Abstract
Late-instar larvalTenebrio molitor L. were found to be attracted to aqueous extracts of conspecific larval frass. The attraction was evident at both the individual and group level. The attraction of larval groups to frass indicated the possibility of an aggregation pheromone that would be chemically distinct in the mealworm environment. Chemical analysis of short carbon chain acids present in both the mealworm frass and the diet indicated that lactic acid was present in the mealworm frass only. Acetic acid was identified in both the diet and the larval frass. Larvae aggregated on filter papers treated with aqueous frass extracts that had been dried and also on those freshly wetted. The larvae also aggregated on dried or freshly wetted papers treated with lactic acid, but failed to aggregate on freshly wetted papers or dried papers treated with acetic acid. The role of excreted lactic acid as a discriminant of already infested and, therefore, safer environmental regions is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burk, T., andBell, W.J. 1973. Cockroach aggregation pheromone: inhibition of locomotion (Orthoptera: Blattidae).J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 46:36–41.
Cotton, R.T. 1963. Pests of Stored Grain and Grain Products. Burgess Publishing, Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Happ, G.M. 1969. Multiple sex pheromones of the mealworm beetle,Tenebrio molitor (L.).Nature 222:180–181.
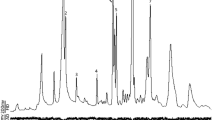
Jones, D.W., andKay, J.J. 1976. Determination of volatile fatty acids C1-C6 and lactic acid in silage juice.J. Sci. Food Agric. 27:1005–1014.
McFarlane, I.E., andAlli, I. 1986. Aggregation of larvae ofBlattella germanica (L.) by lactic acid present in the excreta.J. Chem. Ecol. 12:1369–1375.
McFarlane, J.E., andAlli, I. 1987. The effect of lactic acid and the volatile fatty acids on the aggregation behavior ofPeriplaneta americana (L.).Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 86C:45–47.
McFarlane, J.E., Steeves, E., andAlli, I. 1983. Aggregation of larvae of the house cricket,Acheta domesticus (L.), by propionic acid present in the excreta.J. Chem. Ecol. 9:1307–1315.
Prokopy, R.J. 1981. Epideictic pheromones influencing spacing patterns of phytophagous insects, pp. 181–213,in D.A. Nordland, R.L. Jones, and W.J. Lewis (eds.). Semiochemicals: Their Role in Pest Control. Wiley, New York.
Ross, M.H., andTignor, K.R. 1986. Response of german cockroaches to aggregation pheromone emitted by adult females.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 41:25–31.
SAS. 1982. SAS Users Guide: Statistics (1982 ed.). Statistical Analysis Systems Institute, Inc., Gary, North Carolina.
Sinha, R.N., andWatters, F.L. 1985. Insect pests of flour mills, grain elevators, and feed mills and their control. Agriculture Canada Publ. 1776E.
Tanaka, Y., Honda, H., Ohsawa, K., andI. Yanamoto. 1986. A sex attractant of the yellow mealworm,Tenebrio molitor L., and its role in the mating behavior.J. Pestic. Sci. 11:49–55.
Tschinkel, W., Willson, C., andBern, H.A. 1967. Sex pheromone of the mealworm beetle (Tenebrio molitor).J. Exp. Zool. 164:81–85.
Weaver, D.K., andMcFarlane, J.E. 1988. Aggregation in yellow mealworms,Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) Larvae: II. Observations and analyses of behavioral parameters in aggregation.J. Chem. Ecol. 15:1617–1627.
Weaver, D.K.,McFarlane, J.E., andAlli, I. 1990. Repellency of volatile fatty acids present in the frass of yellow mealworms,Tenebrio molitor L. larvae, to larval conspecifics.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:
Wynn-Edwards, V.C. 1962. Animal Dispersion in Relation to Social Behavior. Hafner, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weaver, D.K., McFarlane, J.E. & Alli, I. Aggregation in yellow mealworms,Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) larvae. J Chem Ecol 15, 1605–1615 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01012387
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01012387