Abstract
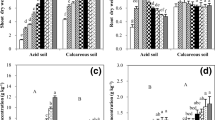
A green house experiment was conducted to study the interaction effect of Zn and N in wheat (S-308). Zinc was applied as ZnSO4.7H2O at 0, 5, 10 and 20 mg per kg, and nitrogen as urea at 0, 75 and 150 mg per kg. In the absence of added N and lime 5 mg Zn per kg increased the grain, straw and root weight, but the application of either N (75 and 150 mg per kg) or lime (4000 mg CaCO3 per kg), 10 mg Zn per kg responded significantly. However, when N and lime were added together, 20 mg Zn per kg increased the grain, straw and root weight significantly. Irrespective of Zn and N, the grain, straw and root weights were higher in limed that in unlimed soils.
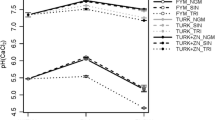
The application of N increased the Zn concentration in wheat tops and roots in unlimed soils, and decreased it in limed soils. However, because of an increase in wheat yield, the uptake of Zn by wheat tops and roots also increased with N application both in limed and unlimed soils. The addition of Zn to 10 mg per kg, increased the N concentration in the absence of N, but in the presence of N, the addition of Zn to 20 mg per kg decreased the N concentration in wheat tops and roots. The applied Zn to 10 mg per kg in unlimed soils and to 20 mg per kg in limed soils increased the N uptake by wheat tops and roots, respectively. The Zn concentration was higher in absence of lime than in its presence while a reverse trend was true for N concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhichandani CT and Patnaik S (1961) Effect of lime application on nitrogen availability and rice yields in waterlogged soils. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 9: 55–62
Brummer G, Tiller KG, Herms U and Clayton PM (1983) Adsorption — desorption and/or precipitation — dissolution processes of zinc in soils. Geoderma 31: 337–354
Chaudhry FM and Loneragan JF (1972) Zinc absorption by wheat seedlings II. Inhibition by hydorgen ions of micronutrient cations. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 36: 327–331
Court MN, Stephen RC and Waid JS (1964) Toxicity as a cause of the inefficiency of urea as fertilizer I. Review. J Soil Sci 15: 42–48
Dev S and Shukla UC (1980) Nitrogen-zinc content in maize as affected by their different sources. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 28: 336–341
Ekpete DM (1972) Assessment of the lime requirements of Eastern Nigerian soils. Soil Sci 113: 363–372
Giordano PM, Naggle JC and Mortvedt JJ (1974) Zinc uptake by rice as affected by metabolic inhibitors and competing cations. Plant and Soil 41: 637–646
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India Ltd; New Delhi
Jurinak JJ and Baver N (1956) Thermodynamics of zinc absorption on calcite, dolomite, magnesite type minerals. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 20: 466–471
Kumar V. Bhatia BK and Shukla UC (1981) Magnesium and zinc relationship in relation to dry matter yield and the concentration and uptake of nutrients in wheat. Soil Sci 131: 151–155
Kumar V, Ahalawat and Anil RS (1985) Interaction of nitrogen and zinc in pearl millet. I. Effect of N and Zn levels on dry matter yield and concentration and uptake of N and Zn in pearl millet. Soil Sci 139: 351–356
Langin EJ, Ward RC, Olsen RS and Rhoades HF (1962) Factors responsible for poor response of corn and grain sorghum to phosphorus fertilisation. II. Lime and phosphorus placement effects on phosphorus-zinc relations. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 26: 574–578
Lindsay WL and Norvall WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Am J 42: 421–428
Lutz JA Jr and Jones GD (1975) Fertilizer and lime effects on the growth, yield and chemical composition of soybean. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 23: 469–476
Mandal SC, Sinha MK and Sinha H (1975) Acid soils of India and liming. ICAR Tech Bull No 51
Miller WJ, Adams RE, Nussabaumer R, McCreedy RS and Parkins H (1964) Zinc content of coastal bermuda grass as influenced by frequency and season of harvest, location and level of N and lime. Agron J 56: 198–201
Mortvedt JJ and Giordano PM (1967) Zinc movement in soils from fertilizer granules. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 31: 608–611
Munns DN and Fox RL (1976) Depression of legume growth by liming. Plant and Soil 45: 701–704
Ozanne PG (1955) The effect of nitrogen on zinc deficiency in subterranean clover. Aust J Biol Sci 8: 47–55
Seethambaram Y and Das VSR (1986) Effect of Zndeficiency on enzyme activities of nitrate reduction and ammonia assimilation of oryza sativa L. and pennisetum americanum L. leeke. Proc Indian National Sci Aca (Biol Sci) 52: 491–494
Sharma KC, Krantz BA, Brown AL and Quick J (1968) Interaction of phosphorus and zinc on two dwarf wheats. Agron J 60: 329–332
Shukla VC and Morris HD (1967) Relative efficiency of several zinc sources for corn (Zea maize). Agron J 50: 200–202
Singh, M and Singh KS (1979) Response of wheat to zinc fertilization at different levels of phosphorus in a loamy sand soil. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 29: 314–320
Subhiah DV and Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the estimation of available nitrogen in soils. Curr Sci 25: 259–260
Takkar PN, Mann MS and Randhawa NS (1975) Effect of direct and residual available zinc on yield, zinc concentration and its uptake by wheat and groundnut crops. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 23: 91–95
Verma TS and Tripathi BR (1983) Zinc and iron interaction in submerged paddy. Plant and Soil 71: 107–116.
Verma TS and Minhas RS (1987) Zinc and phosphoros interaction in a wheat-maize cropping system. Fert Res 13: 77–86
Viets FG Jr, Boawn LC and Crawford CL (1957) The effect of N-carrier on plant uptake in indigenous and applied zinc. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 21: 197–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, T.S., Bhagat, R.M. Zinc and nitrogen interaction in wheat grown in limed and unlimed acid alfisol. Fertilizer Research 22, 29–35 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054804