Summary
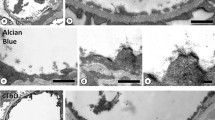
To obtain contrast-staining of glycogen in electron microscopy, various contrast-enhancing additives can be used in combination with potassium osmate. Examples are potassium ferrocyanide and certain nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, such as triazoles. In the reaction sequence leading to contrast-stained glycogen, a primary reaction is the formation of glycogen osmate. This reaction was studied with isolated glycogen. On the basis of the stoichiometric findings, a molecular structure of the reaction product is proposed; apparently, osmate is bound by glycogen because of the presence of suitably located hydroxyl groups. The resulting compound is not itself sufficiently electron dense, but it binds 1,2,4-triazole as an additional ligand. Secondary reactions can result in additional osmium binding, and finally to osmium (IV) deposits, leading to contrast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aanderson, W. A. (1972) Methods for electron microscopic localization of glycogen. In:Techniques for Biochemical and Biophysical Morphology (edited byGlick, D. andRosenbaum, R. M.), Vol. 1, pp. 1–23. New York: Wiley.
Bahr, G. f. (1954) Osmium tetroxide and ruthenium tetroxide and their reactions with biologically active substances.Expl. Cell Res. 7, 457–79.
Boeseken, J. (1949) The use of boric acid for determination of the configuration of carbohydrates.Adv. Carboh. Res. 4, 189–210.
Coffey, S. (1967) (editor)Rodd's Chemistry of Carbon Compounds, 2nd edn., Vol. I, pp. 678–84. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
collin, r. j., jones, j. & griffith, w. p. (1974) Reaction of OsO4 with alkenes.J. chem. Soc. (Dalton Transactions) 1094–7.
Cramer, F. &Hettler, H. (1967) Inclusion compounds of cyclodextrins.Naturwissenschaften 54, 625–32.
Criegee, R. (1936) Osmiumsäure-Ester als Zwischenprodukte bei Oxydationen.Annls. Chem. 522, 75–96.
Criegee, R., Marchand, B. &Wannowius, H. (1942) Zur Kenntnis der organischen Osmium-Verbindungen.Annls. Chem. 550, 99–133.
De Bruijn, W. C. (1968) A modified OsO4-(double) fixation procedure which selectively contrasts glycogen.Proc. of 4th Europ. Conference on Electron Microscope. (edited byBocciarelli, D. S.), Vol. II, 5–11. Rome: Tipografia Polyglotta Vaticana.
De Bruijn, W. c. (1973) Glycogen, its chemistry and morphological appearance. I. A modified OsO4 fixative which selectively contrasts glycogen.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 42, 29–50.
De Bruijn, W. c. &Den Breejen, P. (1974) Selective glycogen contrast by hexavalent osmium compounds. InElectron Microscopy and Cytochemistry (edited byWisse, E., Daems, W. th., Molenaar, I. andvan Duijn, P.), pp. 259–66. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Co.
De Bruijn, W. c. &Den Breejen, P. (1975) Glycogen, its chemistry and morphological appearance in the electron microscope. II. The complex formed in the selective contrast-staining of glycogen.Histochem. J. 7, 205–29.
De Bruijn, W. c. &Den Breejen, P. (1976) Glycogen, its chemistry and morphological appearance in the electron microscope. III. Identification of the tissue ligands involved in the glycogen contrast-staining with the osmium(VII)-iron(II) complex.Histochem. J. 8, 121–42.
De Bruijn, W. c., Memelink, A. a. &Riemersma, J. c. (1983) Cellular membrane contrast and contrast differentiation by osmium triazole and tetrazole complexes.Histochem. J. 16, 37–50.
De Bruijn, W. c. &van Buitenen, J. m. h. (1980) X-ray microanalysis of aldehyde-fixed glycogen contrast-stained by OsVI. FeII and OsVI. RuIV complexes.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 1242–50.
De Bruijn, W. c. &van Buitenen, J. m. h. (1981) X-ray microanalysis of non-aldehyde-fixed glycogen.Histochem. J. 13, 125–36.
Fales, F. w. (1980) Variation in the degree of branching in glycogen.Biopolymers 19, 1543–53.
French, D. (1957) The Schardinger dextrins.Adv. Carboh. Chem. 12, 189–260.
karnovsky, m. j. (1971) Use of ferrocyanide-reduced OsO4 in electron microscopy. Abstracts.Am. Soc. Cell Biol., 11th Annual Meeting, New Orleans, p. 146.
Korn, E. d. (1966a) Synthesis of bis (methyl 9,10-dihydroxy-stearate) osmate from methyl oleate.Biochim. biophys. Acta 116, 317–24.
Korn, E. d. (1966b) Modification of oleic acid during fixation of amoebae by osmium tetroxide.Biochim. biophys. Acta 116, 324–35.
Korn, E. d. (1967) A chromatographic and spectrophotometric study of the products of the reaction of osmium tetroxide with unsaturated lipids.J. Cell Biol. 34, 627–38.
Lingane, J. j. (1958)Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2nd edn. New York, London: Interscience Publishers.
lott, k. a. k. & symons, m. c. r. (1960) Structure and reactivity of the oxyanions of transition metals.J. chem. Soc. 973–6.
Manners, D. j. (1962) Enzymic synthesis and degradation of starch and glycogen.Adv. Carboh. Chem. 17, 371–430.
Pearse, A. g. e. (1980)Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied, 4th edn., Vol. I, pp. 114–9. Edinburgh, London, New York: Churchill-Livingstone.
Riemersma, J. c. (1968) Osmium tetroxide fixation for electron microscopy.Biochim. biophys. Acta 152, 718–27.
Riemersma, J. c. (1970) Chemical effects of fixation on biological specimens. InSome Biological Techniques in Electron Microscopy (edited byParsons, D. f.), pp. 69–98 New York: Academic Press.
Riemersma, J. c. &Booij, H. l. (1962) The reaction of osmium tetroxide with lecithin.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 89–95.
Ruff, O. &Bornemann, F. (1910) Ueber das Osmium, seine analytische Bestimmung, seine Oxyde und seine Chloride.Z. Anorg. Chem. 65, 429–56.
Schlenk, H. &Sand, D. m. (1961) The association of α-and β-cyclodextrins with organic acids.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 2313–20.
Schröder, M. (1980) Osmium tetroxidecis-hydroxylation of unsaturated substrates.Chem. Rev. 80, 187–213.
Thiéry, J. p. (1967) Mise en évidence des polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopie électronique.J. Microscopie 6, 987–1018.
White, D. l. (1976) The chemical nature of osmium tetroxide fixation.Biochim. biophys. Acta 436, 577–92.
White, D. l., Mazurkiewicz, J. c. &Barrnett, R. j. (1979) A chemical mechanism for tissue staining by OsO4-ferrocyanide mixtures.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 1084–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riemersma, J.C., Alsbach, E.J.J. & de Bruijn, W.C. Chemical aspects of glycogen contrast-staining by potassium osmate. Histochem J 16, 123–136 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003544
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01003544