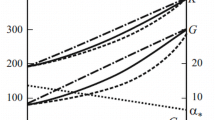
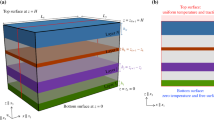
Abstract
To investigate the thermal response of composed anisotropic structures, a numerical study has been carried out. By the use of a numerical mapping technique it was possible to handle complex multi-body geometries very efficiently. Due to the transformation method the restriction of the well known finite difference method to simple solution regions is removed. For the iterative solution of the corresponding finite difference equations the Strongly Implicit Procedure (SIP) has been employed. Based on the solution methodology, several numerical examples revealing the effects of anisotropy in thermal conductivity and composite structures are presented.
Zusammenfassung
Um das thermische Verhalten von zusammengesetzten anisotropen Körpern zu untersuchen, wurden numerische Rechnungen durchgeführt. Unter Verwendung einer numerischen Transformationsmethode war es möglich, auch komplexe Geometrien, die aus mehreren Körpern bestehen, effektiv zu behandeln. Die Beschränkung der bekannten Finiten Differenzen Methode auf relativ einfache Lösungsgebiete, wird durch diese Transformationsmethode beseitigt. Zur iterativen Lösung des entsprechenden Gleichungssystems wurde ein implizites Verfahren (SIP) angewandt. Mit Hilfe dieser Lösungsmethode wurden anisotrope Wärmeleitvorgänge in Körpern komplexer und zusammengesetzter Geometrie berechnet und der Einfluß der Anisotropie auf zusammengesetzte Gebiete aufgezeigt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D:
-
domain
- J:
-
Jacobian of transformation (=xξyη−xηyξ)
- k n11 , k n12 , k n22 :
-
dimensionless thermal conductivities in macro element n (k nlk =λ nlk /λ 111 )
- m:
-
total number of grid points
- N:
-
total number of macro elements
- P,Q:
-
coordinate control functions
- q:
-
heat flux per unit area
- Res:
-
residuum
- x, y:
-
cartesian coordinate directions in physical plane
- α,β,γ:
-
transformation factors (α=x 2η +y 2η ;β=xξxη+yξyη;γ=x 2ξ +y 2ξ )
- Γ:
-
bounding surface of geometry
- λ:
-
thermal conductivity
- θ:
-
dimensionless temperature
- ξ,η:
-
coordinate directions in transformed plane
- ―:
-
matrix notation
- x:
-
derivative with respect to x
- y:
-
derivative with respect to y
- n:
-
normal
- ij:
-
nodal point i,j
- ξ:
-
derivative with respect to ξ
- η:
-
derivative with respect to η
- →:
-
vector notation
- n:
-
number of macro element
Literature
Thompson, J.F.; Thames, F.C.; Mastin, C.W.: Automatic Numerical Generation of Body-Fitted Curvilinear Coordinate System for Fields Containing Any Number of Arbitrary Two-Dimensional Bodies. J. of Computational Physics 15 (1974) 299–319
McWhorter III, J.C.; Sadd, M.H.: Numerical Anisotropic Heat Conduction Solutions Using Boundary-Fitted Coordinate Systems. J. of Heat Transfer 102 (1980) 308–311
Projahn, U.; Rieger, H.: The Application of a Coupled Strongly Implicit Procedure to the Problem of Natural Convection in an Enclosed Cavity. In: Jones, I.P.; Thomson, C.P.(ed).: A Comparison Problem on Natural Convection in an Enclosed Cavity. AERE-R9955, HMSO 1981
Projahn, U.; Rieger, H.; Beer, H.: A Numerical Analysis of Laminar Natural Convection Between Concentric and Eccentric Cylinders. Numerical Heat Transfer (accepted for publication)
Di Carlo, A.; Piva, R.; Guj, G.: A Study on Curvilinear Coordinates and Macro-Elements for Multiply Connected Flow Fields, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of Numerical Methods on Fluid Dynamics. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1979
Di Carlo, A.; Piva, R.; Guj, G.: Numerically Mapped Macro-Elements for Multiply Connected Flow Fields, Numerical Methods in Laminar and Turbulent Flow. Proceedings of the Forst International Conference, Swansea 1978
Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, I.C.: Conduction of Heat in Solids. Oxford University Press 1973
Stone, H.L.: Iterative Solution of Implicit Approximations of Multidimensional Partial Differential Equations. SIAM-Journal on Numerical Analysis 5 (1968) 530–558
Chang, Y.P.; Kang, C.S.; Chen, D.J.: The Use of Fundamental Green's Functions for the Solution of Problems of Heat Conduction in Anisotropic Media. International J. of Heat and Mass Transfer 16 (1973) 1905–1918
Chang, Y.P.; Poon, K.C.: Three Dimensional. Steady State Heat Conduction in Cylinders of General Anisotropic Media. J. of Heat Transfer 101 (1979) 548–553
de Vahl Davis, G.: A Note on a Mesh for Use with Polar Coordinates. Numerical Heat Transfer 2 (1979) 261–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Projahn, U., Rieger, H. & Beer, H. Wärmeleitung in anisotropen zusammengesetzten Körpern beliebiger Gestalt. Wärme- und Stoffübertragung 15, 223–232 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003642
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003642