Abstract
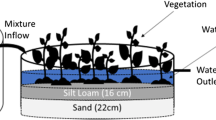
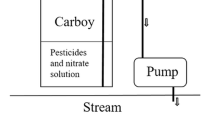
The environmental persistence of pesticides, their terminal residues and their contaminants, has played a major role in environmental regulations. To demonstrate degradation in field studies is difficult, both because of the length of time required and because of the complexity of demonstrating degradation of metabolites as well as of the pesticide itself. These difficulties can be circumvented by evaluating radiolabeled pesticides in a terrestrial aquatic laboratory model ecosystem which provides qualitative and quantitative data on persistence, bioaccumulation, and degradation both of the parent compound and of its metabolites. This microcosm was used to obtain data on the environmental degradation of pesticides with major roles in conservation tillage: paraquat, atrazine, linuron, oryzalin, alachlor, and paraquat paired with each of the other herbicides. The results suggest that alachlor, atrazine, linuron, and oryzalin do not pose serious risks of environmental accumulation when applied alone. The results of paired-herbicide eco-system evaluations compared to evaluations of each herbicide separately demonstrate that: paraquat is only minimally transported to aquatic organisms or to water; differences in herbicide application are more important in determining residue levels for these herbicides than are interactions between the herbicide and paraquat, although the latter do occur; and the addition of paraquat does not significantly alter the capacity of these herbicides for bioaccumulation or ecological magnification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Au LA (1979) Pesticide interactions in the laboratory rice paddy model ecosystems. PhD Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Esser HO, Depuis G, Ebert E, Vogel C, Marco G (1975) s-Triazines. In: Kearney PC, Kaufman DD, (eds) Herbicides, 2nd ed, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 129–208
Francis BM, Metcalf FL (1981) Screening of pesticides for potential adverse environmental effects in Illinois. IES Monograph, Institute for Environmental Studies, University of Illinois, Urbana IL
— (1984) Evaluation of mirex, photomirex, and chlordecone in the terrestrial aquatic laboratory model ecosystem. Environ Health Perspec 54:341–346
Freeman L (1953) A standardized method for determining toxicity of pure compounds in fish. Sewage Ind Wastes 25:845–848
Geissbuhler H, Martin H, Voss G (1975) The substituted ureas, In: Kearney PC, Kaufman DD (eds) Herbicides, 2nd ed, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 349–376
Gillett JW, Witt JW (1980) Chemical Evaluation: Projected application of terrestrial microcosm technology, In: Giesy JP Jr (ed) Microcosms in ecological research, Dept of Energy, Technical Information Ctr, CONF-781101 National Technical Information Service, Springfield VA, pp 1008–1033
Hammons AS (1981) Methods for ecological toxicology: A Critical review of laboratory multispecies tests. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI
Jaworski EG (1975) Chloroacetamides. In: Kearney PC. Kaufman DD (eds), Herbicides, 2nd ed, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 349–376
Knake EL, McGlamery MD (1980) In: Thirty-second Illinois Custom Spray Operators Training School, Illinois Crop Extension Service, University of Illinois College of Agriculture and Illinois Natural History Survey, Urbana IL, pp 338–342
Lee A-H, Lu P-Y, Metcalf RL, Hsu E-L (1976) The environmental fate of three dichlorophenyl nitroether herbicides in a rice paddy model ecosystem. J Environ Qual 5:482–486
Lichtenstein EP, Liang TT, Anderegy BN (1973) Synergism of insecticides by herbicides. Science 181:847–849
Lu P-Y, Metcalf RL, Hirwe AS, Williams JW (1975) Evaluation of environmental distribution and fate of hexachlorocyclopentadiene, chlordane, heptachlor, and heptachlor epoxide in a laboratory model ecosystem. J Agric Food Chem 23:967–973
Metcalf RL (1975) Organochlorine insecticides, survey and prospects. In: Metcalf RL, McKelvey JJ (eds) The future for insecticides, Wiley, New York, pp 223–285
— (1977) Model ecosystem approach to insecticide degradation: A critique. Ann Rev Entomol 22:241–261
Metcalf RL, Kapoor IP, Lu P-Y, Schuth CK, Sherman P (1973) Model ecosystem studies of the environmental fate of six organochlorine pesticides. Environ Health Perspec 35–46
Metcalf RL, Sanborn JR (1975) Pesticides and environmental quality in Illinois. Ill Nat History Survey Bull 31:379–436
Metcalf RL, Sangha GK, Kapoor IP (1971) Model ecosystem for the evaluation of pesticide biodegradability and ecological magnification. Environ Sci Technol 5:709–7131 (1971)
Sanborn, JR (1974) The fate of select pesticides in the aquatic environment. EPA-660/3-74-025, US Environmental Protection Agency, Corvallis OR
Sanborn JR, Francis BM, Metcalf RL (1977) The degradation of selected pesticides in soil: A review of published literature. EPA-600/9-77-022, National Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA
Sanborn JR, Metcalf RL, Bruce WN and Lu P-Y (1976) The fate of chlordane and toxaphene in a terrestrial aquatic model ecosystem. Environ Entomol 5:533–538
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, B.M., Lampman, R.L. & Metcalf, R.L. Model ecosystem studies of the environmental fate of five herbicides used in conservation tillage. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 14, 693–704 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055776
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055776