Abstract
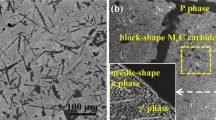
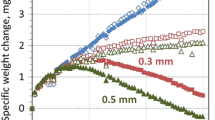
An investigation was carried out to study the kinetics and products of oxidation of a wrought Ni−Cr−W−Mn−Si−La alloy at temperatures in the range of 950 to 1150°C. Oxidation kinetics were evaluated from measurements of weight change, metal loss, and internal penetration. Analytical electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, and X-ray diffraction were used to characterize the scale microstructure. Initially, La was observed to segregate within a surface layer of about 5 μm thick, which promoted selective oxidation of Cr and Mn. Oxidation kinetics were found to follow a parabolic-rate law with an activation energy of about 232kJ/mol. During steady-state oxidation, the scale consisted of an inner adherent layer of α-Cr2O3 modified by the presence of La and Si, and shielded by an outer layer of MnCr2O4. Most of the La was segregated to grain boundaries of the α-Cr2O3 scale, however, Si was homogeneously distributed. It was concluded that the characteristic oxidation resistance of the alloy was related to the synergistic effects of Ni and Cr and to the effective minor additions of La, Si, and Mn; however, the useful life of the scale was limited by rupture and surface depletion in Cr, leading to accelerated internal oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. L. Smialek and G. H. Meier, inSuperalloys II, C. T. Sims, N. S. Stoloff, and W. C. Hagel, eds. (Wiley Interscience, New York, 1987), p. 293.
E. A. Gulbranson and S. A. Jansson, inHeterogeneous Kinetics at Elevated Temperatures, G. R. Belton and W. L. Worrell, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1970), p. 181.
C. S. Tedmon,J. Electrochem. Soc. 113, 766 (1966).
E. A. Gulbranson and K. F. Andrew,J. Electrochem. Soc. 104, 334 (1957).
R. A. Perkins, inProc. Conf. Corrosion/Erosion of Coal Conversions System Materials, A. W. Levy, ed. (NACE Houston, 1979), p. 351.
H. M. Tawancy,Structure and Properties of High-Temperature Alloys: Applications of Analytical Electron Microscopy (KFUPM Press, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia 1993), Chap. 6, p. 265.
G. Y. Lai,High-Temperature Corrosion of Engineering Alloys (ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1990). Chap. 3, p. 28.
D. L. Klarstrom, U.S. Patent No. 4476091, October 9, 1984.
H. M. Tawancy, D. L. Klarstrom, and M. F. Rothman,J. Met. 36 (9), 58 (1984).
D. L. Klarstrom, H. M. Tawancy, D. E. Fluck, and M. F. Rothman, 29th Int. Gas Turbine Conf., ASME 84-GT-40, 1984.
M. F. Rothman, 30th Gas Turbine Conf., ASME 85-GT-10, 1985.
P. J. Goodhew,Specimen Preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy of Materials (Royal Microscopy Society, Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1984), p. 26.
M. J. Bennett and D. P. Moon, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behavior of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 111.
T. A. Ramanarayanan, R. Ayers, R. Petkovic-Luton, and D. P. Leta,Oxid. Met. 29 (5/6), 445 (1988).
P. Kofstad, inChemical and Mechanical Behavior of Inorgnic Materials, A. W. Searcy, D. N. Ragone, and U. Colombo, eds. (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1970), Chap. 13, p. 45.
K. Hoshino and N. L. Peterson,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 66, 202 (1983).
A. Atkinson and R. I. Taylor, inTransport in Non-Stoichiometric Compounds G. Simkovich and V. S. Stubican, ed. (Plenum Press, New York, 1985), p. 285.
H. V. Atkinson,Oxid. Met. 24(3/4), 177 (1985).
K. P. Lillerud and P. Kofstad,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127, 2397 (1980).
D. Caplan and G. I. Sprouce,Oxid. Met. 9, 459 (1975).
J. H. Park, W. E. King, N. L. Peterson, and S. J. Rothman, inOxidation of Metals and Associated Mass Transport, M. A. Dayanada, ed. (TMS-AIME, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1987), p. 103.
N. J. Zaluzec, inIntroduction to Analytical Electron Microscopy, J. J. Hren, J. I. Goldstein, and D. C. Joy, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1979), Chap. 4, p. 121.
F. H. Stott, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behavior of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 3.
G. E. Wasielewski and R. A. Rapp, inThe Superalloys, C. T. Sims and W. C. Hagel, eds. (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1972), Chap. 10, p. 287.
M. Levy, P. Farrell, and F. S. Pettit, Corros.-NACE42 (12), 708 (1986).
D. P. Whittle, inHigh Temperature Corrosion, R. A. Rapp, ed. (NACE, Houston 1984), p. 171.
F. H. StottMater. Charact. 28, 311, (1992).
G. M. Raynaud and R. A. Rapp, inCorrosion, Microstructure, and Metallography, D. O. Northwood, W. E. White, and G. F. Vander Voort, eds.Microstructural Science vol. 12 (ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1985), p. 197.
G. Beranger, F. Armanet, and M. Lambertin, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behavior of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 33.
D. P. Whittle and J. S. Stringer,Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 295, 309 (1980).
P. Kofstad, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behavior of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 367.
H. Hindam and D. P. Whittle,Oxid. Met. 18 (5/6), 245 (1982).
A. M. Huntz, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed., (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 81.
J. Jedlinski, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 131.
J. R. Nicholls and P. Hancock, inThe Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behavior of High Temperature Metals and Alloys, E. Lang, ed. (Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York, 1989), p. 195.
C. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit,Met. Trans. 2, 1071 (1971).
G. Y. Lai,J. Met. 41, (7), 21 (1989).
C. M. Cotell, G. J. Yurek, and R. J. Hussey, D. F. Mitchell, and M. J. Graham,Proc. Electrochem. Soc. 88 (5), 268 (1988).
K. Przybylski and G. J. Yurek,J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 517 (1988).
G. J. Yurek, K. Przybylski, and A. J. Garrett-Reed,J. Electrochem. Soc. 134, 2643 (1987).
C. H. Yang, P. A. Labun, G. E. Welsch, T. E. Mitchell, and M. J. Bennett,J. Mater. Sci. 22, 449 (1987).
M. J. Bennett, B. A. Bellamy, C. F. Knights, N. Medows, and N. J. Eyre,J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 69, 359 (1985).
G. C. Wood and D. P. Whittle,Corros. Sci. 7, 763 (1967).
F. H. Stott,Rep. Prog. Phys. 50, 861 (1987).
J. E. Harris,J. Met. 39 (1), 34 (1987).
J. Stringer,Werks. Korros. 23, 747 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tawancy, H.M. High-temperature oxidation behavior of a wrought Ni-Cr-W-Mn-Si-La alloy. Oxid Met 45, 323–348 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046988
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046988