Summary
A diagnostic model for complete heat budgets in the free atmosphere is presented and is applied to the African-Atlantic sector between 35°S–30°N for May 1979. The model is based on the conservation equations for latent and sensible heat. These are evaluated in a form integrated over 24 hours in time and over atmospheric boxes of 2.5°×2.5° in horizontal and 100 hPa in vertical direction. Grid-scale input data are the 3D-ECMWF-diagnoses of the FGGE period plus parameterized fields of surface rain, evaporation and sensible Heat flux. This leads to an overspecification of latent and sensible heat budgets for any atmospheric column between surface and top of the atmosphere and thus yields an objective column imbalance. In order to separate the vertical subscale fluxes of rain, moisture and heat in the free atmosphere the model uses a closure assumption for the coupling between moisture and sensible heat flux as well as one for the vertical imbalance profiles; it is demonstrated that the budgets are not too sensitive with respect to these parameterizations.
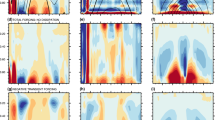
Results are presented in terms of vertical profiles of the subscale vertical fluxes of rain, moisture and heat. These are interpeted as measures of convective activity, with particular emphasis on the ITCZ. May 1979 averages as well as results for a respresentative single day are discussed. The imbalance (=the error) can be sufficiently well separated from the signal. It is shown that the low-level mass flux divergence does not coincide with the position of the ITCZ while the maximum of the subscale fluxes does coincide. Over the continent, it is not the horizontal mass flux convergence which feeds the ITCZ and the rainbelt but rather the subscale moisture flux and its convergence in the vertical. Over the Saharan latitudes, there is considerable convective flux of sensible heat, but not of latent heat. Over the ocean, deep convection in the ITCZ is weaker than over Africa, and it is consistently correlated with upward converging subscale moisture flux. The fields of the subscale vertical fluxes are coherent in space and time. It is argued from these results that the presented diagnostic model is potentially useful for testing parameterizations of convection in general circulation and climate models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin, P. A., 1979: The relationship between practional coverage of high cloud and rainfall accumulations during GATE over the B-Scale array.Mon. Wea. Rev.,107, 1382–1387.
Beutgen, A., 1990: Flächenniederschlag in Afrika aus IRMETEOSAT-Daten. Met. Inst. d. Univ. Bonn, Diplomathesis, 95 p.
Burkhardt, T., 1990: Subgrid-scale vertical energy fluxes over the African-Atlantic region.Bonner Met. Abh.,39, 105p.
Budyko, M. I., 1963:Atlas der Wärmebilanz der Erdkugel. Internat. Geophys. Komitee d. Akad. d. Wissenschaften d. UdSSR, Geophys. Hauptobs. A. I. Voeikov, Moskau.
Burpee, R. W., 1972: The origin and structure of easterly waves in the lower troposphere of North Africa.J. Atmos. Sci.,29, 77–90.
Dopplick, T., 1979: Radiative heating of the global atmosphere: Corrigendum.J. Atmos. Sci.,36, 1812–1817.
Eberz, B., 1987: Westwärts wandernde atmosphärische Wellenstörungen der afrikanischen Tropen: Ihre Dynamik und Energetik. Mitteilungen aus dem Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie der Universität zu Köln37, 77 p.
Emeis, S., Hantel, M., 1984: ALPEX-diagnostics: subsynoptic heat fluxes.Contrib. Atmos. Phys.,57, 495–511.
Emeis, S., 1985: Subsynoptic vertical heat fluxes in the atmosphere over Europe.Bonner Meteorol. Abhandl.,32, 106 p.
Emeis, S., 1986: Subsynoptic vertical energy fluxes in midlatitude cyclones.Meteorol. Rdsch.,39, 161–172.
Fuhrhop, R., 1988: Einfluß von Wellenstörungen auf die konvektive Bewölkung im Bereich der innertropischen Konvergenzzone über Afrika. Inst. f. Meeresk. der Univ. zu Kiel, Diplomathesis, 99 p.
Hacker, J. M., 1981: Der Massen-und Energiehaushalt der Nordhemisphere,Bonner Meteorol. Abhandl.,27, 93 p.
Hantel, M., 1982: Alpex. Subsynoptische Vertikaltransporte.Ann. Met. (N. F.),19, 79–80.
Hantel, M., 1987: Subsynoptic vertical heat fluxes from highresolution synoptic budgets.Meteorol. Atmos. Phys.,36, 24–44.
Hantel, M., 1989: Eine neue Gleischung für die atmosphärischen Energiehaushalte.Wetter und Leben,41, 95–108.
Hantel, M., Haase, S., 1983: Mass consistent heat budget of the zonal atmosphere.Bonner Met. Abh.,29, 84 p.
Heckley, W. A., 1985: Systematic errors of the ECMWF forecasting system in tropical regions.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,111, 709–738.
Johnson, R. H., 1984: Partitioning tropical heat and moisture budgets into cumulus and mesoscale components: implications for cumulus parameterization.Mon. Wea. Rev.,112, 1590–1601.
Nitta, T., 1972: Energy budget of wave disturbances over the Marshall Islands during the years of 1956 and 1958.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,50, 71–84.
Reed, R. J., Recker, E. E., 1971: Structure and properties of synoptic-scale wave disturbances in the equatorial western Pacific.J. Atmos. Sci.,28, 1117–1133.
Riehl, H., Malkus, J. S., 1958: On the heat balance in the equatorial through zone.Geophysica,6, 503–538.
Shao, Y., Hantel, M., 1989: Vertical subsynoptic momentum flux in the atmosphere over central Europe.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,115, 1355–1372.
Thompson, R. M., Payne, S. W., Recker, E. E., Reed, R. J., 1979: Structure and properties of synoptic-scale wave disturbances in the Innertropical Convergence Zone of the Eastern Atlantic.J. Atmos. Sci.,36, 53–72.
Yanai, M., Esbensen, S., Chu, J.-H., 1973: Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budgets.J. Atmos. Sci.,30, 611–627.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 19 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burkhardt, T. Subgrid-scale vertical heat fluxes for the African region. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 46, 155–168 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027340
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027340