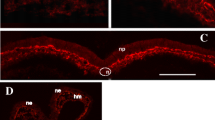
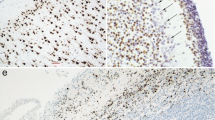
Synopsis
Cultured mouse neuroblastoma C1300 cells were examined for acid glycosaminoglycans using the Alcian Blue and periodic acid-Schiff staining techniques. It was found that the cells contained hyaluronidase-resistant sulphated glycosaminoglycans; hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulphate, and sialoglycoproteins were not demonstrated. These properties are held in common with foetal mouse brain spongioblasts in culture. In contrast to the latter cells, but in common with some peripheral neuronsin vivo, C1300 cells were stained by the periodic acid-Schiff technique for neutral polysaccharides. The results are discussed in relation to the poor adhesive properties of neuroblastoma cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broughton, P. M. G., Dykes, J. R. W., Holt, S., Ridley, J. W. &Steel, A. E. (1970). Mucopolysaccharide in the blood of a patient with neuroblastoma.J. clin. Path. 23, 246–8.
Cunningham, W. L. &Goldberg, J. M. (1968). The determination of glycosaminoglycans present in various mammalian brains.Biochem. J. 110, 35P-36P.
Defendi, V. &Gasic, G. (1963). Surface mucopolysaccharides of polyoma virus transformed cells.J. cell comp. Physiol. 62, 23–6.
Erichson, D., Eng, J. &Morgan, H. R. (1961). Comparative studies in Rous sarcoma with virus tumour cells and chick embryo cells transformedin vitro by virus. I. Production of mucopolysaccharides.J. exp. Med. 114, 435–40.
Furmanski, P., Silverman, D. J. &Lubin, M. (1971). Expression of differentiated functions in mouse neuroblastoma mediated by dibutyryl-cyclic adenosine monophosphate.Nature (Lond.) 233, 413–15.
Hess, A. (1953). The ground substance of the central nervous system revealed by histochemical staining.J. comp. Neurol. 98, 69–91.
Kates, J. R., Winterton, R. &Schlessinger, K. (1971). Induction of acetylcholinesterase activity in mouse neuroblastoma tissue culture cells.Nature (Lond.) 229, 345–7.
Kuriyama, K. &Okada, T. A. (1971). Incorporation of35S sulphate into developing mouse brain: Subcellular fractionation and electron microscopic studies.Exp. Neurol. 30, 18–29.
Margolis, R. K. &Margolis, R. U. (1970). Sulphated glycopeptides from rat brain glycoproteins.Biochemistry, N.Y. 9, 4389–96.
Moss, C. A. (1973). Glycosaminoglycans of disaggregated foetal mouse brain tissue cultures.Histochem. J. 5, 547–56.
Nordling, S., Vaheri, A., Saxén, E. &Penttinen, K. (1965). The effects of anionic polymers on cell attachment and growth behaviour, with a note on the similarity in the effect of fresh human serum.Expl Cell Res. 37, 406–19.
Schubert, D., Humphreys, S., Baroni, C. &Cohn, M. (1969).In vitro differentiation of a mouse neuroblastoma.Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 64, 316–23.
Scott, J. E. &Dorling, J. (1965). Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans by Alcian Blue in salt solutions.Histochemie 5, 221–33.
Scott, J. E. &Dorling, J. (1969). Periodate oxidation of acid polysaccharides. III. A PAS method for chondroitin sulphates and other glycosaminoglycuronans.Histochemie 19, 295–301.
Seeds, N. W., Gilman, A. G., Amano, T. &Nirenberg, M. W. (1970). Regulation of axon formation by clonal lines of a neural tumour.Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 66, 160–7.
Singh, M., Chandrasekaran, V., Cherian, R. &Bachhawat, B. K. (1969). Isolation and characterisation of glycosaminoglycans in brain of different species.J. Neurochem. 16, 1157–62.
Vos, J., Kuriyama, K. &Roberts, E. (1969). Distribution of acid mucopolysaccharides in subcellular fractions of mouse brain.Brain Res. 12, 172–9.
Young, I. J. &Abood, L. G. (1960). Histological demonstration of hyaluronic acid in the central nervous system.J. Neurochem. 6, 89–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moss, C.A. Acid glycosaminoglycans of mouse neuroblastoma C1300 cells. Histochem J 6, 1–5 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01011533
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01011533