Abstract
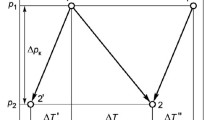
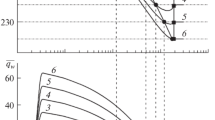
The calorimetric method for determining the heat flux at a permeable (or sublimating) surface requires the solution of several specific heat-transfer problems, since the calorimeter, bringing about discontinuities in the boundary conditions at the wall (the cessation of blowing, a jump in the temperature of the wall and of its catalytic properties, etc.), introduces perturbations into the boundary layer and measures a heat flux differing from the flux in the absence of a calorimeter. Within the framework of the boundary layer, schematization of such problems is usually based on the isolation of an internal boundary layer (sublayer), which is the region of the effect of the new phenomena at the wall, and develops in the main boundary layer [1–5]. To take account of the effect of the inhomogeneity of the flow in the main boundary layer on heat transfer through the sublayer, here the method of mean-mass values is used, which, as has been demonstrated using various examples in [4] and in the present work, has a good degree of accuracy (even in the neighborhood of the breakaway point) and is suitable for the profiles of an inhomogeneous flow of rather general form. Based on this, for a laminar boundary layer finite formulas are obtained below for the heat flux to a calorimeter of relatively small size at a permeable wall, which can be used for the analysis of experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. Goldstein, “Concerning some solutions of boundary layer equations in hydro-dynamic,” Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc.,26, P. 1 (1930).
M. R. Denison and E. Baum, “Compressible free shear layer with finite initial thickness,” AIAA J.,l, No. 2 (1963).
V. N. Shmanenkov, “Investigation of a laminar boundary layer after the point of a jumpwise change in the boundary conditions,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekharn Zhidk. i Gaza, No. 3 (1966).
V. V. Lunev, “The method of mean-mass values for the boundary layer in an external flow with transverse inhomogeneity,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekhan. Zhidk. i Gaza, No. 1 (1967).
Yu. A. Dem'yanov, “A method for constructing the solution of equations of the Prandtl type in the neighborhood of points of breakdown of the analytical boundary conditions,” Zh. Vychisl. Mat. i Mat. Fiz.,7, No. 4 (1969).
H. W. Emmons and D. C. Leigh, “Tabulation of Blasius function with blowing and suction,” Aeronaut. Res. Council, No. 157 (1954).
C. F. Dewey, “Use of local similarity concepts in hypersonic viscous interaction problems,” AIAA J.,l, No. 1 (1963).
H. Schlichting and K. Bussman, “Exacte Losungen für die laminar Grenzchicht mit Absaugung und Ausblasen,” Deutsche Acad. d. Luftfahrt-forschung. Schriften,7B, No. 2 (1943).
P. A. Libby and K. Chen., “Laminar boundary layer with uniform injection,” Phys. Fluids,8, No. 4 (1965).
I. N. Murzinov, “The laminar boundary layer at a sphere in a hypersonic flow of equilibrium dissociating air,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekhan. Zhidk. i Gaza, No. 2 (1966).
I. F. Golubev, The Viscosity of Gases and Gas Mixtures [in Russian], Izd, Fizmatgiz, Moscow (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Mekhanika Zhidkosti i Gaza, No. 5, pp. 101–109, September–October, 1974.
The authors thank V. V. Lunev for his evaluation of the work and for his most useful observations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zemlyanskii, B.A., Marinin, V.P. Theory of a calorimeter at a permeable surface. Fluid Dyn 9, 765–773 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01017424
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01017424