Summary
In this study an attempt is made to estimate theinherent limits to tropical cyclone mean absolute track position errors out to 72 hours ahead and to compare these estimates with the position errors currently being obtained inpractice at weather centres around the world. A knowledge of the magnitude of the difference between the lower limit to predictability and that being achieved with state-of-the-art numerical weather prediction (NWP) models is of vital importance. A small difference would indicate that there is little further need for continued initiatives in the prediction of tropical cyclone tracks. On the other hand, a large difference would imply either that the problem requires continued emphasis or if there has been no significant trend towards reducing the forecast track errors, that present research and development techniques need to be extended or new procedures developed.
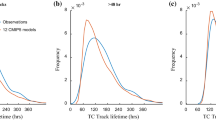
It was found that the difference between the inherent and practical limits of tropical cyclone track position errors is presently about 35 to 40 per cent for advanced baroclinic NWP systems, a moderate to large difference, and one that is almost invariant between tropical cyclone basins. For simpler models, such as barotropic models, the difference is closer to 45 per cent but is again almost invariant. As far as the authors are aware, these are the first estimates of the lower bounds of tropical cyclone track predictability. Finally, very recent research studies with emerging range of high quality data, high density data sources, improved models and new data assimilation techniques suggest that the difference possibly is now down to about 30 to 35 per cent. This value is encouragingly small but still large enough to continue active research programs in improving tropical cyclone motion prediction. Much of the forecast track errors now come from major forecast errors associated with tropical cyclones that follow erratic tracks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsberry, R. L., 1990: International experiments to study tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific.Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc.,71, 1305–1316.
Fraedrich, K., Leslie, L. M., 1989: Estimates of cyclone track predictability. I: Tropical cyclones in the Australian region.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,115, 79–92.
Fraedrich, K., Ziehmann-Schlumbohm, C., 1994: Predictability experiments with persistence forecasts in a rednoise atmosphere.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,120, 387–428.
Leith, C. E., 1974: Theoretical skill of Monte Carlo Forecasts.Mon. Wea. Rev. 102, 409–418.
LeMarshall, J. F., Leslie, L. M., Pescod, N., Spinoso, C., Morison, R., 1997: The importance of direct readout satellite data in sub-synoptic scale data assimilation and numerical weather prediction.Adv. Space Res. 19, 413–422.
Leslie, L. M., Skinner, T. C. L., 1994: Real-time forecasting of the Western Australian summertime trough: evaluation of a new regional model.Wea. Forecasting. 9, 371–383.
Lorenz, E. N. 1963: Deterministic nonperiodic Flow.J. Atmos. Sci.,20, 130–141.
Mullen, S. L., Baumhefner, D. P., 1989: The impact of initial uncertainty on numerical simulations of large scale explosive cyclogenesis.Mon. Wea. Rev.,117, 2800–2821.
Speer, M. S., Leslie, L. M., 1997: An example of the utility of ensemble rainfall forescasting.Aust. Meteor. Mag. 46, 75–78.
Velden, C. S., Hayden, C. M., Menzel, W. P., Franklin, J. L., Lynch, J. S., 1992: The impact of satellite-derived winds on numerical hurricane track forecasts.Wea. Forecasting,7, 107–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 3 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leslie, L.M., Abbey, R.F. & Holland, G.J. Tropical cyclone track predictability. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 65, 223–231 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01030790
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01030790