Abstract
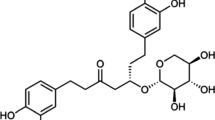
The Rose-of-Sharon,Hibiscus syriacus (L.), can be a significant alternate host plant for the boll weevil,Anthonomus gradis (Boh.). Boll weevils are known to be deterred from feeding and ovipositing in the buds unless the calyx is removed. This investigation was initiated to identify calyx allelochemicals that deter feeding with the eventual strategy of breeding for cotton lines high in these allelochemicals in the appropriate tissues. The feeding deterrency of calyx tissue from the buds of Rose-of-Sharon for the boll weevil was confirmed. The most active deterrent fraction was found to contain mostly fatty acids and their methyl esters. Saturated fatty acids and their methyl esters were generally found to be stimulatory, while the unsaturated species were found to be deterrent. Higher quantities of the fatty acids, particularly the unsaturated species, were found in Rose-of-Sharon calyx tissue than in the buds without calyx. This supports the hypothesis developed through the isolational work and testing of standards that the unsaturated fatty acids are significant deterrents of boll weevil feeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, A.C. 1967. Genetic markers in the boll weevil.J. Hered. 58:159–163.
Bird, T.G., andHedin, P.A. 1986. An improved feeding bioassay for the boll weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 79:882–886.
Coad, B.R. 1914. Feeding habits of the boll weevil on plants other than cotton.J. Agric. Res 2:235–245.
Hanny, B.W., Henson, R.D., Thompson, A.C., Gueldner, R.C., andHedin, P.A. 1972. Identification of carotenoid constituents inHibiscus syriacus (L.).J. Agric. Food Chem. 20:914–916.
Hanny, B.W., Thompson, A.C., Gueldner, R.C., andHedin, P.A. 1973. An investigation of the essential oil ofHibiscus syriacus (L.).J. Agric. Food Chem. 21:1001–1004.
Lindig, O.H. 1979. A replacement for cottonseed meal and meats in boll weevil diets.J. Econ. Entomol. 72:291–292.
Loschiavo, S.R. 1965. The chemosensory influence of some extracts of brewers' yeast in cereal products on the feeding behavior of the confused flour beetle,Tribolium confusum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae).Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 58:576–588.
Maxwell, F.G., Parrott, W.L., Jenkins, J.N., andLafever, H.N. 1965. A boll weevil feeding deterrent from the calyxes of an alternate host,Hibiscus syriacus (L.).J. Econ. Entomol. 58:985–988.
Parrott, W.L., Maxwell, F.G., andJenkins, J.N. 1966. Feeding and oviposition of the boll weevil,Anthonomus grandis (Boh.) on the Rose-of-Sharon, an alternate host.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 59:547–550.
SASInstitute. 1982. SAS User's Guide: Statistics. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina.
Stenhagen, E., Abrahamsson, S., andMcLafferty, F.W. 1974. Registry of Mass Spectral Data, Vol. 1–4, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 3358 pp.
Thompson, A.C., andSikorowski, P.P. 1979. Effects ofNosema heliothidis on fatty acids in larvae and pupae of the bollworm.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 63A:325–328.
Vinson, S.B., Thompson, J.L., andGreen, H.B. 1967. Phagostimulants for the imported fire ant,Solenopsis saevissima var. Richteri.J. Insect Physiol. 13:1729–1736.
Vinson, S.B., Frankie, G.W., Blum, M.S., andWheeler, J.W. 1978. Isolation, identification, and function of the Dufour's gland secretion ofXylocopa virginica texana.J. Chem. Ecol. 4:315–323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Coleoptera: Curculionidae.
Malvales: Malvaceae.
Mention of a commercial or proprietary product in this paper does not constitute endorsement of this product by Delta State University or USDA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bird, T.G., Hedin, P.A. & Burks, M.L. Feeding deterrent compounds to the boll weevil,Anthonomus grandis Boheman in Rose-of-Sharon,Hibiscus syriacus L.. J Chem Ecol 13, 1087–1097 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020540
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01020540