Abstract
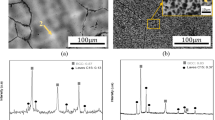
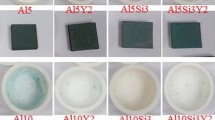
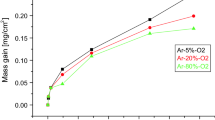
Twenty-four ternary element additions were made to a binary TiAl alloy (Ti−34.5 wt.% Al), and the oxidation behavior was studied. As a result of the oxidation tests in air at 1173 K for 360 ks, ternary elements were classified into three groups according to their effects, namely, (a) detrimental; V, Cr, Mn, Pd, Pt, Cu; (b) neutral; Y, Zr, Hf, Ta, Fe, Co, Ni, Ag, Au, Sn, O; (c) beneficial; Nb, Mo, W, Si, Al, C, B. This classification was valid for Cr, Mn, Mo, and W under several other temperature and time conditions. The influence of the additions was very significant, the difference in the weight gain between the best and the worst alloys being approximately two orders of magnitude. As a result of detailed examinations, it was confirmed that Cr and Mn additions caused linear-oxidation behavior from the outset at 1173 K, virtually no Al2O3 barrier being formed. This is probably due to the doping of those elements in TiO2. The beneficial elements, such as Mo, Nb, W, resulted in protectiveoxidation behavior. The characteristic features of the scale on those alloys were the presence of a continuous Al2O3 layer as the second layer from the outer surface and the relatively massive precipitation of Al2O3 in the vicinity of the scale-metal interface. Also, these alloys did not show any evidence of internal oxidation. The scale types and the proposed mechanism for the innerscale formation are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Shida and H. Anada,Mater. Trans. JIM 34, 236 (1993).
Y. Shida and H. Anada,J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 55, 690 (1991).
Y. Shida and H. Anada,Corros. Sci. 35, 945 (1993).
Y. Shida and H. Anada, inHigh Temperature Corrosion of Advanced Materials and Protective Coatings, by Y. Saito, B. Onay and T. Maruyama, eds. (Elsevier, New York, 1992), pp. 325–332.
H. Anada and Y. Shida, Report of the 123rd Committee on Heat Resisting Metals and Alloys, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science No. 32, 1991, p. 347.
H. Anada and Y. Shida,Sumitomo Search No. 52, 83 (1993).
M. J. Bennett and A. T. Tuson,High Temperature Intermetallics (Royal Society of London, 1991).
T. Shimizu, T. Iikubo, and S. Isobe, Report of the 123rd Committee on Heat Resistant Metals and Alloys, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science No. 31, 1990, p. 309.
K. Kasahara, T. Hashimoto, H. Doi, and T. Tsujimoto,J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 54, 948 (1990).
S. Becker, A. Rhamel, M. Schorr, and M. Schuetze,Oxid. Met. 38, 425 (1992).
R. A. Perkins, K. T. Chiang, G. H. Meier, and R. Miller, inOxidation of High Temperature Intermetallics, T. Grobstein and J. Doychak, eds. (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1989), pp. 157–169.
N. S. Choudhurry, G. H. Graham, and J. W. Hinze, inProperties of High Temperature Alloys with Emphasis on Environmental Effects, Z. A. Foroulis and F. S. Pettit, eds. (The Electrochemical Society, Pennington, NJ, 1976), p. 668.
K. Tsurumi, H. Hino, J. Fujioka, and Y. Nishiyama, ibid. No. 29 in, (1988), p. 77.
Y. Ikematu, T. Hanamura, and H. Morikawa, 26th Corrosion and Protection Symp. Proc., Japan Society of Corrosion Engineers, 1991, p. 18.
K. Shibue, M. Kumagai, and H. Kim,J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 56, 1457 (1992).
R. A. Perkins, K. T. Chiang, and G. H. Meier,Scripta Metall. 21, 1505 (1987).
Y. Kim and F. H. Froes, inHigh Temperature Aluminides and Inter Metallics, S. H. Whang, C. T. Liu, D. P. Pope, and J. O. Stiegler, eds. (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1990), p. 465.
Y. Shida and H. Anada,Mater. Trans. JIM 35, 623 (1994).
H. Anada and Y. Shida,J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 58, 746 (1994).
H. Anada and Y. Shida,J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 58, 1036 (1994).
P. Kofstad, inHigh Temperature Corrosion (Elsevier Applied Science, 1988).
H. Hindam and D. P. Whittle,Oxid. Met. 18, 245 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shida, Y., Anada, H. The effect of various ternary additives on the oxidation behavior of TiAl in high-temperature air. Oxid Met 45, 197–219 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046826
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046826