Abstract
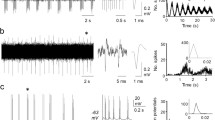
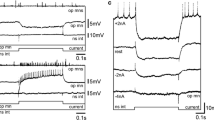
In experiments on rat brain slices, we carried out intracellular recording from neurons of the red nucleus (RN). Passive electrical properties of these neurons (input resistance, membrane time constant) were evaluated. We detected voltage-dependent rebound depolarization and time dependent inward rectification when passing hyperpolarizing pulses of current through the cell. Injections of depolarizing currents caused rhythmical firing of the neurons; the frequency of these firings depends upon the strength of injected current. Rhythmical firings were also characterized by rapid frequency adaptation when currents of different frequency were injected. Stimulation of regions of slices presumably corresponding to the decussion of the brachium conjunctivum mainly evoked EPSPs with a "fast" rise time in RN neurons. This suggests activation of synaptic input from the cerebellar nucleus interpositus. Stimulation of this same region sometimes evoked EPSP-IPSP mixtures and "pure" IPSPs in RN neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
D. Albe-Fessard, F. Stutinsky, and S. Libouban, Atlas du Stereotaxique du Diencephale du Rat Blanc [in French], C. R. Rech. Sci., Paris (1966).
K. A. Caughell and B. A. Flumerfelt, "The organization of the cerebellorubral projection: an experimental study in the rat," J. Comp. Neurol.,176, 2, 295–306 (1977).
H. Daniel, P. Angaut, C. Batini, and J. M. Billard, "Topographic organization of the interpositorubral connections in the rat. A WGA-HRP study," Behav. Brain Res.,28, 1/2, 69–70 (1988).
R. Gardette, M. Debono, J.-L. Dupont, and F. Crepel, "Electrophysiological studies on the postnatal development of intracerebellar nuclei neurons in rat cerebellar slices maintained in vitro. I. Postsynaptic potentials," Dev. Brain Responses.,19, 1, 47–55 (1985).
U. Gerber, R. W. Greene, and R. W. McCarley, "Repetitive firing properties of medial pontine reticular formation neurons of the rat recorded in vitro," J. Physiol.,410, March, 533–560 (1989).
R. Giuffrida, G. Li Volsi, and V. Perciavalle, "Influences of cerebral cortex and cerebellum on the red nucleus of the rat," Behav. Brain Res.,28, 1/2, 109–111 (1988).
H. Jansen, "Electrophysiological characteristics of neurons of the guinea-pig deep cerebellar nuclei in vitro," J. Physiol.,372, March, 129–147 (1986).
H. Jansen and R. Llinas, "Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurons: an in vitro study," J. Physiol.,349, April, 205–226 (1984).
H. Jansen and R. Llinas, "Ionic basis for the electroresponsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig red nucleus neurons in vitro," J. Physiol.,249, April, 227–247 (1984).
M. Kubota, M. Nakamura, and N. Tsukahara, "Ionic conductance associated with electrical activity of the guinea-pig red nucleus neurons in vitro," J. Physiol.,362, May, 161–171 (1985).
R. Llinas, S. A. Greenfield, and H. Jansen, "Electrophysiology of pars compacta cells in the in vitro substantia nigra — a possible mechanism for dendritic release," Brain Res.,294, 1, 127–132 (1984).
R. Llinas and Y. Yarom, "Electrophysiology of mammalian inferior olivary neurons in vitro. Different types of voltage-dependent ionic conductances," J. Physiol.,315, June, 549–567 (1981).
R. Llinas and Y. Yarom, "Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neurons in vitro, J. Physiol.,315, June, 569–584 (1981).
F. Murakami, S. Higashi, H. Katsamaru, and Y. Oda, "Formation of new corticorubral synapses as a mechanism for classical conditioning in the cat," Brain Res.,437, 2, 379–382 (1987).
Y. Nishimura, P. C. Schwindt, and W. E. Crill, "Electrical properties of facial motoneurons in brainstem slices from guinea-pig," Brain Res.,502, 1, 127–142 (1989).
K. H. Reid, H. L. Edmonds Jr., A. Schurr, et al., "Pitfalls in the use of brain slices," Progr. Neurobiol.,31, pp. 1–18 (1988).
H. Sakaguchi, M. Kubota, M. Nakamura, and N. Tsukahara, "Effect of amino acids on cat red nucleus neurons in vitro," Exp. Brain Res.,54, 1, 150–156 (1984).
M. Segal, "Properties of rat medial septal neurons recorded in vitro," J. Physiol.,379, Oct., 309–330 (1986).
K. Toyama, N. Tsukahara, K. Kosaka, and K. Matsunami, "Synaptic excitation of red nucleus neurons by fibers from interpositus nucleus," Exp. Brain Res.,11, 3, 187–198 (1970).
N. Tsukahara, H. Hultborn, F. Murakami, and Y. Fujito, "Electrophysiological study of formation of new synapses and collateral sprouting in red nucleus neurons after partial denervation," J. Neurophysiol.,38, 6, 1359–1372 (1975).
Additional information
L. A. Orbeli Institute of Physiology, Armenian Academy of Sciences, Erevan. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 23, No. 5, pp. 607–616, September–October, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babalyan, A.L., Fanardzhyan, V.V. Electrophysiological properties of neurons of the red nucleus in rat brain slices. Neurophysiology 23, 454–461 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052452
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052452