Abstract
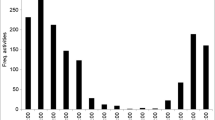
Take-off activity of the desert locust,Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk.), phasegregaria, was studied in a temperature-controlled laboratory environment and possible relationships with certain meteorological factors were analysed. A statistically significant relationship between the passage of cold fronts and an increased take-off rate was found. The reaction of the locusts could not be correlated to changes in VLF electromagnetic radiation or to the atmospheric pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adey WR (1978) Experiment and theory in long range interactions of electromagnetic fields at brain cell surfaces. Proceedings of the biomagnetic effects workshop. Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, pp 53–78
Allen A (ed) (1982) SAS user's guide: basics. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina
Balachandran NK (1979) Infrasonic signals from thunder. J Geophys Res 84:1735–1745
Baumer H, Eichmeier J (1983) A hypothesis concerning the absorption of atmospherics in photo gelatin films. Int J Biometeorol 27:125–131
Bennet RR, Tunstall J, Horridge GA (1967) Spectral sensitivity of single retinula cells of the locust. Z Vergl Physiol 55:195–206
Bergh JE (1979) Electromagnetic activity in the VLF range and take-off by locusts. Int J Biometeorol 23:195–204
Bergh JE (1983) Individual variation of take-off activity inSchistocerca gregaria (Forskål). Acta Entomol Fenn 42:23
Bergh JE (1985) Insect take-off activity as a response to meteorological stimuli effective over long distances. Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis. Comprehensive summaries of Uppsala dissertations from the Faculty of Science 6:1–27
Bergh JE, Israelsson S (1984) On the occurence of very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic radiation and its relation to some important physical conditions of the atmosphere. Arch Met Geophys Biocl Ser B 35:113–125
Chauvin R (1941) Variations du phototropisme du criquet Pélerin (Schistocerca gregaria Forsk.) suivant différentes longueurs d'onde. Bull Soc Zool France 66:27–32
Clark DP (1969) Night flight of the australian plague locust,Chortoicetes terminifera Walk., in relation to storms. Aust J Zool 17:329–352
Flitters NE (1963) Observations on the effect of hurricane “Carla” on insect activity. Int J Biometeorol 6:85–90
Gossard EE, Hooke WH (1975) Waves in the atmosphere. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hosni MH (1966) Meteorological factors affecting invasions of the United Arab Republic by the Desert Locust (Schistocerca gregaria Forskål). United Nations Development Program —Desert Locust Project Progress Report. No UNSF/DLP/RFS/9:1–26
Hunter-Jones P (1966) rearing and breeding locusts in the laboratory. Anti-Locust Research Centre, London (now: Centre for Overseas Pest Research)
Jacobi E, Richter O, Kruskemper G (1981) Simulated VLF-fields as a risk factor of thrombosis. Int J Biometeorol 25:133–142
Kennedy JS (1951) The migration of desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria Forsk.) I. The behaviour of swarms. II. A theory of long-range migration: Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 235:163–290
König HL (1977) Unsichtbare Umwelt. König, München
Lambert MRK (1981) Observations on the laboratory take-off behaviour of the desert locust,Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk.) (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Bull Ent Res 71:481–498
Liszka L (1977) Infrasonic waves — Interaction with the atmosphere. In: Grandahl B, Holtet JA (eds) Dynamical and chemical coupling between the neutral and ionized atmosphere. Reidel, pp 63–71
Martin H, Lindauer M (1977) The effect of the earth's magnetic field on the gravity orientation in the honey bee (Apis mellifica). J Comp Physiol 122:145–187
Pedgley DE (1970) Recent studies on weather systems affecting movements and breeding of the desert locust,Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk.), in countries around the Red Sea. Proc Int Study Conf current and future problems, pp 221–227
Pedgley DE (1979) Weather during desert locust plaque upsurges. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 287:387–391
Rainey RC (1951) Weather and the movements of locust swarms: a new hypothesis. Nature 168:1057–1060
Rainey RC (1978) The evolution and ecology of flight: the “oceanographic” approach. In: Dingle H (ed) Evolution of insect migration and diapause. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 33–48
Rainey RC, Waloff Z (1948) Desert locust migrations and synoptic meteorology in the Gulf of Aden area. J Anim Ecol 17:101–112
Ramchandra Rao Y (1942) Some results of studies on the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria Forsk.) in India. Bull Ent Res 33:241–265
Reiter R (1960) Meteorobiologie und Elektrizität der Atmosphäre. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig
Reiter R (1982) Biolgoical effects of atmospherics and manmade noise. In: Volland H (ed) CRC Handbook of atmospherics. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 291–305
Sansom HW (1951) A study of cold fronts over the British Isles. Quart JR Met Soc 77:96–120
Smith III TJ, Hayden BP (1984) Snow goose migration phenology is related to extratropical storm climate. Int J Biometeorol 28:225–233
Viehmann W (1983) Eine Analyse des Orientierungsverhaltens nachtziehender Vögel im Merkel-Wiltschko-Käfig. J Orn 124:259–269
Wait JR (1970) Electromagnetic waves in stratified media. Pergamon Press, New York
Waloff Z (1972) Orientation of flying locusts,Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk.), in migrating swarms. Bull Ent Res 62:1–72
Warnke U (1973) Physikalisch-physiologische Grundlagen zur luftelektrisch bedingten “Wetterfühligkeit” der Honigbiene (Apis mellifica). Dissertation, Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken
Wever R (1968) Einfluß schwacher elektromagnetischer Felder auf die cirkadiane Periode des Menschen. Naturwissen-schaften 55:29–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergh, J.E. Take-off activity in caged desert locusts,Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk.) (Orthoptera, Acrididae) in relation to meteorological disturbances. Int J Biometeorol 32, 95–102 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044901
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044901