Abstract
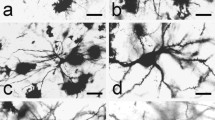
Three types of Golgi-stained neurons were discovered in brain stem reticular nuclei of 30-day-old kittens: sparsely branching reticular neurons, those with densely branching dendritic trees, and giant multipolar neurons (Leontovich's classification). Adopting computerized morphometric techniques enabled 23 different parameters to be measured in cells of these types. The measurements taken from the neuronal groups investigated revealed statistically significant differences between them for most parameters. It was concluded from this that each of the neuronal types distinguished has its own morphological identity (or stability). Characteristics of structural differences and properties of differing cell types in reticular nuclei are discussed in relation to their functional properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
N. A. Veretennikov, Microchemical Identification and Structural Aspects of Three Neuronal Classes in the Rat Brain, Author's MSc Thesis, Moscow (1987).
N. G. Gladkovich, T. A. Leontovich, and K. V. Shuleikina, "Measuring morphological parameters in developing neurons of the brain stem reticular formation," Neirofiziologiya,12, No. 1, 53–60 (1980).
N. G. Gladkovich, E. A. Lushchekina, K. V. Shuleikina, and T. A. Leontovich, "Measuring morphological parameters of developing neurons in sensorimotor nuclei of the trigeminal nerve in kittens," Neirofiziologiya,14, No. 5, 592–600 (1982).
N. G. Gladkovich, L. I. Naumova, A. D. Vorob'eva, et al, "Changed orientation of dendrites of spinal neurons developing under conditions of restricted sensory flow," in: The Developing Brain [in Russian], Moscow (1987), pp. 131–138.
N. G. Gladkovich, A. D. Vorob'eva, V. S. Lushchekin, et al, "Computerized techniques for investigating morphometric parameters of developing nerve cells," Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat,39, No. 3, 580–583 (1989).
E. G. Zvegintseva, "The dendritic system of the olfactory bulb in the dog brain," Arkh. Anatom. Histolog. Émbriolog.,82, No. 3, 21–28 (1982).
T. A. Leontovich, Neuronal Organization of Subcortical Forebrain Structures [in Russian], Moscow, Meditsina (1978).
M. E. Shaibel' and A. B. Shaibel', "The structural substrate of integration in the brain stem reticular nucleus," in: Cerebral Reticular Formation [in Russian], State Medical Literature Publishers (1962), pp. 38–71.
E. M. Glaser, H. Van der Loos, and M. Gissler, "Tangential orientation and spatial order in dendrites of cat auditory cortex: a computer microscopic study of Golgi-impregnated material," Exp. Brain Res.,36, 411–431 (1979).
R. P. Hammer. R. D. Linday, and A. B. Scheibel, "Development of the brain stem reticular core: an assessment of dendritic state and configuration in the perinatal rat," Dev. Brain Res.,1, 179–190 (1981).
G. Y. Szekely and M. Antal, "Significance of the dendritic pattern in the function of the neuron," Adv. Physiol. Sci. Neural Commun. Contr.,30, 171–182 (1981).
Additional information
Institute of Higher Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Moscow. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 23, No. 4, pp. 399–409, July–August, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gladkovich, N.G., Vorob'eva, A.D., Lushchekin, V.S. et al. Morphometric parameters of neurons in reticular nuclei of the brain stem in kittens. Neurophysiology 23, 289–296 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052559
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052559