, Driscoll CT, Likens GE, Pratt MJ (1985) Physical, chemical, and biological consequences of episodic aluminium additions to a stream. Limnol Oceanogr 30:212–220
Harriman R, Morrison BRS (1982) Ecology of streams draining forested and nonforested catchments in an area of central Scotland subject to acidic precipitation. Hydrobiologia 88:251–263
Henriksen A, Skogheim OK, Rosseland BO (1984) Episodic changes in pH and aluminium speciation kill fish in a Norwegian salmon river. Vatten 40:255–260
Howell R (1985) Effect of zinc on cadmium toxicity to the amphipodGammarus pulex. Hydrobiologia 123:245–249
Jackson GE (1982) Studies on the chelation of aluminium for biological application. Part 1. Citric acid. S Afr J Chem 35:89–92
Jensen KW, Snekvik E (1972) Low pH levels wipe out salmon and trout populations in southern Norway. Ambio 1:223–225
Kay J, Cryer A (1986) Environmental cadmium and metallothionein gene expression in freshwater fish. Natural Environment Research Council News Journal, June, pp 9–11
Kimmel WG, Murphey DJ, Sharpe WE, DeWalle DR (1985) Macroinvertebrate community structure and detritus processing rates in two southwestern Pennsylvania streams acidified by atmospheric deposition. Hydrobiologia 124:97–102
Litchfieid JT (1949) A method for rapid graphic solution of timeper cent effect curves. J Pharm Exp Ther 97:399–408
Lynam S (1985) Measurement of aluminium in freshwater—a method for laboratory and field use. TPRD/L/BY/075/M85 Central Electricity Research Laboratories: Leatherhead
McCahon CP, Pascoe D, McKavanagh C (1987) Histochemical observations on the salmonidsSalmo salar L. andSalmo trutta L. and the EphemeropteransBaetis rhodani (Pict.) andEcdyonurus venosus (Fabr.) following a simulated episode of acidity in an upland stream. Hydrobiologia 153:3–12
McCahon CP, Pascoe D (in press) Use ofGammarus pulex (L.) in safety evaluation tests—culture and selection of a sensitive life stage. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety
McCartney TH (1976) Sodium-potassium dependent adenosine triphosphatase activity in gills and kidneys of Atlantic salmon (Salrno salar). Comp Biochem Physiol 53:351–353
Muniz IP, Leivestad H (1980) Toxic effects of aluminium on the brown troutSalmo trutta L. In: Drabløs D, Tollan A (eds) Ecological Impact Of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F.: Oslo, pp 320–321
Norton RL, Orpwood JR (1980) Multi-element analysis using an inductively coupled plasma spectrophotometer. Part 1. Commissioning and preliminary evaluation of performance. Water Research Centre Technical Report 141
Ormerod SJ, Boole P, McCahon CP, Weatherley NS, Pascoe D, Edwards RW (1987a) Short-term experimental acidification of a Welsh stream: Comparing the biological effects of hydrogen ions and aluminium. Freshwater Biol. 17:341–356
Ormerod SJ, Weatherley NS, French P, Blake S, Jones WM (1987b) The physiological response of brown troutSalmo trutta to induced episodes of low pH and elevated aluminium in a Welsh hill stream. In: Witters H, Vanderborght, O (eds) Ecophysiology of Acid Stress in Aquatic organisms. Ann Soc R Zool Beig 117:(Suppl 1)435–447
Orr PL, Bradley RW, Sprague JB, Hutchinson NJ (1986) Acclimation-induced change in toxicity of aluminium to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43:243–246
Pascoe D, Beattie JH (1979) Resistance to cadmium by pretreated rainbow trout alevins. J Fish Biol 14:303–308
Pascoe D, Shazili NAM (1986) Episodic pollution—a comparison of brief and continuous exposure of rainbow trout to cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 12:189–198
Rosseland BO, Sevaldrud IH, Svalastog D, Muniz IP (1980) Studies of freshwater fish populations—effects of acidification on reproduction, population structure, growth and food selection. In: Drabløs D, Tollan A (eds) Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F: Oslo, pp 336–337
Rosseland BO, Skogheim OK (1984) A comparative study on salmonid fish species in acid aluminium rich water. II Physiological stress and mortality of one and two year old fish. Rep Inst Freshwater Res Drottningholm 61:186–194
Rosseland BO, Skogheim OK, Sevaldrud IH (1986) Acid deposition and effects in Nordic Europe. Damage to fish populations in Scandinavia continue to apace. Water Air Soil Pollut 30:65–74
Rosseland BO (1986) Ecological effects of acidification on tertiary consumers. Fish population responses. Water Air Soil Pollut 451–460
Saunders RL, Henderson EB (1978) Changes in gill ATPase activity and smolt status of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Fish Res Board Can 35:1542–1546
Siddens LK, Seim WK, Curtis LR, Chapman GA (1986) Comparison of continuous and episodic exposure to acidic, aluminium-contaminated waters of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Can J Fish Aquatic Sci 43:2036–2040
Stoner JH, Gee AS, Wade KR (1984) The effects of acidification on the ecology of streams in the Upper Tywi Catchment in West Wales. Environ Pollut 35:125–157
Weatherley NS, Ormerod SJ, Thomas SP, Edwards RD (in press) The response of macroinvertebrates to experimental episodes of low pH with different forms of aluminium during a natural spate. Hydrobiologia
Weatherley NS, Ormerod SJ (1987) The impact of acidification on macroinvertebrate assemblages in Welsh streams: towards an empirical model. Environ Pollut 46:223–240
Witters HE (1986) Acute acid exposure of rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri Richardson: Effects of aluminium and calcium on ion balance and haematology. Aquatic Toxicol 8:197–210
Zischke JA, Arthur JW, Nordlie KJ, Hermanutz RO, Standen DA, Henry TP (1983) Acidification effects on macroinvertebrates and fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) in outdoor experimental channels. Water Res 17:47–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCahon, C.P., Pascoe, D. Short-term experimental acidification of a Welsh stream: Toxicity of different forms of aluminium at low pH to fish and invertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 18, 233–242 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056208
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056208