Summary
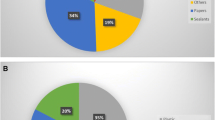
Vaious methods of heavy metal impregnations were performed on human platelets. The optimal technique consisted of glutaraldehyde fixation, incubation in warm uranyl acetate at a pH of 3.5, followed by a double solution of lead and copper, and finally overnight immersion in cold osmium tetroxide. Semi-thin sections, viewed at 90 kV, revealed three types of platelets: (1) ‘reticular’ cells, with a prominent tubular network and very dark granules in a pale cytoplasm; (2) ‘dark’ cells, with an electron-dense cytoplasm; and (3) ‘pale’ cells, with microvesicles and non-staining granules. Pre-treatments with EGTA, aspirin and various platelet activators altered the appearances and proportions of the three cell types.
A cell-partitioning two-phase polymer system showed that the sub-grouping is related to surface membrane properties, the cells retained in the top phase being exclusively type 2 ‘dark’ cells.
The changes in cell type distribution produced by activation show that metal impregnation may be a useful method for studying structure-function correlations in platelets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini, B. &Hasselbach, N. (1971) Electron cytochemistry of calcium uptake in fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum.Histochemie 28, 55–67.
Bolton, T. B. (1979) Mechanism of active transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle.Physiol. Rev. 59, 606–718.
Carash, L., Tan, H. &Gralnick, H. R. (1977) Heterogeneity of human whole blood platelet subpopulations. I. Relationship between buoyant density, cell volume and ultrastructure.Blood 49, 71–87.
Daimon, T., Misuhira, V. &Uchida, K. (1978) Ultrastructural localization of calcium around the membrane of the surface connected systems in human platelet.Histochemistry 55, 271–9.
Davis, W. L., Matthews, J. L. &Martin, J. H. (1974) An electron microscopic study of myofilament calcium building sites in native EGTA-related and Ca-reloaded glycerolated mammalian skeletal muscle.Calc. Tiss. Res. 14, 139–52.
Detwiler, T. C., Charo, I. F. &Feinman, R. D. (1978) Evidence that calcium regulates platelet function.Thrombos. Haemast. 40, 207–11.
Droz, B., Rambourg, A. &Koenig, H. L. (1975) The smooth endoplasmic reticulum; structure and role in the renewal of axonal membrane and synaptic vesicles by fast axonal transport.Brain Res. 93, 1–13.
Eastwood, A. B., Wood, D. S., Bock, K. L. &Sorenson, M. M. (1979) Chemically skinned mammalian skeletal muscle.Tiss. Cell. 11, 553–66.
Favard, R. &Carasso, N. (1972) The preparation and observation of thick biological sections in the high voltage electron microscope.J. Microsc. 97, 59–81.
Freedman, M. L. &Karpatkin, S. (1975) Heterogeneity of rabbit platelets. IV. Thrombocytosis with absolute megathrombocytosis in phenylhydrazine induced haemolytic anaemia in rabbits.Thrombos. Diathes. Haemorrh. 33, 335–40.
Gerrard, J. M., White, J. G. &Paterson, D. A. (1978) The platelet dense tubular system and its relation to calcium flux.Thrombos. Diathes. Haemorrh. 40, 224–8.
Grant, R. A. &Zucker, M. B. (1978) EDTA-induced increase in platelet surface charge associated with the loss of aggregability. Assessment by partition in aqueous two-phase polymer system and electrophoretic mobility.Blood 52, 515–23.
Gwynn, I. Ap, Evans, P. M., Jones, B. M. &Chandler, J. A. (1976) Shape changes and reduced calcium level in the surface membrane region of human platelets exposed to manganese.Cytobios. 16, 97–106.
Hellmann, H. G. (1976) The subcellular localization of calcium in vertebrate smooth muscle: calcium containing and calcium accumulating structures in muscle cells of mouse intestine.Cell Tiss. Res. 169, 221–31.
Karpatkin, P. (1978) Heterogeneity of human platelets. VI. Correlation of platelet function with platelet volume.Blood 51, 307–16.
Luft, J. H. (1971) Ruthenium red and violet II tissues.Anat. Rec. 171, 369–75.
Massini, P., Kaser-Glanzmann, R. &Luscher, E. F. (1978) Movement of calcium ions and their role in the activation of platelets.Thrombos. Haemost. 40, 212–17.
Minassian, H. &Huang, S. (1979) Effect of sodium azide on the ultrastructural preservation of tissues.J. Microsc. 117, 243–53.
Murer, E. H. &Steward, G. J. (1977) Insights into mechanism of platelet action through studies at pH 5.3.Thrombos. Haemost. 38, 1018–29.
Murer, E. H. (1972) Factors influencing the initiation and extrusion phase of the platelet release reaction.Biochem. biophys. Acta 261, 435–43.
Mustard, J. F. (1978) Platelet survival.Thrombos. Haemost. 40, 154–62.
Paulus, J. M. (1975) Platelet size in man.Blood 46, 321–36.
Peachey, L. D. (1978) Stereoscopic electron microscopy: principles and methods.EMSA Bull. 15–20.
Penington, D. G., Streatfield, K. &Roxburgh, A. E. (1976) Megakaryocytes and the heterogeneity of circulating platelets.Br. J. Haemat. 34, 639–53.
Phillips, D. R. &Jakabova, M. (1977) Ca2+-dependent protease in human platelets.J. biol. Chem. 252, 5602–4.
Sato, T., Herman, L., Chandler, J. A., Stracher, A. (1975) Localization of a thrombin sensitive calcium pool in platelets.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 103–6.
Seaman, G. V. F. (1976) Electrochemical features of platelet interactions.Thrombos. Res. Suppl. II8, 235–45.
Stahl, K., Themann, H. &Dame, W. R. (1978) Ultrastructural morphometric investigations on normal platelets.Hemostasis 7, 242–8.
Stibbe, J. &Holmsen, H. (1977) Effects of sodium azide on platelet function.Thrombos. Haemostas. 38, 1042–53.
Thiery, G. &Rambourg, A. (1976) A new technique for studying thick sections in the electron-microscope.J. microsc. Biol. Cell. 26, 103–6.
Thiery, G. (1979) Colorations signaletiques electives sur coupes epaisses du reticulum endoplasmic, de la chromatine et des surfaces cellulaires libres de cellules assimales.Bio. Cellulaire 35, 159–64.
Walter, H., Tung, R., Jackson, L. Y. &Seaman, G. F. (1972) The nature of the cell membrane charge measured by partition in aqueous two polymer systems.Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 48, 565.
Weibel, E. R. (1979) A stereological method for estimation volume and surface of sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Microsc. 95, 229–42.
White, J. G. (1977) InMorphology of Platelets in Haematology (edited byWilliams, N. Y., Bentler, E., Ersler, A. J. andRundles, R. W.), pp. 1159–1175. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Yarom, R., Blatt, J., Gorodetsky, R. &Robin, G. C. (1980) Microanalysis and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry of platelets in diseases with elecated muscle calcium.Eur. J. clin. Invest. 10, 143–7.
Yarom, R., Peters, P. D., Scripps, M. &Rogel, S. (1974) Effect of specimen preparation on intracellular myocardial calcium.Histochemistry 38, 143–53.
Yarom, R., Lijovetzky, G. &Havivi, Y. (1981) Platelet heterogeneity and dense tubular system changes on activation.Experientia 37, 96.
Zucker, M. B. &Grant, R. A. (1978) Nonreversible loss of platelet aggregability induced by calcium deprivation.Blood 52, 505–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yarom, R., More, R., Havivi, Y. et al. Studies of platelets with heavy metal impregnation techniques. Histochem J 14, 73–86 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041131
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01041131