Abstract
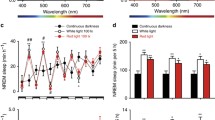
Unrestrained male rats continuously exposed to far-infrared radiation exhibited a significant increase in slow wave sleep (SWS) during the light period but not in the dark period. The change was largely due to the elevated occurrence of SWS episodes but not to the prolongation of their duration. Paradoxical sleep was not affected throughout the observation period except for a significant decrease at the end of the dark period. Thus the far-infrared radiation exerted a sleep modulatory effect closely related to the circadian activity-rest cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Honda K, Inoué S (1978) Establishment of a bioassay method for the sleep-promoting substance. Rep Inst Med Dent Eng 12:81–85
Honda K, Inoué S (1981) Effects of sleep-promoting substance on sleep-waking patterns of male rats. Rep Inst Med Dent Eng 15:115–123
Inoué S, Honda K (1986) Growth of rats exposed to far-infrared radiation. Zool Sci 3:731–732
Wolken JJ (1971) Invertebrate photoreceptors — A comparative analysis. Academic Press, New York London, p 3
Yamazaki T (1987) Ensekigaisen ryoho no kagaku. Ningen-to-Rekishi-sha, Tokyo
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honda, K., Inoué, S. Sleep-enhancing effects of far-infrared radiation in rats. Int J Biometeorol 32, 92–94 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044900
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044900