Abstract
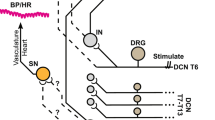
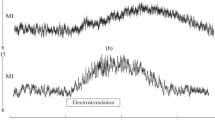
The effects of electrically stimulating different groups of nerve fibers supplying the skin and muscle on evoked potentials in cat spinal cord dorsal columns were studied. Significant differences in the configuration of dorsal column potentials recorded in response to stimulation of these nerves were found. It was shown that cutaneous nerve unmyelinated fibres were connected to unmyelinated dorsal column fibers. In addition, excitation of cutaneous C-fibers lead to activation of dorsal column fibers with the maximum conduction velocity. The somatic nerve was only connected to myelinated dorsal column fibers, and excitation of its non-myelinated fibers did not cause other types of dorsal column fibers to be activated. It is suggested that the acceleration of cutaneous signal transmission in the dorsal column system may be brought about by the necessity for rapid warning of potentially harmful stimuli.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. V. Zeveke, "On the mechanism of cutaneous excitation due to temperature stimulation," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,62, No. 1, 91–96 (1976).
A. V. Zeveke and G. I. Malysheva, "Types of fibers that conduct impulses during cutaneous nociception," Byull. Exp. Biol. Med., No. 9, 3–5 (1971).
A. V. Zeveke and V. L. Shaposhnikov, "Do specialized cold-receptors exist?" Byull. Exp. Biol. Med., No. 9, 270–272 (1979).
B. L. Shaposhnikov, "Some physiological characteristics of myelinated and unmyelinated fibers with an extremely slow conduction velocity," Neirofiziologiya,6, No. 5, 542–550 (1974).
V. L. Shaposhnikov, "Transmission of signals in the cat spinal cord dorsal columns due to electrical stimulation of cutaneous nerve afferent fibers," in: Restoration of Processes in the Nervous System, and Their Correction [in Russian], Gorkii (1990), pp. 85–92.
V. L. Shaposhnikov and A. V. Zeveke, "Afferent activity in thin myelinated and unmyelinated cutaneous nerve fibers due to mechanical stimulation of cutaneous receptors," Neirofiziologiya,8, No. 1, 67–75 (1976).
S. A. Andersson, "Projection of different spinal pathways to the second sensory area in cat," Acta Physiol. Scand.,56, Suppl. 194, 4–74 (1962).
H. Barbas and B. O. Dubrovsky, "Characteristics of dorsal neck muscle afferent input to the cat frontal cortex before and after dorsal funiculi section," Exp. Neurol.,67, No. 1, 35–51 (1980).
A. G. Brown, "Cutaneous afferent fibre collaterals in the dorsal columns of the cat," Exp. Brain Res.,5, No. 2., 293–305 (1968).
A. G. Brown, "Neuronal organization in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord," Acta Morphol. Hung.,31, No. 1/3, 87–100 (1983).
M. Fitzgerald and C. J. Woolf, "Effects of cutaneous nerve and intraspinal conditioning of C fiber afferent terminal excitability in decerebrate spinal rats," J. Physiol.,318, 25–39 (1981).
H. Hayashi, "Morphology of terminations of small and large myelinated terminal primary afferent fibers in the cat," J. Comp. Neurol.,240, No. 1, 71–89 (1985).
T. Hongo, N. Kudo, S. Sasaki et al., "Trajectory of group Ia and Ib afferent fibres at the L3–L4 segments in the cat," Neurosci. Lett., Suppl. No. 13, 129 (1976).
J. B. Horsh, "Relayed impulses in ascending branches of dorsal root fibers," J. Neurophysiol.,3, No. 2, 166–174 (1940).
K. W. Horch, P. R. Burgess, and D. Whitehorn, "Ascending collaterals of cutaneous neurons in the fasciculus gracilis of the cat," Brain Res.,117, No. 1, 1–17 (1976).
Y.-C. Huang, E. J. Hinsman, and O. F. Roesel, "Caliber spectra of fibers in the Fasciculus gracilis of the cat cervical spinal cord: a quantitative electron microscopic study," J. Comp. Neurol.,162, No. 2, 195–203 (1975).
L. A. Langford and R. E. Coggleshall, "Unmyelinated axons in the posterior funiculi," Science,211, No. 4478, 176–177 (1981).
D. P. C. Lloyd and A. K. McIntyre, "Dorsal column conduction of group muscle afferent impulses and their relay through Clarke's column," J. Neurophysiol.,13, No. 1, 39–55 (1950).
S. B. McMahon and P. D. Wall, "A system of rat spinal cord lamina I cells projecting through the contralateral dorsolateral funiculus," J. Comp. Neurol.,214, No. 2, 217–223 (1983).
P. W. Nathan, M. C. Smith, and A. W. Cook, "Sensory effects in the man lesions of the posterior columns and some other afferent pathways," Brain,109, No. 5, 1003–1041 (1986).
W. A. H. Rushton, "The site of excitation in the nerve trunk of the frog," J. Physiol.,109, No. 2, 314–326 (1949).
J. Schouenborg and A. Dickenson, "The effects of distant noxious stimulation on A and C' fibre-evoked flexion reflexes and neuronal activity in the dorsal horn of the rat," Brain Res.,328, No. 1, 23–32 (1985).
N. Underberg, "Differential localization in dorsal funiculus of fibres originating from different receptors," Exp. Brain Res.,4, 367–376 (1968).
P. D. Wall, "The sensory and motor role of impulses travelling in the dorsal columns towards cerebral cortex," Brain,93, 505–534 (1970).
C. J. Woolf and P. D. Wall, "Chronic peripheral nerve section diminishes the primary afferent A-fibre mediated inhibition of the rat dorsal horn neurones," Brain Res.,242, No. 1, 77–87 (1982).
Additional information
Medical Institute, Russian Federation Ministry of Public Health, Nizhny Novgorod. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 625–635, September–October, 1992.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaposhnikov, V.L. Excitation of cat spinal cord dorsal column fibers during stimulation of different fiber groups of cutaneous and somatic nerves. Neurophysiology 24, 417–424 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052862
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052862