Abstract
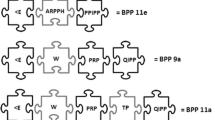
Several bradykinin potentiating peptides (BPPs) were isolated from the venom of the Brazilian arboricole snake Bothrops insularis by gel filtration on Sephadex G-150-120, followed by sequencial high-voltage paper electrophoreses atpH 3.5, 6.5, and 2.1. The BPPs were assayed by their ability to potentiate the contractile activity, on the isolated guinea pig ileum, and the hypotensive activity, on anesthetized rats, of bradykinin. Eight BPPs, containing 3–13 amino acid residues, were sequenced and their primary structures were shown to have a marked degree of homology with those of several BPPs from other venoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken, J. W., and Vane, J. R. (1970).Nature 228, 30–34.
Amorin, D. S., Ferreira, S. H., Manco, J. C., Tanaka, A., Sader, A. A., and Cardoso, S. (1967).Cardiologia 50, 23–32.
Antonio, A. (1967). InInternational Symposium on Vasoactive Polypeptides: Bradykinin and Related Kinins (Rocha e Silva, M., and Rothschild, H. A., eds.), Edart, São Paulo, pp. 87–90.
Camargo, A., and Ferreira, S. H. (1971).Br. J. Pharmacol. 42, 305–307.
Chang, J. Y., Creaser, E. H., and Bentley, K. W. (1976).Biochem. J. 153, 607–611.
Cheung, H. S., and Cushman, D. W. (1973).Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 293, 451–463.
Cushman, D. W., Pluscec, J., Williams, N. J., Weaver, E. R., Sabo, E. F., Kocy, O., Cheung, H. S., and Ondetti, M. A. (1973).Experientia 29, 1032–1035.
Cushman, D. W., and Ondetti, M. A. (1980).Progress in Medical Chemistry 17, 42–103.
Eliseeva, Y. E., Orekhovich, V. N., Pavlikhina, L. V., and Alexeenko, L. P. (1971).Clin. Chim. Acta. 31, 413–418.
Engel, S. L., Schaeffer, T. R., Gold, B. I., and Rubim, B. (1972).Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 140, 240–244.
Ferreira, S. H., and Rocha e Silva, M. (1965).Experientia 21, 347–349.
Ferreira, S. H. (1965).Brit. J. Pharmacol. 24, 163–169.
Ferreira, S. H., Bartelt, D. C., and Greene, L. J. (1970).Biochemistry 9, 2583–2593.
Ferreira, S. H., and Greene, L. J. (1970).Nature 225, 379–380.
Folk, J. E., Karl, A., Piez, A., William, E., Carrol, R., and Gladner, J. A. (1960).J. Biol. Chem. 235, 2272–2277.
Giglio, J. R. (1977).Anal. Biochem. 82, 262–264.
Graeff, F. G., Ferreira, S. H., Corrado, A. P., and Rocha e Silva, M. (1965).Experientia 21, 607–608.
Gray, W. R. (1972). InMethods in Enzymology (Hirs, C. M., and Timasheff, S., eds.) Vol. XXV, Academic Press, New York, pp. 333–344.
Homsi-Brandeburgo, M. I., Queiroz, L. S., Santo-Neto, H., Rodrigues-Simioni, L., and Giglio, J. R. (1988).Toxicon 26, 615–627.
Itzhaki, R. F., and Gill, D. M. (1964).Anal. Biochem. 9, 401–410.
Khrairallah, P. A., and Hal, M. M. (1977). InHypertension.: Physiopathology and Treatment (Genest, J., Joiw, E., and Kuchel, O., eds.) McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 179.
Neurath, H. (1955). InMethods in Enzymology (Colowick, S. P., and Kaplan, N. O., eds.), Vol. II, Academic Press, New York, pp. 77–83.
Offord, R. E. (1966).Nature (London) 211, 591–593.
Ondetti, M. A., Willians, N. J., Sabo, E. F., Pluscec, E. R., Weaver, E. R., and Kocy, O. (1971).Biochemistry 10, 4033–4039.
Ondetti, M. A., and Cushman, D. W. (1982).Ann. Rev. Biochem. 51, 283–308.
Peach, M. J. (1977).Physiol. Reviews 57, 313–370.
Rydon, H. N., and Smith, P. W. G. (1952).Nature 169, 922–923.
Rocha e Silva, M., Beraldo, W. T., and Rosenfeld, G. (1949).Am. J. Physiol. 156, 261–273.
Selistre, H. S., and Giglio, J. R. (1987).Toxicon 25, 1135–1144.
Selistre, H. S., Queiroz, L. S., Cunha, O. A. B., Souza, G. E. P., and Giglio, J. R. (1990).Toxicon 28, 261–273.
Skeggs, L. T. J. R., Dorer, F. E., Kahn, J. R., Lentz, K. E., and Levine, M. (1976).Am. J. Med. 60, 737–747.
Spackman, D. H., Stein, W. H., and Moore, S. (1958).Anal. Chem. 30, 1190–1206.
Szewczuk, A., and Kwiatkowska, J. (1970).Eur. J. Biochem. 15, 92–96.
Ufkes, J. G. R., Aarsen, P. N., and Van Der Meer, C. (1976).Eur. J. Pharmacol. 40, 137–144.
Ufkes, J. G. R., Aarsen, P. N., and Van Der Meer, C. (1977).Eur. J. Pharmacol. 44, 89–97.
Yagi, Y., Tsugimura, T., and Sato, K. (1957).J. Biochemistry 44, 11–23.
Yang, H. Y. T., Erdös, E. G., and Levin, J. (1971).J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 177, 291–300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cintra, A.C.O., Vieira, C.A. & Giglio, J.R. Primary structure and biological activity of bradykinin potentiating peptides fromBothrops insularis snake venom. J Protein Chem 9, 221–227 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025312
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025312