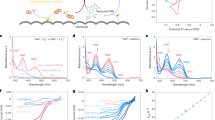
Abstract
Porous electrodes are required to achieve satisfactory performance of the aqueous sulphide/polysulphide redox couple in energy conversion and storage applications. A flow cell for testing flow-through porous electrodes was constructed and operated. The effects of electrode material, temperature, flow rate, and electrolyte composition were studied. Catalytic electrode surface layers of Co and MoS2 demonstrated performances which were more than adequate to meet a design goal of 10–20 mA cm−2 at less than 50mV overpotential. Flow rate variation had only a small effect on the current density-overpotential behaviour, whereas raising the temperature and/or adding dimethylformamide to the electrolyte had much larger effects. These observations are consistent with steady-state results obtained on rotating disc electrodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a 0 :
-
Interfacial area per unit volume (cm−1)
- A :
-
area (cm2)
- d :
-
wire diameter (cm)
- D :
-
diffusion coefficient (cm2s−1)
- F :
-
Faraday (96487 C mol−1)
- i :
-
current density (A cm−2)
- L :
-
defined by Equation 5 (cm)
- m :
-
mesh size (wires/cm)
- m 0 :
-
mass transfer coefficient (cm s−1)
- n :
-
number of electrons
- Q :
-
volumetric flow rate (cm3 sec−1)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- w :
-
mass (g)
- δ:
-
electrode thickness (cm)
- ε:
-
porosity or open area ratio
- μ:
-
viscosity (g cm−1 s−1)
- ϱ:
-
density (g cm−3)
- b:
-
bulk
- e:
-
electrolyte
- i :
-
speciesi
- L:
-
limiting
- DMF:
-
dimethylformamide
- FEP:
-
fluorinated ethylenepropylene
- PEC:
-
photoelectrochemical cell
- PTFE:
-
polytetrafluoroethylene
References
G. Schwarzenbach and A. Fischer,Helv. Chim. Acta. 43 (1960) 1365.
A. Teder,Acta Chem. Scand. 25 (1971) 1722.
W. Giggenbach,Inorg. Chem. 11 (1972) 1201.
A. Teder,Ark. Kemi 30 (1969) 379.
,31 (1969) 173.
S. Licht, G. Hodes, and J. Manassen,Inorg. Chem. 25 (1986) 2486.
A. Teder, Sv.Papperstidn. 71 (1968) 149.
Z. V. Bogomolova, K. I. Tikhonov, and A. L. Rotinyan,Elekrokhimiya 15 (1979) 1237.
P. Lessner, J. Winnick, F. R. McLarnon and E. J. Cairns,J. Electrochem. Soc. 133 (1986) 2510.
133 (1986) 2517.
,134 (1987) 2669.
N. Ardoin and J. Winnick,135 (1988) 1719; J. Winnick, P. M. Lessner, F. R. McLarnon and E. J. Cairns,Appl. Phys. Lett. 53 (1988) 1985.
M. Matlosz and J. Newman, ‘Use of a Flow-Through Porous Electrode for Removal of Mercury from Contaminated Brine Solutions,’in ‘Transport processes in electrochemical systems,’ (edited by R. S. Yeo, T. Katan and D. T. Chin), The Electrochemical Society Symposium Proceeding Series, The Electrochemical Society, Pennington, NJ (1982) p. 53.
M. A. Reid and L. H. Thaller, ‘Improvement and Scale-Up of the NASA Redox Storage System,’ Proceedings of the 15th Intersociety Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, New York (1980) p. 1471.
M. Barak, ‘Electrochemical Power Sources. Primary and Secondary Batteries,’ Institution of Electrical Engineers, London (1980).
G. Hodes, J. Manassen, and D. Cahen,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127 (1980) 544.
,J. Appl. Electrochem. 7 (1977) 181.
R. J. Remick and E. H. Camara, ‘Electrochemistry of the Sulfide/Polysulfide Couple’, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Report No. LBL-16850 (1983).
P. L. Allen and A. Hickling,Trans. Faraday Soc. 53 (1957) 1626.
J. C. Armour and J. N. Cannon,AIChE J. 14 (1968) 415.
Anonymous,Electroplating 3 (1951) 89.
J. E. Dutrizac,Can. Met. Quart. 9 (1970) 449.
R. E. Sioda,Electrochim. Acta. 22 (1977) 439.
J. Cano and U. Böhm,Chem. Eng. Sci. 32 (1977) 213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lessner, P.M., McLarnon, F.R., Winnick, J. et al. Aqueous polysulphide flow-through electrodes: Effects of electrocatalyst and electrolyte composition on performance. J Appl Electrochem 22, 927–934 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01024141
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01024141