Abstract
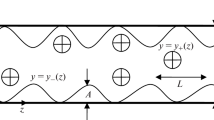
The stability of plane two-layer Couette and Poiseuille flows, where the lower layer consists of a Grad-model fluid and the upper layer is a viscous Newtonian fluid, is investigated. The disturbances are assumed to be of the long-wave type, and the analysis involves expansion in wave numbers and is limited by two approximations. Numerical calculations are made for some values of the parameters. The calculations indicate that the rotational energy of the fluid in the lower layer has a destabilizing effect on the flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
H. Grad, “Statistical mechanics, thermodynamics and fluid dynamics of systems with an arbitrary number of integrals,” Comm. Pure Appl. Math.,5, No. 4 (1952).
S. R.de Groot and P. Mazur, Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics, North-Holland Publ. Co., Amsterdam (1962).
C. S. Yih, “Instability due to viscosity stratification,” J. Fluid Mech.,27, Pt. 2 (1967).
A. T. Listrov, “Stability of flow of a layer of Grad-model liquid down an inclined plane,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekh. Zhidk., Gaza, No. 6 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Mekhanika Zhidkosti i Gaza, No. 4, pp. 125–127, July–August, 1978.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleinikov, S.M., Listrov, A.T. Effect of fluid microstructure on stability of plane two-layer flows. Fluid Dyn 13, 586–588 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055110
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055110