Synopsis
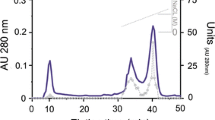
A peptidase, capable of hydrolysing naphthylamides of alanyl-alanine, leucyl-leucine and glycyl-phenylalanine, as well as amides of glycyl-phenylalanine and glycyl-tyrosine, with a dipeptide and naphthylamine or ammonia as reaction products, was partially purified from hog kidney tissue. The enzyme preparation did not hydrolyse amino acid naphthylamides. The purification procedure included acid precipitation of particles, ammonium sulphate fractionation, gel filtration on Sephadex G 200 and chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. The enzyme was shown to be optimally active at pH 5.0–6.0, dependent on sulphydryl groups, and activated by chloride ions. It was heat stable at 60°C, its isoelectric point was between 4.8 and 6.0, and its molecular weight was 134,000 as determined on gel filtration. The enzyme was suggested as being identical to cathepsin C (E.C. 34. 4. 9).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fruton, J. S., Hearn, W. R., Ingram, V. M., Wiggans, D. S. &Winitz, M. (1953). synthesis of polymeric peptides in proteinase-catalysed transamidation reactions.J. biol. Chem. 204, 891–902.
Fruton, J. S. &Mycek, M. J. (1956). Studies on beef spleen cathepsin C.Archs. Biochem. Biophys. 65, 11–20.
Gelotte, B. (1964). Fractionation of proteins, peptides and amino acids by gel filtration. In:New Biochemical Separations (eds. A. T. Sames and L. S. Morris), pp. 93–109. London, Toronto, Princeton: D. van Nostrand Company Ltd.
Glenner, G. G., Cohen, L. A. &Folk, J. E. (1965). The enzymatic hydrolysis of amino acid β-naphthylamides: I. Preparation of amino acid and dipeptide-β-naphthylamides.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 57–64.
Grabar, P. &Williams, C. A. jr (1955). Méthode immuno-electrophoretique d'analyse de mélanges de substances antigéniques.Biochim. biophys. Acta 17, 67–74.
Haba, de la, G., Cammarata, P. S. &Timasheff, S. N. (1959). The partial purification and some physical properties of cathepsin C from beef spleen.J. biol. Chem. 234, 316–19.
Hopsu-Havu, V. K. &Glenner, G. G. (1966). A new dipeptide naphthylamidase hydrolysing glycyl-prolyl-β-naphthylamide.Histochemie 7, 197–201.
Hopsu-Havu, V. K., Rintola, P. &Glenner, G. G. (1968). A hog kidney aminopeptidase liberating N-terminal dipeptides. Partial purification and characteristics.Acta chem. scand. 22, 299–308.
Hopsu-Havu, V. K. &Sarimo, S. R. (1967). Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase hydrolysing glycyl-proline naphthylamide.Hoppe-Seyler's Z. physiol. Chem. 348, 1540–50.
Izumiya, N. &Fruton, J. S. (1956). Specificity of cathepsin C.J. biol. Chem. 218, 59–76.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. &Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol-reagent.J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–75.
Mcdonald, J. K., Reilly, T. J., Zeitman, B. B. &Ellis, S. (1966). Cathepsin C: A chloride-requiring enzyme.Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 24, 771–5.
Metrione, R. M., Neves, A. G. &Fruton, J. S. (1966). Purification and properties of dipeptidyl transferase (cathepsin C).Biochemistry 5, 1597–1604.
Planta, R. J., Gorter, J. &Gruber, M. (1964). The catalytic properties of cathepsin C.Biochim. biophys. Acta 89, 511–9.
Planta, R. J. &Gruber, M. (1963). A simple estimation of cathepsin C using a new chromogenic substrate.Anal. Biochem. 5, 360–2.
Planta, R. J. &Gruber, M. (1964). Chromatographic purification of the thiol enzyme cathepsin C.Biochim. biophys. Acta 89, 503–10.
Tallan, H. H., Jones, M. E. &Fruton, J. S. (1952). On proteolytic enzymes of animal tissues. X. Beef spleen cathepsin C.J. biol. Chem. 194, 793–805.
Vanha-Perttula, T., Hopsu, V. K. &Glenner, G. G. (1965a). A dipeptide napthylamidase from hog kidney.Histochemie 5, 448–9.
Vanha-Perttula, T., Hopsu, V. K. &Glenner, G. G. (1966). Enzymes in hog kidney hydrolysing amino acid naphthylamides.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 314–25.
Vanha-Perttula, T. P. J., Hopsu, V. K., Sonninen, V. &Glenner, G. G. (1965b). Cathepsin C activity as related to some histochemical substrates.Histochemie 5, 170–81.
Walker, P. G. (1952). The preparation and properties of β-glucoronidase.Biochem.J. 51, 223–32.
Wurz, H., Tanaka, A. &Fruton, J. S. (1962). Polymerization of dipeptide amides by cathepsin C.Biochemistry 1, 19–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopsu-Havu, V.K., Rintola, P. A sulphydryl-dependent and chloride-activated peptidase (cathepsin C) that hydrolyses alanyl-alanine naphthylamide. Histochem J 1, 1–17 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054289
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01054289