Abstract
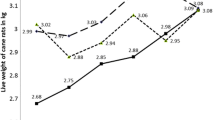
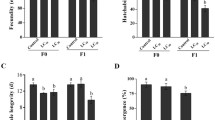
Reproductive success was impaired in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) chronically exposed to food treated at a rate of 10 ppm (μg/g) polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) (Aroclor® 1254). Mice in which PCBs exposure was initiated at adulthood (wild-caught and subsequently paired) and laboratory-raised mice paired and first exposed to PCBs-treated food at 16 weeks of age weaned significantly smaller numbers of young. Other parameters of reproductive success (interval between births, litter size at birth) were unaffected.
Laboratory-raised white-footed mice paired and first exposed to PCBs-treated food at 12 weeks of age exhibited longer intervals between births, smaller litter sizes at birth, and smaller litter sizes at weaning.
These results suggest that exposure to PCBs-contaminated natural foods can contribute to declines in natural populations of white-footed mice by reducing the number of young mice entering the breeding population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M (1978) Transfer of 2,4,5,2′,4′,5′-hexachlorobipheny! and 2,2-bis-(p-chlorophenyl), 1,1,1-trichloroethane (p,p′-DDT) from maternal to newborn and suckling rats. Arch Toxicol 41:179–186
Aulerich RJ, Ringer RK (1977) Current status of PCB toxicity to mink, and effect on their reproduction. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 6:279–292
Bowman RE, Heironimus MP, Allen JR (1978) Correlation of PCB body burden with behavioral toxicology in monkeys. Pharmacol and Biochem Behav 9:49–56
Chen RC, Chang YC, Tung TC, Chang KJ (1983) Neurological manifestations of chronic polychlorinated biphenyls poisoning. Proc NatI Sci Council, Part A: Appl Sci 7:87–91
Chen TS, DuBois KP (1973) Studies on the enzyme inducing effect of polychlorinated biphenyls. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 26:504–512
Chen RC, Tang SY, Miyata H, Kashimoto YC, Chang YC, Chang KJ, Tung TC (1985) Polychlorinated biphenyl poisoning: Correlation of sensory and motor nerve conduction, neurologic symptoms, and blood levels of polychlorinated biphenyls, quarterphenyls, and dibenzofurans. Environ Res 37:340–348
Choudary JB, Greenwald GS (1969) Luteotropic complex of the mouse. Anat Rec 163:373–388
Conney AH, Burns JJ (1972) Metabolic interactions among environmental chemicals and drugs. Science 178:576–586
Finn CA, Martin L (1972) Endocrine control of the timing of endometrial sensitivity to a decidual stimulus. Biol Reprod 7:82–86
Fishbein L (1974) Toxicity of chlorinated biphenyls. Ann Rev Pharmacol 14:139–156
Fleming WJ, Clark DR, Henry CJ (1983) Organochlorine pesticides and PCBs: A continuing problem for the 1980s. Trans 48th N Amer Wildl Conf 186–198
Hori S, Kashimoto T, Kunita N (1981) Transfer of PCB, PCT, and PCQ from the mother to litters through the milk or placenta and their distribution in the mother's body in rats and mice. J Food Hyg Soc Japan 22:501–507
Jonsson HT, Keil JE, Gaddy RG, Loadholt CB, Henigar GR, Walker EM (1976) Prolonged ingestion of commercial DDT and PCB: Effects on progesterone levels and reproduction in the mature female rat. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 3:479–490
Keplinger ML, Fancher OE, Calandra JC (1971) Toxicologic studies with polychlorinated biphenyls. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 19:402–403
Linder RD, Gaines TB, Kimbrough RD (1974) The effect of polychlorinated biphenyls on rat reproduction. Food Cosmetic Toxicol 12:63–77
Litterst CL, Farber TM, Baker AM, Van Loon EJ (1972) Effect of polychlorinated biphenyls on hepatic microsomal enzymes in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 23:112–122
Merson MH, Kirkpatrick RL (1976) Reproductive performance of captive white-footed mice fed a PCB. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 16:392–398
Orberg J, Kihlstrom JE (1973) Effects of long-term feeding of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB, Clophen® A 60) on the length of the oestrous cycle and on the frequency of implanted ova in the mouse. Environ Res 6:176–179
Peakall DB (1970)p,p′DDT: Effect on calcium metabolism and concentration of estradiol in the blood. Science 168:592–594
Platonow NS, Karstad LH (1973) Dietary effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on mink. Can Comp Med 37:391–400
Risebrough RW, Rieche P, Peakall DB, Herman SG, Kirven MN (1968) Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ecosystem. Nature 220:1098–1102
Saito M, Ikegami S, Aizawa T, Innami S (1983) Effect of the degradation of cytochrome p-450 heme by secobarbital on polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB)-induced hepatic vitamin A reduction and lipid peroxide formation in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 29:467–480
Sanders OT, Kirkpatrick RL (1975) Effects of a polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) on sleeping times, plasma corticosteroids, and testicular activity of white-footed mice. Environ Physiol Biochem 5:308–313
— (1977) Reproductive characteristics and corticoid levels of female white-footed mice fed ad libitum and restricted diets containing a polychlorinated biphenyl. Environ Res 13:358–363
Sanders OT, Kirkpatrick RL, Scanion PE (1977) Polychlorinated biphenyls and nutritional restriction: Their effects and interactions on endocrine and reproductive characteristics of male white mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 40:91–98
Sanders OT, Zepp RL, Kirkpatrick RL (1974) Effect of PCB ingestion on sleeping times, organ weights, food consumption, serum corticosterone and survival of albino mice. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 12:394–399
Seegal RF, Bush B, Brosch KO (1985) Polychlorinated biphenyls induce regional changes in brain norepinephrine concentrations in adult rats. Neurotoxicol 6:13–24
Shull LR, Bleavins MR, Olson BA, Aulerich RJ (1982) Polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclors® 1016 and 1242): Effect on hepatic microsomal mixed function oxidases in mink and ferrets. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11:313–321
Smith DM (1968) The effect of the time of oestrogen injection on implantation in ovariectomized pregnant mice. J Endocrinol 41:11–15
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1969) Biometry. WH Freeman, San Francisco, CA, 776 pp
Storm JE, Hart JL, Smith RF (1981) Behavior of mice after pre- and postnatal exposure to Aroclor® 1254. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 3:5–9
Tori GM, Peterle TJ (1983) Effects of PCBs on mourning dove courtship behavior. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 30:44–49
Welch RM, Levin W, Kuntzman R, Jacobson M, Conney AH (1971) Effect of halogenated hydrocarbon insecticides on the metabolism and uterotropic action of estrogens in rats and mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 19:234–246
Zepp RL, Kirkpatrick RL (1976) Reproduction in cottontails fed diets containing a PCB. J Wildl Manage 40:491–495
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linzey, A.V. Effects of chronic polychlorinated biphenyls exposure on reproductive success of white-footed mice (peromyscus leucopus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 455–460 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055267
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055267