Summary
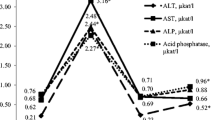
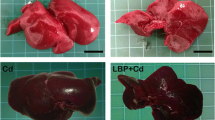
Female Wistar rats received an oral dose of 700 mg salicylic acid/kg body wt., given as sodium salicylate. Some of the salicylate-treated rats received two subcutaneous injections of 100 μmol kg−1 ZnCl2 (24 h before and simultaneously with the salicylate administration). Other animals were given one subcutaneous injection of 100 μmol kg−1 ZnCl2 simultaneously with the salicylate treatment. Control rats were similarly injected with ZnCl2. Twenty four hours after salicylate treatment, serum and livers were taken for histochemical and biochemical analysis. The most remarkable effects of the treatment were enrichment of lipid droplets and iron and a reduction of glycogen, particularly in the periportal hepatocytes. The effects of salicylate were partially prevented by two ZnCl2 injections. The protective effects of ZnCl2 may be due to lower iron uptake into hepatocytes and by the induction of zinc metallothionein, which can serve as a scavenger for oxygen radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckett, G. J., Foster, G. R., Hussey, A. J., Oliveira, D. G. B., Donavan, J. W., Prescott, L. F. &Proud-Foot, A. T. (1989) Plasma glutathione S-transferase and F protein are more sensitive than alanine aminotransferase as markers of paracetamol (acetaminophen)-induced liver damage.Clin. Chem. 35, 2186–9.
Bellomo, G., Jewell, S. A., Thor, H. &Orrenius, S. (1982) Regulation of intracellular calcium compartmentation: Studies with isolated hepatocytes and t-butyl hydroperoxide.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 6842–6.
Bettger, W. J. &O'Dell, B. L. (1981) A critical physiological role of zinc in the structure and function of biomembranes.Life Sci. 28, 1425–38.
Cagen, S. Z. &Klaassen, C. D. (1980) Carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity: studies in developing rats and protection by zinc.Fred. Proc. 39, 3124–8.
Chengelis, C. P., Dodd, D. C., Means, J. R. &Kotsonis, F. N. (1986) Protection by zinc against acetaminophen induced hepatotoxicity in mice.Fund. Appl. Toxicol. 6, 278–84.
Cho, C. H. (1989) Current views of zinc as a gastrohepatic protective agent drug.Drug Developm. Res. 17, 185–97.
Dar, M. S., Towsend, S. M. &Wooles, W. R. (1986) Protective effect of zinc against ethanol toxicity in mice.J. Toxicol. Environm. Hlth. 18, 41–8.
Eaton, D. L. &Toal, B. F. (1982) Evaluation of the Cd/hemoglobin affinity assay for the rapid determination of metallothionein in biological tissues.Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 66, 134–42.
Gossrau, R., Van Noorden, C. J. F. &Frederiks, W. M. (1989) Enhanced light microscopic visualization of oxidase activity with the cerium capture method.Histochemistry 92, 349–53.
Gossrau, R., Frederiks, W. M., Kooij, A., Van Noorden, C. J. F. & Ruhnke, M. (1990) Light microscopical detection of H2O2-generating oxidases using cerium ions and aequous incubation media.Acta Histochem. (in press).
Günther, T., Gossrau, R., Vormann, J., Höllriegl, V. &Graf, R. (1988a) Maternal and fetal iron accumulation in Zn-deficient and salicylate treated rats.Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 18, 49–58.
Günther, T., Höllriegl, V. &Vormann, J. (1988b) Effects of salicylate and zinc deficiency on the serum concentrations of magnesium, calcium and parathyroid hormone.Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 16, 129–35.
Günther, T. &Höllriegl, V. (1989) Lipid peroxidation in mitochondria and microsomes from adult and fetal rat tissues. Effects of Zn deficiency, Fe, and salicylate.Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 22, 165–77.
Günther, T., Rebentisch, E. &Vormann, J. (1989a) Protection against salicylate ototoxicity by zinc.J. Trace Elem. Health Dis. 3, 52–3.
Günther, T., Vormann, J. &Ghaida, J. (1989b) Induction of metallothionein by salicylate in adult rats.Biol. Trac. Elem. Res. 20, 243–9.
Günther, T., Merker, H. J. & Vormann, J. (1990) Protection against salicylate-induced hypocalcemia in pregnant rats by magnesium deficiency.Mag. Bull. (in press).
Gutknecht, J. (1990) Salicylates and proton transport through lipid bilayer membranes: A model for salicylate-induced uncoupling and swelling in mitochondria.J. Membrane Biol. 115, 253–60.
Hamer, D. H. (1986) Metallothionein.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55, 913–51.
Jungermann, K. &Katz, N. (1989) Functional specialization of different hepatocyte populations.Physiol. Rev. 69, 708–64.
Kotsonis, F. N. &Klaassen, C. D. (1979) Increase in hepatic metallothionein in rats treated with alkylating agents.Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 51, 19–27.
Lojda, Z., Gossrau, R. &Schiebler, T. H. (1979)Enzyme Histochemistry. A Laboratory Manual. Berlin: Heidelberg, New York: Springer.
McMillan, D. A. &Schnell, R. C. (1984) Zinc protection against bromobenzene induced hepatotoxicity in the rat.Toxicologist 4, 45.
Mimura, T., Tsujikawa, K., Yasuda, N., Nakajima, H., Harujama, M., Ohmura, T. &Okabe, M. (1988) Suppression of gastric ulcer induced by stress and HCl-ethanol of intravenously administered metallothionein. II.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 151, 725–9.
Miranda, C., Henderson, M., Reed, R., Schmitz, J. &Bühler, D. (1982) Protective action of zinc against pyrrolizidine alkaloid induced hepatotoxicity in rats.J. Toxicol. Environ. Hlth. 9, 359–66.
Miyahara, J. T. &Korler, R. (1965) Effect of salicylate on oxidative phosphorylation and respiration of mitochondrial fragments.Biochem. J. 47, 194–8.
Oh, S. H., Deagen, J. T., Whanger, P. D. &Weswig, P. H. (1978) Biological function of metallothionein. V. Its induction in rats by various stresses.Am J. Physiol. 234, E282–5.
Onosaka, S. &Cherian, M. G. (1982) Comparison of metallothionein determination by polarography and cadmium-saturation methods.Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 63, 270–4.
Rick, W. (1974)Klinische Chemie und Mikroskopie. 3. Aufl. p. 47. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer.
Romeis, B. (1968)Mikroskopische Technik. München: Oldenbourg.
Sevier, E. D. &Cano, C. (1978) Spectrofluorometric assay of salicylate metabolic in serum and urine.Clin. Chem. 24, 1059.
Thomas, J. P., Bachowski, G. J. &Girotti, A. W. (1986) Inhibition of cell membrane lipid peroxidation by cadmium- and zinc-metallothionein.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 884, 448–61.
Thornalley, P. J. &Vasak, M. (1985) Possible role for metallothionein in protection against radiation-induced oxidative stress. Kinetics and mechanism of its reaction with superoxide and hydroxyl radicals.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 827, 36–44.
Tsokos-Kuhn, J. O. (1989) Evidence in vivo for elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ in the liver after diquat, acetaminophen and CCl4.Biochem. Pharmacol. 38, 3061–5.
Ungemach, F. R. (1987) Pathobiochemical mechanisms of hepatocellular damage following lipid peroxidation.Chem. Phys. Lipids. 45, 171–205.
Waalkes, M. P., Hjelle, J. J. &Klaassen, C. D. (1984) Transient induction of hepatic metallothionein following oral ethanol administration.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 74, 230–6.
Wormser, U. &Calp, D. (1988) Increased levels of hepatic metallothionein in rat and mouse after injection of acetamorphen.Toxicol. 53, 323–9.
Yaki, K., Ozawa, T. &Okada, K. (1959) Mechanism of inhibition ofd-amino acid oxidase. II. Inhibitory actions of benzene derivatives.Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 35, 102–10.
Zaman, J. &Verwilghen, R. L. (1981) Influence of zinc on iron uptake by monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes and the hepatocellular ferritin.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 675, 77–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Günther, T., Gossrau, R., Vormann, J. et al. Protection against salicylate-induced hepatic injury by zinc. A histochemical and biochemical study. Histochem J 23, 75–82 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01047111
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01047111