Abstract
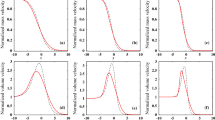
In this paper a planar stationary shock-wave-like solution of the Enskog equation obtained via a Monte Carlo technique is studied; both the algorithm used to obtain the solution and the qualitative behavior of the macroscopic quantities are discussed in comparison with the corresponding solution of the Boltzmann equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Enskog,Kinetische Theorie (Svenska Akad., 63, 1921).
S. Chapman and T. G. Cowling,The Mathematical Theory of Nonuniform Gases (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1960).
P. Resibois and M. De Leener,Classical Kinetic Theory of Fluids (Wiley, London, 1977).
N. Bellomo, M. Lachowicz, J. Polewczac, and G. Toscani,Mathematical Topics in Nonlinear Kinetic Theory II: The Enskog Equation (World Scientific, Singapore, 1991).
L. Arkeryd and C. Cercignani, Global existence in L1 for the Enskog equation and convergence of the solutions to solutions of the Boltzmann equation,J. Stat. Phys. 59:845–867 (1990).
B. L. Holian, W. G. Hoover, B. Moran, and G. K. Straub, Shock-wave structure via nonequilibrium molecular dynamics and Navier-Stokes continuum mechanics,Phys. Rev. 22A:2798–2808 (1980).
H. M. Mott-Smith, The solution of the Boltzmann equation for a shock-wave,Phys. Rev. 82:885–900 (1951).
A. V. Orlov, Extension of the Mott-Smith method to denser gases,Phys. Fluids A 4(8):1856–1858 (1992).
A. Nordsieck and B. Hicks, Monte Carlo evaluation of the Boltzmann collision integral, inRarefied Gas Dynamics, Vol. 2, C. L. Brundin, ed. (Academic Press, New York, 1967, pp. 695–710.
F. G. Tcheremissine, Fast solutions of the Boltzmann equation, inRarefied Gas Dynamics, Vol. 1, A. E. Beylich, ed. (VCH, Aachen, 1991), pp. 273–284.
V. V. Aristov, Development of the regular method of the Boltzmann equation, inRarefied Gas Dynamics, Vol. 1, A. E. Beylich, ed. (VCH, Aachen, 1991), pp. 879–885.
G. A. Bird,Molecular Gas Dynamics (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1976).
K. Nambu, Theoretical basis of the direct simulation Monte Carlo method, inRarefied Gas Dynamics, Vol. 2, V. Boffi and C. Cercignani, eds. (Teubner, Stuttgart, 1986), pp. 379–383.
K. Koura, Null collision technique in the direct simulation Monte-Carlo method,Phys. Fluids 29:3509–3511 (1986).
V. V. Aristov and F. G. Tcheremissine, The conservative splitting method for solving the Boltzmann equation,USSR Comp. Math. Phys. 20:208 (1980).
M. H. Kalos and P. A. Whitlock,Monte Carlo Methods (Wiley, New York, 1986).
A. Frezzotti and R. Pavani, Direct numerical solution of the Boltzmann equation for a relaxation problem of a binary mixture,Meccanica 24:139 (1989).
M. N. Kogan,Rarefied Gas Dynamics (Plenum Press, New York, 1969).
H. Van Beijeren and M. H. Ernst, The modified Enskog equation,Physica 68:437–456 (1973).
P. Resibois, H-theorem for the (modified) nonlinear Enskog equation,J. Stat. Phys. 19:593–609 (1978).
K. A. Fiscko and D. R. Chapman, Comparison of Burnett, Super-Burnett and Monte Carlo solutions for hypersonic shock structure, inRarefied Gas Dynamics, Vol. 1, E. P. Muntz, D. P. Weaver, and D. H. Campbell, eds. (AIAA, Pasadena, California, 1988), pp. 374–395.
E. Salomons and M. Mareschal, Usefulness of the Burnett description of strong shock waves,Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(2):269–272 (1992).
B. L. Holian, C. W. Patterson, M. Mareschal, and E. Salomons, Modeling shock waves in an ideal gas: Going beyond the Navier-Stokes level,Phys. Rev. E 47(1):R24–27 (1993).
W. Marques and G. M. Kremer, On Enskog's dense gas theory. II. The linearized Burnett equations for monatomic gases,Rev. Bras. Fis. 21(3):402–417 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frezzotti, A., Sgarra, C. Numerical analysis of a shock-wave solution of the Enskog equation obtained via a Monte Carlo method. J Stat Phys 73, 193–207 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052757
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052757