Abstract
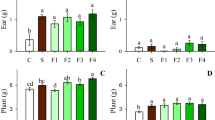
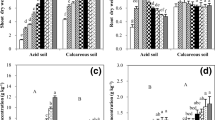
To study the interaction effect of Zn and P in a wheat-maize cropping system, a field experiment was conducted at the H.P. Agricultural University Research Station, Palampur (India). Zinc was applied as ZnSO4·7H2O at the rate of 0, 20 and 40 kg per ha and P as superphosphate at the rate of 0, 60 and 120 kg per ha. The direct Zn-P interaction effect was investigated on wheat (S—308) and its residual effect on maize (early composite). Added Zn did not increase the grain and straw yield of wheat when P was not applied, but when P was applied, 20 kg per ha added Zn responded significantly. Contrary to this, in maize, only 20 kg per ha added Zn responded significantly when P was not applied, but when P was applied, even 40 kg per ha Zn increased the grain and straw yield of maize. The grain and straw yield of wheat and maize were higher under limed than under unlimed conditions.
The concentration of Zn increased with the application of Zn and decreased with the application of P. The concentration of Zn was comparatively higher in grain than in straw of wheat and maize. The P concentration in wheat and maize plants decreased with the increasing levels of applied Zn. The concentrations of Zn were lower under limed than under unlimed condition, whereas the reverse was true for P concentrations.
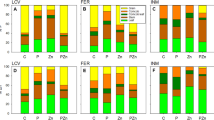
The respective absorption of Zn and P in wheat was 9.7 and 7.3 per cent upto tillering, 47.9 and 49.4 per cent between tillering and flowering, and 42.3 and 43.3 per cent between flowering and maturity. The corresponding absorption of Zn and P in maize was 11.7 and 9.4, 59.9 and 52.1, and 29.3 and 38.5 per cent before booting stage, between booting and tasseling stage and between tasseling and maturity stage, respectively. At maturity, about 53.1 and 13.0 per cent of the Zn and P taken up were retained by wheat straw and 46.9 and 87.0 per cent by wheat grain. The respective values for Zn and P in maize straw and grain were 66.8 and 30.3 and 33.2 and 69.7 per cent. When more Zn was applied, less Zn was translocated to grains; when more P was added, more Zn was translocated to grains. The effects of P and Zn on P distribution at maturity were opposite to that of Zn distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham FT and Garber MJ (1960) Solubility and availability of micronutrients in relation to fertilisers. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 24: 209–213
Boawn LC and Ramussen EP (1969) Phosphorus fertilisation of hops. Agron J 61: 211–214
Boawn LC, Krantz BA and Eddings JL (1970) Zinc-phosphorus fertilisation in the zinc nutrition of several irrigated crops. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 34: 365–368
Brown AL, Krantz BA and Eddings (1970) Zinc phosphorus interaction as measured by plant response and soil analysis. Soil Sci 110: 415–420
Chaudhry FM and Loneragan JF (1972) Zinc absorption by wheat II. Inhibition by hydrogen ions of micronutrient cations. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 36: 327–331
Giordane PM and Mortvedt JJ (1972) Rice response to zinc in flooded and non flooded soil. Agron J 64: 521–524.
Giordane PM, Naggle JC and Mortvedt JJ (1974) Zinc uptake by rice as affected by metabolic inhibitors and competing cations. Plant and Soil 41: 637–646
Kalyanasundaram NK and Mehta BV (1970) Availability of zinc, phosphorus and calcium in soils treated with varying levels of zinc and phosphate—A soil incubation study. Plant and Soil 33: 699–706
Kankoulakes P (1973) Effect of phosphorus and zinc interaction and time on plant growth in the presence of high levels of extractable zinc. Rapport Instituut voor Bodem vruchtbaarheid, No. 4, p. 65
Lindsay WL (1972) Inorganic phase equilibria of micronutrients in soils. In: Micronutrients in Agriculture, p. 57. Soil Sci Soc Am Inc.
Malavalala E and Govasliaga OL (1974) Studies on the zinc and phosphorus relationship in plants. In: Plant Analysis and Fertiliser Problems, Vol. 2, Proc 7th Int Colloq German Soc Plant Nutr, pp 261–272
Mongia AD (1966) Phosphorus-zinc relationship in wheat as affected by sources and rates of applied phosphorus. M.Sc. thesis, Pb Agric Univ Hissar
Reddy GD, Venkatasubbiah V and Venkateshwaralu J (1973) Zinc-phosphorus interaction in maize. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 21: 433–437
Seatz LF and Jurinak JJ (1957) Soils, the 1957 Year Book of Agric, USDA
Sharma KC, Krantz BA, Brown AL and Quick J (1968) Interaction of P and zinc on two dwarf wheats. Agron J 60: 329–332
Singh M and Singh KS (1979) Response of wheat to Zn fertilisation at different levels of phosphorus in a loamy sand soil. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 29: 314–320
Singh M and Singh SP (1980) Zinc and phosphorus interaction in submerged paddy. Soil Sci 129: 282–289
Singh BP, Singh AP and Sakal R (1983) Differential response of crops to zinc applications in calcareous soils. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 31: 534–538
Stanten DA and Burger RD (1979) Agrochemophysica 2: 33
Stuckenholtz DD, Olsen RJ, Gogan G and Olson RA (1966) On the mechanism of phosphorus-zinc interaction in corn nutrition. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 30: 759–763
Takkar PN, Mann MS and Randhawa NS (1975) Effect of direct and residual available zinc on yield, zinc concentration and its uptake by wheat and groundnut crops. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 23: 91–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, T.S., Minhas, R.S. Zinc and phosphorus interaction in a wheat-maize cropping system. Fertilizer Research 13, 77–86 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049804
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049804