Abstract
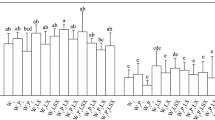
A pot study with four levels each P (control, 6.5, 13.0, 19.5 mg kg−1) and Cl− in irrigation water (control, 30, 60, 90me l−1) was carried out to test Cl− and P interaction on wheat. It has been found that optimum P nutrition alleviates the toxic effect of excess Cl−. Highest P rate resulted in a significant yield increase upto a Cl− level of 60me l−1. Cl− depressed P content in the plant only at a Cl− level of 90me l−1, while P rates had no major impact on the Cl− concentration in the plant. Lower Cl− concentration at higher P rates are rather a dilution effect than an antagonistic one. With optimum P supply higher Cl− contents in the plants were tolerated than with a low P supply.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrol IP (1974) Recent advances in fertilizer use in salt-affected soils. Fert News, December 12–16
Antonio Cerda, Bigham FT and Hoffman GJ (1977) Interactive effect of salinity and phosphorus on Sesame. Soil Sci Soc Amer J 41, 915–918
Bernstein L, Francois LE and Clark RA (1974) Interactive effects of salinity and fertility on yields of grains & vegetables. Agro J 66, 412–421
Chapman HD and Pratt FP (1961) Methods of analysis for soils, plant and waters. University of California, Devision of Agricultural Sciences
Chhabra R (1973) Kinetics of absorption of chloride and phosphorus, their interaction effect on growth and composition of tomato plants Ph.D. Thesis, Catholic University, Belgium
Dregne HE and Hessam Mojallali (1969) Salt-fertilizer specific ion interactions in soils. New Mexico state University, Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 541, 1–16
Ferguson WS and Heldin RA (1963) Effect of soluble salts on plant responses and absorption of P. Candian J Soil Sci 43, 210–218
Khalil MA, Amer F and Elgabaly MM (1967) A salinity fertility interaction study on corn & cotton. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 31, 683–686
Labanauskas CK, Bingham FT and Antonio Cerda (1978) Free & protein amino acid and nutrient concentration in wheat grain as affected by phosphorus nutrition at various salinity levels. Pl Soil 49, 581–593
Manchanda HR and Singh JP (1982) Wheat growth in chloride and sulphate dominant saline soil and the effect of phosphorus application. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 30, 53–57
Ravikovitch S and Porath AC (1967) The effect of nutrients on salt tolerance of crops. Pl Soil 26, 49–71
Richard LA (1954) United State Department of Agriculture Handbook No 60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, R., Chauhan, C. Effect of P fertilizer on alleviating chloride toxicity in wheat. Fertilizer Research 6, 171–176 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01051011
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01051011