Abstract
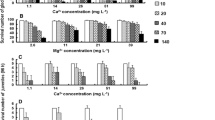
JuvenileArgopecten irradions andSpisula solidissima were exposed to Cu, Pb, Se, or Zn in a 96-hour static bioassay. The order of toxicity for both bivalve species was the same: Cu > Se > Zn > Pb. With the exception of lead,A. irradians was more sensitive thanS. solidissima to the metals tested.
JuvenileMytilus edulis were exposed in 96-hour static bioassays to Cd, Cu, Hg, or Ag. The order of toxicity was Cu = Hg = Ag > Cd.M. edulis was less sensitive to Ag and Hg when compared toA. irradians and less sensitive to Cu thanA. irradians orS. solidissima. M. edulis was as sensitive to Cd asA. irradians.
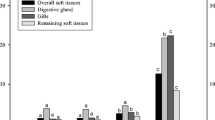
In a 126-day exposure, 45 young-of-the-yearA. irradians orS. solidissima, or 45 adultM. edulis were exposed to Cu, using a proportional diluter apparatus. Copper was added to test tanks at concentrations of 0.002, 0.010, or 0.020 mg/L, while control tanks received untreated seawater. Of the three species exposed to the three concentrations of Cu, young-of-the-yearS. solidissima were the most sensitive, followed by young-of-the-yearA. irradians. Least sensitive was the adultM. edulis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsanullah M (1976) Acute toxicity of cadmium and zinc to seven invertebrate species from Western Port, Victoria. Aust J Mar Fresh Res 27:187–196
Ahsanullah M, and Palmer DH (1980) Acute toxicity of selenium to three species of marine invertebrates, with notes on a continuous-flow test system. Aust J Mar Fresh Res 31:795–802
Bryan GW (1973) The occurrence and seasonal variation of trace metals in the scallopsPecten maximus (L.) andChlamys opercularis (L.). J Mar Biol Assoc U K 53:145–166
Calabrese A, MacInnes JR, Nelson DA, Greig RA, Yevich PP (1984) Effects of long-term exposure to silver or copper on growth, bioaccumulation, and histopathology in the blue musselMytilus edulis. Mar Environ Res 11:253–274
Davenport J (1977) A study of the effects of copper applied continuously and discontinuously to specimens ofMytilus edulis (L.) exposed to steady and fluctuating salinity levels. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 57:63–74
Eisler R (1977) Acute toxicities of selected heavy metals to soft-shell clams,Mya arenaria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 17(2): 137–145
Eyster LS, Morse MP (1984) Development of the surf clam (Spisula solidissima) following exposure of gametes, embryos, and larvae to silver. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 13:641–646
Litchfield JT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharm Exper Ther 96:99–113
MacInnes JR, Calabrese A (1979) Combined effects of salinity, temperature, and copper on embryos and larvae of the American oyster,Crassostrea virginica. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 8:553–562
Martin M, Osborn K, Billig P, Glickstein N (1981) Toxicities of ten metals toCrassostrea gigas andMytilus edulis embryos andCancer magister larvae. Mar Pollut Bull 12(9):305–308
Mount DI, Brungs WA (1967) A simplified dosing apparatus for fish toxicology studies. Water Res 1:21–29
Nelson DA, Calabrese A, Nelson BA, MacInnes JR, Wenzloff DR (1976) Biological effects of heavy metals on juvenile scallops,Argopecten irradians, in short-term exposures. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 16(3):275–282
Olsen KR, Harrel RC (1973) Effect of salinity on acute toxicity of mercury, copper, and cadmium forRangia cuneata (Pelecypods, Matridae). Contrib Mar Sci 17:9–13
Pesch G, Stewart N, Pesch C (1979) Copper toxicity to the bay scallop, (Argopecten irradians). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 23(6):759–765
Pringle BH, Hissong DE, Katz EL, Mulawka ST (1968) Trace metal accumulation by estuarine mollusks. J Sanit Engineer Div 94:455–475
Shuster CN, Pringle BH (1968) Effects of trace metals on estuarine mollusks. Proc 1st Mid-Atlantic Ind Waste Conf U Delaware CE-5:285-304, Univ Delaware
Sommani P (1980) Toxicity of heavy metals to clam (Donax faba Chemnitz) and shrimp(Paneaus merquiensis de Man). In: Studies on the effects of water pollution and aquatic animals and fisheries at Si Racha Bay. Notes from Faculty of Fisheries, Kasetsart University, Bangkok
Sprague JB (1969) Measurement of pollutant toxicity of fish. I. Bioassay methods for acute toxicity. Water Res 3:793–821
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, D.A., Miller, J.E. & Calabrese, A. Effect of heavy metals on bay scallops, surf clams, and blue mussels in acute and long-term exposures. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17, 595–600 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055828
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055828