Abstract
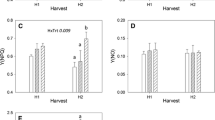
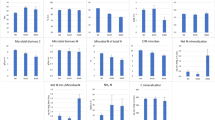
In a pot trial with spruce seedlings growing in washed quartz sand, Zn concentration in needles could be reduced to 13 ppm in dry matter, but no visual symptoms of Zn deficiency appeared within two years. With Zn applied at 0.31 mg/kg substrate concentrations in seedlings were up to 133 ppm with no symptoms of damage or inhibition of growth. Needle contents of Zn, Ca, Mg, Fe and Al increased from year 1 to year 2. Zn content decreased in case of Ca- or Mg- and especially in combined Ca and Mg deficiency; when no Zn was applied in the second year, the lowest values were recorded. Zn content was positively correlated with N, K, Ca, Mn, and Fe, and N with Mg and Mn. There were no other antagonistic effects of Zn. The best growth of 2 year old seedlings was at needle Zn contents of 28–36 ppm in one year old and of 93–112 ppm in two year old needles. Spruce on areas of new forest damage has a lowered Mg content and lessened accumulation of Ca and Mn with increasing needle age as well as low Zn content (despite atmospheric deposition of Zn). Such low Zn levels could only be achieved in pot culture by taking strong precautions against contamination. Ca + Mg + Zn fertilizer should be tested on strongly acid upland soils low in Zn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann W and Neubert P (1976) Pflanzendiagnose und Pflanzenanalyse. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Dietrich H and Lentschig S (1968) Über die Mikronährstoffversorgung der Fichte auf ausgewählten Standorten des Mittelgebirges und Hügellandes. DAL Berlin Tag.-Ber Nr 84: 157–171
Fiedler HJ (1988) Zur Zinkausstattung der Fichtenökosysteme in Gebieten mit ‘neuartigen’ Waldschäden. Beiträge fd Forstwirschaft 22: 61–66
Fiedler HJ, Höhne H, Ilgen G and Glowna E (1988) Der forstliche Gefäßversuch Teil III, TU Dresden, Sektion Forstwirtschaft
Fiedler HJ (1989) Neuartige Waldschäden aus ökologischer Sicht. Richtig düngen — mehr ernten. VEB Kombinat Kali (Erfurt) Heft 3
Getahun A (1989) Zur Zinkernährung höherer Pflanzen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Fichtensämlingen. Dipl-Arbeit TU Dresden, Tharandt
Lucas A (1988) Nadelanalytische Untersuchungen an Fichte zur Diagnose von Immissionsschäden im Staatlichen Forstwirtschaftsbetrieb Gotha, Dipl-Arbeit, Tharandt
Marschner H and Cakmak J (1989) High light intensity enhances chlorosis and necorsis in leaves of zinc, potassium, and magnesium deficient bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. J Plant Physiol 134: 308–315
Osswald WF und Elstner EF (1986) Mechanismen der pathologischen Pigmentbleichung bei Pflanzen. Ber Deutsch Bot Ges 99: 341–365
Vieth M (1986) Modellversuche zur Auswaschbarkeit von Mineralstoffen durch ‘sauren Regen’ aus Fichtennadeln nach verschiedenen Vorbehandlungen (SO2, O3, SO2/O3, oxidierte Terpene) Dissertation (A), TU Dresden, Tharandt
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiedler, H.J., Ilgen, G. & Getahun, G.B.A. Pot experiments on the zinc nutrition of spruce seedlings in relation to the new kind of forest decline. Fertilizer Research 26, 237–242 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048761
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048761