Abstract
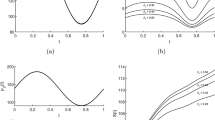
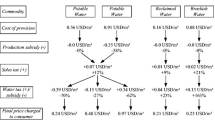
This paper examines the pricing strategy of water services relative to marginal cost and second-best pricing rules, which is a principal concern of utility commissions. The water utility is viewed as a multiproduct firm providing residential and nonresidential services, and a translog multiproduct cost function is estimated for a cross section of U.S. water utilities. Marginal costs are estimated and combined with demand elasticities to simulate second-best prices for water services. Results show that while the existing price structure is quite different from the one suggested by marginal costs, it does not depart substantially from the second-best optimum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumol, William J. and David F. Bradford (1970) ‘Optimal Departures from Marginal Cost Pricing’,American Economic Review 60, 265–283.
Baumol, William J., John C. Panzar, and Robert D. Willig (1982)Contestable Markets and the Theory of Industry Structure, New York: Harcourt Brace Javanovich.
Christensen, Laurits R., Dale W. Jorgenson, and Lawrence J. Lau (1973) ‘Transcendental Logarithmic Production Frontiers’,Review of Economics and Statistics,55, 28–45.
Clark, Robert M. and Richard G. Stevie (1981) ‘A Water Supply Cost Model Incorporating Spatial Variables’,Land Economics,57, 18–32.
Crain, W. Mark and Asghar Zardkoohi (1978) ‘A Test of the Property-Rights Theory of the Firm: Water Utilities in the United States’,Journal of Law and Economics,21, 395–408.
Feldstein, Martin S. (1972) ‘Distributional Equity and the Optimal Structure of Public Prices’,American Economic Review,62, 32–36.
Goddard, Haynes,et al. (1978)Planning Water Supply: Cost Differentials and Plumbing Permits, EPA Report, Cincinnati, OH: US EPA.
Griffin, James M. (1982) ‘The Welfare Implications of Externalities and Price Elasticities for Telecommunications Pricing’,Review of Economics and Statistics,69, 59–66.
Huettner, David A. (1982) ‘Optimal Second Best Pricing of CATV Pole Attachments’,Southern Economic Journal,48, 996–1015.
Kim, H. Youn (1985)Economic Modelling of Water Supply: An Econometric Analysis of the Multiproduct Firm, EPA Report, Cincinnati, OH: US EPA.
Mann, Patrick C. (1981) ‘Water Service: Regulation and Rate Reform’, Occasional Paper No. 4, National Regulatory Research Institute, Ohio State University, November.
Ramsey, F.P. (1927) ‘A Contribution to the Theory of Taxation’,Economic Journal,37, 47–61.
Scott, Frank A. (1986) ‘Assessing USA Postal Ratemaking: An Application of Ramsey Prices’,Journal of Industrial Economics,39, 279–290.
Turvey, Ralph (1976) ‘Analyzing the Marginal Cost of Water Supply’,Land Economics,52, 159–168.
Willig, Robert D. and Elizabeth E. Bailey (1979) ‘The Economic Gradient Method’,American Economic Review,69, 96–101.
Willig, Robert D. and Elizabeth E. Bailey (1981) ‘Income-Distribution Concerns in Regulatory Policymaking’, in G. Fromm (ed.),Studies in Public Regulation, Cambridge: MIT Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The research underlying this paper was supported by a cooperative agreement grant from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. The author would like to thank Robert Clark, Richard Stevie, Haynes Goddard, John Wassom, Philip Fanara and Curt Grimm for helpful comments and suggestions, and Pat Pearson who prepared many drafts of this paper. Special thanks go to referees for their comments and suggestions to improve the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.Y. Marginal cost and second-best pricing for water services. Rev Ind Organ 10, 323–338 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027078
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027078