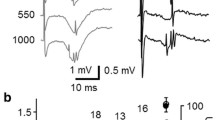
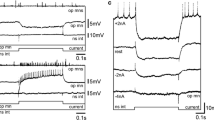
Abstract
Postsynaptic mechanisms of the connection between the interneuron in the visceral ganglion initiating bursting activity in RPal and B7 neurons and these neurons themselves were investigated in the snail (Helix pomatia). Using voltage clamping at the membrane of these cells, stimulation of the interneuron gave rise to a slow inward current with a 2 sec latency; it rose in amplitude as stimulation increased in duration. Reducing the temperature from 25 to 5°C diminished the rise and decay rate of this current with a temperature coefficient of about 10. The current-voltage relationship of the slow inward current was nonlinear, with a maximum of −65 mV. Reducing the concentration of sodium ions in the extracellular fluid increased the amplitude of the current. While hyperpolarization of the burster neuron membrane produced a burst of inward current prior to stimulation, this same hyperpolarization induced a pulse of outward current at the peak of the slow inward current. Stimulating the interneuron is thus thought to activate at least two types of ionic channel in the cell body of the burster neurons: a steady sodium and a voltage- and time-dependent channel for outward current. This process could well be mediated by a biochemical cytoplasmic chain reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. N. Airapetyan, R. A. Zakharyan, G. E. Rychkov, et al., "RNA as a stimulator of neuronal pacemaker activity," Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,284, No. 6, 1499–1502 (1985).
L. M. Koval', N. I. Kononenko, and G. G. Skivo, "Axosomatic junctions in theHelix pomatia burster neuron and histochemical manifestation of adenylate cyclase in their activity," Neirofiziologiya,14, No. 4, 435–437 (1982).
N. I. Kononenko, "Ionic mechanisms of bursting activity inHelix pomatia neurons," Neirofiziologiya,10, No. 2, 193–202 (1978).
N. I. Kononenko and O. N. Osipenko, "Effects of tolbutamide on the electrical activity of theHelix pomatia burster neuron," Neirofiziologiya,15, No. 3, 327–329 (1983).
N. I. Kononenko and O. N. Osipenko, "Monosynaptic pathway responsible for generation of bursting activity in theHelix pomatia RPal neuron," Neirofiziologiya,19, No. 1, 20–28 (1987).
N. I. Kononenko and A. V. Stefanov, "A factor modulating the electrical activity of theHelix pomatia burster neuron," Neirofiziologiya,10, No. 3, 319–321 (1978).
W. B. Adams, "Slow depolarizing and hyperpolarizing currents which mediate bursting inAplysia neuron R I5," J. Physiol.,360, 51–68 (1985).
R. A. Chaplain, "Metabolic control of neuronal pacemaker activity and the rhythmic organization of central nervous functions," J. Exp. Biol.,81. (Rev. vol.), 113–130 (1979).
M. Gola, "Electrical properties of bursting pacemaker neurons," in: Neurobiology of Invertebrates, Academiai Kiado, Budapest (1976), pp. 381–423.
R. Horn, "Propagating calcium spike in an axon ofAplysia," J. Physiol.,281, No. 3, 513–534 (1978).
I. B. Levitan, "Modulation of neuronal activity by peptides and cyclic nucleotides," in: The Neurosciences: Fourth Study Program, MIT Press, Basel (1979), pp. 1043–1055.
N. I. Kononenko, "Modulation of the endogenous electrical activity of the bursting neuron in the snailHelix pomatia. 1. The generator of the slow rhythms," Neuroscience,4, No. 12, 2037–2045 (1979).
N. I. Kononenko, "Modulation of the endogenous electrical activity of the bursting neuron in the snailHelix pomatia. 2. The membrane characteristics related to modulation of the endogenous activity of the neuron," Neuroscience,4, No. 12, 2047–2054 (1979).
N. I. Kononenko, P. G. Kostyuk, and A. D. Shcherbatko, "The effect of intracellular cAMP injections on stationary membrane conductance and voltage- and time-dependent ionic current in identified snail neurons," Brain Res.,268, No. 2, 321–338 (1983).
T. Pin and M. Gola, "Two identified interneurons modulate the firing pattern of pacemaker bursting cells inHelix," Neurosci. Lett.,37, No. 2, 117–122 (1983).
J. Salanki and I. Vadasz, "Chemical sensitivity at different temperatures of the Br-type, bimodal pacemaker neurons in the CNS of the snailHelix pomatia L." Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung.,44, No. 1, 51–59 (1973).
J. Salanki, I. Vadasz, and M. Vero, "Temperature dependence of the activity pattern in the Br-type cell of the snailHelix pomatia L." Acta Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung.,43, No. 2, 115–124 (1973).
T. G. Smith, J. L. Barker, and H. Gainer, "Requirements for bursting pacemaker activity in molluscan neurons," Nature,253, No. 5491, 450–452 (1975).
F. Strumwasser, "The cellular basis of behavior inAplysia," J. Psychiat. Res.,8, No. 2, 237–257 (1971).
M. V. Thomas and A. L. F. Gorman, "Internal calcium changes in a bursting pacemaker neuron measured with Arsenazo III," Science,196, No. 4289, 531–533 (1977).
H. Wachtel and W. A. Wilson, "Voltage clamp analysis of rhythmic slow wave generation in bursting neurons," in: Neurobiology of Invertebrates, Akademiai Kiado, Budapest (1973), pp. 59–80.
Additional information
A. A. Bogomolets Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR, Kiev. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 28–36, January–February, 1987.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kononenko, N.I., Osipenko, O.N. Postsynaptic mechanisms initiating bursting activity in theHelix pomatia RPal neuron under the influence of an interneuron. Neurophysiology 19, 23–30 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055991
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055991