Abstract
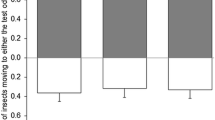
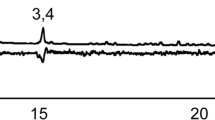
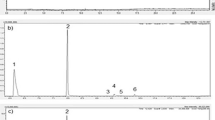
Acrolepiopsis assectella andPlutella xylostella frass volatiles, trapped on Tenax GC, were examined by capillary gas chromatography. In both moths, the same three disulfides, dimethyl, dipropyl, and methyl propyl, were the most abundant substances, but in different proportions. The synthetic disulfides elicited the same behavioral response by the parasitoid,Diadromus pulchellus as frass. The plant origin of these substances is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apparao, M., Kjaer, A., Olsen, O., Rao, E.V., Rasmussen, K.W., andSorensen, H. 1981.Allium in the garlicky taxonAdenocalymma alliaceum (Bignoniaceae).Phytochemistry 20:822–823.
Auger, J.,Lecomte, C., andThibout, E. 1989. Leek odor analysis by gas chromatography. Identification of the most active substance for the leek moth.J. Chem. Ecol. In press.
Bailey, S.D., Bazinet, M.L., Driscoll, J.L., andMcCarthy, A.I. 1961. The volatile sulfur components of cabbage.J. Food Sci. 26:163–170.
Elzen, G.W., Williams, H.J., andVinson, S.B. 1984. Role of diet in host selection ofHeliothis virescens by parasitoidCampoletis sonorensis (Hymenoptera: ichneumonidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 10:1535–1541.
Iversen, P.E., andLund, H. 1974. Electrolytic generation of nucleophiles: IV Reductive alkylation and acylation of disulfides.Acta Chem. Scand. B 28:827–828.
Lecomte, C., andPouzat, J. 1985. Réponses électroantennographiques de deux parasitoïdes Ichneumonides,Diadromus pulchellus etD. collaris aux odeurs de végétaux, du phytophagehôteAcrolepiopsis assectella et du partenaire sexuel.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 39:295–306.
Lecomte, C., andThibout, E. 1983. Analyse en olfactomètre tabulaire, de l'influence de différents stimulus olfactifs dans la recherche de l'hôte parDiadromus pulchellus (Hym. ichneumonidae).Entomophaga 28:217–226.
Lecomte, C., andThibout, E. 1984. Etude olfactométrique de l'action de diverses substances allélochimiques végétales dans la recherche de l'hôte parDiadromus pulchellus (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae).Entomol. Exp. Appl. 35:295–303.
Lecomte, C., andThibout, E. 1986. Analyse, dans deux types d'olfactomètres, du comportement de quête des femelles deDiadromus pulchellus en présence d'odeur du phytophage-hôte et du végétal attaqué ou non.Entomophaga 31:69–78.
Mackenzie, I.A., andFerns, D.A. 1977. The composition of volatiles from different parts ofAllium tuberosum plants.Phytochemistry 16:763–764.
Mae, T., Ohira, K., andFujiwara, A. 1971. Fate of (+)-S-methyl-l-cysteine sulfoxide in Chinese cabbage,Brassica pekinensis Rupr.Plant Cell Physiol. 12:1–11.
Murakami, F. 1960. Studies on the nutritional value ofAllium plants. 36. Decomposition of alliin homologues by micro-organisms and formation of substances with thiamine masking activity.Vitamins 20:126–135.
Thibout, E. 1988. La spécificité deDiadromus pulchellus (Hyménoptère: Ichneumonidae) vis-á-vis de son hôtsAcrolepiopsis assectella, la teigne du poireau.Entomophaga 33:439–452.
Thibout, E., Lecomte, C., andAuger, I. 1988.Diadromus pulchellus: Search for a host and specificity. Coll. INRA Parasitoïds, Lyon. 48:7–14.
Tsuno, S. 1958a. Studies on the nutritional value ofAllium plants. 17. Production of allithiamine from thiamine by the use ofIpheion uniflorum Rof.Vitamins 14:665–670.
Tsuno, S. 1958b. Studies on the nutritional value ofAllium plants. 18. Production of allithiamine from thiamine by the use ofCrucifer plants I. Detection of methyl-alliin.Vitamins 14:671–675.
Van Leerdam, M.B., Smith, J.W., andFuchs, T.W. 1985. Frass-mediated, host finding behavior ofCotesia flavipes, a braconide parasite ofDiatrae saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).Ann. Entomol Soc. Am. 78:647–650.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auger, J., Lecomte, C., Paris, J. et al. Identification of leek-moth and diamondback-moth frass volatiles that stimulate parasitoid,Diadromus pulchellus . J Chem Ecol 15, 1391–1398 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01014838
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01014838