Summary
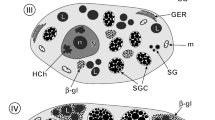
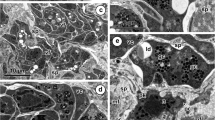
The protein A-gold immunocytochemical technique was used to localize the secretory pathway of oestradiol-induced vitellogenin in hepatic parenchymal cells of the cockerel. Liver was removed from experimental birds on the 1st, 4th and 8th day following oestradiol-treatment, and embedded in Lowicryl K4M resin cured at −20°C. In selected electron, micrographs the fractional surface area of each of the intracellular, compartments was measured by the computer-assisted digitization technique. Labelling was detected over the cisternae of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), the Golgi apparatus, the immature secretory vacuoles (ISV) including condensing vacuoles and the mature secretory vacuoles (MSV). Counts of the gold particles demonstrated an increasing concentration which progressed in the order RER<Golgi<ISV<MSV and identified the secretory pathway of the protein. The highest density of labelling was obtained on the 4th day, when vitellogenin reaches its peak activity. Autophagic activity (or crinophagy) was also found in lysosomes and its labelling intensity increased daily. A hypothesis concerning the secretory pathway of non-stored proteins by the liver is discussed further.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adiga, P. R. &Ramana Murty, C. V. (1983) Vitamin carrier proteins during embryonic development in birds and mammals. InMolecular Biology of Egg Maturation (edited byPorter, R. &Whelan, J.) pp. 111–36. London: Pitman Books Ltd.
Bergink, E. W., Kloosterboer, H. J., Gruber, M. &Ab, G. (1973) Estrogen-induced phosphoprotein synthesis in roosters. Kinetics of induction.Biochim. Biophys. Acta,294, 497–506.
Chandler, J. A. (1985) Experiments with different resins on labelling.Proc. Roy. Micro. Soc.,20(4), GLUG-3.
Clemens, M. J. (1974) The regulation of egg yolk protein synthesis by steroid hormones.Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 28, 71–108.
Deeley, R. G., Mullinix, K. P., Wetekam, W., Kronenberg, H. M., Meyers, M., Eldridge, J. D., &Goldber Ger, R. F. (1975) Vitellogenin synthesis in the avian liver. Vitellogenin is the precursor of the egg yolk phosphoproteins.J. Biol. Chem. 250, 9060–6.
Gebhart, A. M. &Ruddon, R. W. (1986) What regulates secretion of non-stored proteins by eukaryotic cells?BioEssays 4, 213–18.
Geuze, J. J., Slot, J. W. &Brands, R. (1981) The occurrence of albumin in the rat liver. A light and electron microscope immunocytochemical study.Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 5, 463.
Goldberger, R. F. &Deeley, R. G. (1980) The effect of estrogen on gene expression in avian liver. InGene Regulation by Steroid Hormones (edited byRoy, A. K. &Clark, J. H.) pp. 32–56. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Green, C. D. &Tata, J. R. (1976) Direct induction by estradiol of vitellogenin synthesis in organ culture of maleXenopus laevis liver.Cell 7, 131–9.
Grieninger, G. (1983) Isolation hepatocytes in culture: A model for studying the control of plasma protein synthesis. InPlasma Protein Secretion by the Liver (edited byGlaumann, H. G., Peters, Jr, T. &Redman, C.) pp. 155–93. London: Academic Press.
Hamilton, R. L. (1983) Hepatic secretion of nascent plasma lipoproteins. InPlasma Protein Secretion by the Liver (edited byGlaumann, H. G., Peters, Jr, T. &Redman, C.) pp. 357–74. London: Academic Press.
Herbener, G. H., Feldhoff, R. C. &Fonda, M. L. (1983) A correlated morphometric and biochemical study of estrogen-induced vitellogenesis in maleRana pipiens.J. Ultrastr. Res. 83, 28–42.
Herbener, G. H., Bendayan, M. &Feldhoff, R. C. (1984) The intracellular pathway of vitellogenin secretion in the frog hepatocytes as revealed by protein A-gold immunocytochemistry.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 32, 697–704.
Herbener, G. H., Bendayan, M. &Feldhoff, R. C. (1986) Albumin localization in the frog hepatocyte during vitellogenesis as revealed by protein A-gold immunocytochemistry.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34, 665–71.
Jailkhani, M. L. &Talwar, G. P. (1972) Oestradiol-induced synthesis of phosvitin.Nature New Biol. 236, 239–40.
Kami, K. &Stoward, P. J. (1985) Immunogold and immunoperoxidase staining methods for ultrastructural demonstration of vitellogenesis pathway in chicken hepatocytes using cost-embedding techniques.Proc. Roy. Micro. Soc. 20(4), IM-13.
Kami, K. & Stoward, P. J. (1991) Immunoelectron microscopical demonstration of egg-yolk plasma precursor/ vitellogenin in the hepatocyte of oestradiol-treated cockerels.Cell Tissue Res. (submitted).
Kami, K., Yasuda, K. & Stoward, P. J. (1985) The liver oestrogen response for specific protein synthesis in male chickens.Abst. 12th Int. Natl. Cong. Anat. pp. A338. London.
Kelly, R. B. (1985) Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes.Science 230, 25–32.
May, F. E. B., Ryffel, G. U., Weber, R. &Westley, B. R. (1982) Estrogen dramatically decreases albumin mRNA levels and albumin synthesis inXenopus laevis liver.J. Biol. Chem. 257, 13919–23.
Ohata, M. &Ito, T. (1986) Experimental study on the fine structure of chicken liver parenchyme with special references to extrasinusoidal macrophages and sinusoidal blood cells.Arch. Hitol. Jap. 49, 83–103.
Roth, J. (1982) The protein A-gold (pAg) technique. A quantitative and qualitative approach for antigen localization on this sections. InTechniques in Immunocytochemistry (edited byBullock, G. R. &Retrusz, P.) pp. 108–33. New York: Academic Press.
Roth, J., Bendayan, M. &Orci, L. (1978) Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 26, 1074–81.
Roth, J., Bendayan, M., Cablemalm, E., Villiger, W. &Garavito, M. (1981) Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 663–71.
Searle, P. F. &Tata, J. R. (1981) Vitellogenin gene expression in male Xenopus hepatocytes during primary and secondary stimulation with estrogen in cell cultures.Cell 23, 741–6.
Somogyi, P. &Takagi, H. (1982) A note on the use off picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry.Neuroscience 7, 1779–83.
Stanchfield, J. E. &Yager, J. D. (1978) An estrogen responsive primary amphibian liver cell culture system.Exp. Cell Res. 116, 239–52.
Tartakoff, A. M. &Vassali, P. (1978) Comparative studies of intracellular transport of secretory proteins.J. Cell Biol. 79, 694–707.
Tata, J. R. (1986) Coordinated assembly of the developing egg.BioEssays 4, 197–201.
Tata, J. R. &Smith, D. F. (1979) Vitellogenesis: A versatile model for hormone regulation of gene expression.Rec. Prog. Horn. Res. 35, 47–90.
Tata, J. R., James, T. C., Watson, C. S., Williams, J. L. &Wolffe, A. P. (1983) Hormonal regulation and expression of vitellogenin multigene family. InMolecular Biology of Egg Maturation (edited byPoter, R. &Whelan, J.) pp. 96–110. London: Pitman Books Ltd.
Vassey, J., Rissel, M., Kraemer, M., Foucrier, J. &Guillouzo, A. (1984) Ultrastructural indirect immunolocalization of transferrin in cultured rat hepatocytes permeability with saponin.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 32, 538–40.
Wachsmuth, E. D. &Jost, J. P. (1976) Localization of vitellogenin and serum albumin in hepatic parenchymal cells of normal and estradiol-treated immature chickens.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 437, 451–61.
Wallace, R. A. &Jared, D. W. (1968) Estrogen induces lipophosphoprotein in serum of maleXenopus laevis.Science 160, 91–2.
Wangh, L. J. (1982). Glucocorticoids acts together with estrogens and thyroid hormones in regulating the synthesis and secretion ofXenopus vitellogenin, serum albumin and fibrinogen.Dev. Biol. 89, 294–8.
Weibel, E. D., Kistler, G. S. &Scherle, W. F. (1966) Practical stereological methods for morphological cytology.J. Cell Biol. 30, 23–38.
Yokota, S. &Fahimi, H. D. (1981) Immunocytochemical localization of albumin in the secretory apparatus of rat liver parenchymal cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 4970–4.
Zamboni, L. &de Martino, C. (1967) Buffered picric, acidformaldehyde. A new rapid fixation for electron microscopy.J. Cell Biol. 35, 148A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kami, K., Stoward, P.J. Secretory pathway of vitellogenesis in the liver of the cockerel as revealed by immuno-gold and computer-assisted digitization techniques. Histochem J 23, 259–266 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01045044
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01045044