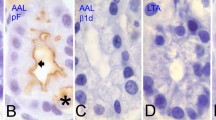
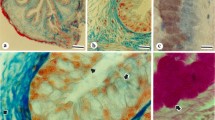
Summary
Two general classes of glycoproteins have been identified in the colonic epithelial cells of New Zealand white rabbits. Each is associated with an ultrastructurally distinct secretory cell. The first of these classes is found in cells, termed vesiculated columnar cells, characterized by electron-translucent vesicles, a small rough endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi complex and prominent microvilli. The glycoproteins of the vesiculated cells contain abundantO-sulphate ester, sialic acids with ester substituents at positions C-8 or C-9 (or with two or three side chain substituents) and neutral sugars withvicinal diols whose periodate oxidation is prevented by anO-acyl ester substituent(s). The second class of glycoproteins occurs in goblet cells characterized by electron-dense vesicles, an abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum, a well-developed Golgi apparatus and few, if any, microvilli. Goblet cells along the entire length of the crypts contain neutral sugars with periodate-oxidisablevicinal diols and a ferriferricyanide-reactive component. Cells in the upper halves of the crypts also contain components that are sulphated, Schiff-reactive and acid-fast. In the lower halves of the crypts, the goblet cells contain smaller quantities of the above components plus sialic acids, some of which possibly have anO-acyl substituent located at position C-8 or C-9 (or which have two or three side chainO-acyl substituents). It is suggested that the function of the glycoproteins from the vesiculated columnar cells is protective and that from the goblet cells is lubricative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, C. W. M. (1956) A stricter interpretation of the ferriferricyanide reaction with particular reference to the demonstration of protein-bound sulphydryl and disulphide groups.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 4, 23–35.
Adams, C. W. M. (1969) Lipid histochemistry.Adv. Lipid Res. 7, 1–62.
Adams, C. W. M. &Bayliss, O. B. (1971) Schiff reactions with lipids and the disputed terminal rinse with hydrochloride acid.Histochemie 28, 220–4.
Al-Suhail, A. A. (1981) Changes in theO-acetyl substituted sialic acids in carrageenan induced large bowel ulceration in rabbit. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Pathology, University of British Columbia.
Al-Suhail, A. A., Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A., Dunn, W. L. &Clay, M. G. (1984) Studies of the degraded carrageenan-induced colitis of rabbits. I. Changes in the epithelial glycoproteinO-acylated sialic acids associated with ulcerationHistochem. J. 16, 543–53.
Altmann, G. G. (1983) Morphological observations on mucus-secreting non goblet cells in the deep crypts of the rat ascending colon.Amer. J. Anat. 167, 95–117.
Bangle, R. (1954) The peracetic acid-Schiff stain.Amer. J. Clin. Pathol. 24, 179–85.
Barger, J. D. &DeLamater, E. D. (1948) The use of thionyl chloride in the preparation of Schiff reagent.Science 108, 121–2.
Berg, J. W. (1953). Acid-fastness as a histochemical test.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1, 436–41.
Chang, W. W. L. &Leblond, C. P. (1971) Renewal of the epithelium in the descending colon of the mouse. I. Presence of three cell populations: vacuolated-columnar, mucous and argentaffin.Amer. J. Anat. 131, 73–100.
Cole, K., Park, C. M., Reid, P. E. &Sheath, R. G. (1985) Comparative studies of the cell walls of sexual and asexual Atropurpurea (Rhodophyta). I. Histochemistry of polysaccharides.J. Phycol. 21, 585–92.
Culling, C. F. A. (1974)Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Technique, 3rd edn. London: Butterworth.
Culling, C. F. A., Reid, P. E. &Dunn, W. L. (1971) The effect of saponification upon certain histochemical reactions of the epithelial mucins of the GI tract.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 19, 654–62.
Culling, C. F. A., Reid, P. E., Dunn, W. L. &Clay, M. G. (1974) The histochemical demonstration ofO-acylated sialic acids in gastrointestinal mucins: their association with the potassium hydroxide-periodic acid-Schiff effect.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 22, 826–31.
Drzeniek, R. (1973) Substrate specificity of neuraminidases.Histochem. J. 5, 271–90.
Elleder, M. &Lojda, Z. (1970) Studies in lipid histochemistry. I. Criticism of performic and peracetic acid-Schiff reactions.Histochemie 24, 7–20.
Elleder, M. &Lojda, Z. (1971a) Studies in lipid histochemistry III. Reaction of Schiff's reagent with plasmalogens.Histochemie 24, 328–35.
Elleder, M. &Lojda, Z. (1971b) Studies in lipid histochemistry. I. Criticism of performic and peracetic reactions. The answer of the authors.Histochemie 25, 193–4.
Elleder, M. &Lojda, Z. (1971c) Studies in lipid histochemistry. IV. The influence of terminal rinsing on the results of methods using Schiff's reagent.Histochemie 25, 286–8.
Faillard, H. &Schauer, R. (1972) Glycoproteins as lubricants, protective agents, carriers, structural proteins and as participants in other functions. InGlycoproteins: Their Composition Structure and Function (edited byGottschalk, A.) BBA library 5B, pp. 1256–67. Amsterdam, London, New York: Elsevier.
Fisher, E. R. &Lillie, R. D. (1954) The effect of methylation on basophilia.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2, 81–7.
Florey, H. (1955) Mucin and protection in the body.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. Ser. B 143, 147–59.
Forstner, J. F. (1978) Intestinal mucin in health and disease.Digestion 17, 234–63.
Hollman, K. H. (1965) Uber den feinbau des rectumepithels.Zeitschr. Zellforsch. 68, 502–42.
Hoskins, L. C. (1978) Degradation of mucus glycoproteins in the gastrointestinal tract. InThe Glycoconjugates (edited byHorowitz, M. I. &Pigman, W.), Vol. II, pp. 235–53. New York, San Francisco, London: Academic Press.
Kent, P. W. (1962) The chemistry of mucoprotein: an introduction to gastrointestinal mucus.Gastroenterology,43, 292–303.
Kiernan, J. A. (1981)Histological and Histochemical Methods: Theory and Practice, 1st edn. Oxford, New York, Toronto, Sydney, Paris, Frankfurt: Pergamon Press.
Lillie, R. D. (1965)Histopathologic Technic and Practical Histochemistry, 3rd edn, New York, Toronto, Sydney, London: Blakiston (Division of McGraw-Hill Book Co.).
Lillie, R. D. (1969)H. J. Conn's Biological Stains, 8th edn. 45 pp. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co.
Lillie, R. D. (1971) Comments about the paper. M. Elleder and Z. Lojda. Studies in Lipid Histochemistry. I. Criticism of performic and peracetic reactions.Histochemie 25, 191–2.
Lillie, R. D. &Burtner, H. J. (1953) The ferric ferricyanide reduction test in histochemistry.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1, 87–92.
Lillie, R. D. &Bangle, R. (1954) The peracetic acid schiff reaction of hair cortex.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2, 300–11.
Lillie, R. D., Bangle, R. &Fisher, E. R. (1954) Metachromatic basophilia of keratin after oxidationcleavage of disulphide bonds.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2, 95–102.
Lillie, R. D., &Donaldson, P. T. (1974) The mechanism of the ferric ferricyanide reduction reaction.Histochem. J. 6, 679–84.
Lillie, R. D. &Pizzolato, P. (1972) Histochemical use of borohydrides as aldehyde blocking reagents.Stain. Technol. 43, 13–16.
Mowry, R. W. (1963) Special value of methods that colour both acidic andvicinal hydroxyl groups in the histochemical study of mucins. With revised directions for the colloidal iron stain, the use of Alcian Blue 8GX and their combination with the periodic acid-schiff reaction.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 106, 402–23.
Nemoto, T. &Yosizawa, Z. (1969) Sulfated glycopeptides and glycosaminoglycan peptide isolated from intestinal mucosa of rabbit.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 192, 37–48.
Park, C. M., Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A. &Dunn W. L. (1987a) Histochemical studies of epithelial cell glycoproteins in normal rat colon.Histochem. J. 19, 546–54.
Park, C. M., Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Dunn, W. L. &Volz, D. (1987b) Histochemical procedures for the simultaneous visualization of neutral sugars and either sialic acid and itsO-acyl variants orO-sulphate ester. II. Methods based upon the periodic acid-phenylhydrazine method.Histochem. J. 19, 257–63.
Park, C. M., Reid, P. E., Walker, D. C. &MacPherson, B. R. (1987c) A simple practical ‘swiss roll’ method of preparing tissues for paraffin and methacrylate embedding.J. Microsc. 145, 115–20.
Pearse, A. G. E. (1985)Histochemistry: Theoretical and Applied. Vol. 2, 4th edn. Edinburgh, London, New York: Churchill Livingstone.
Poon, H., Reid, P. E., Ramey, C. W. &Dunn, W. L. (1983) Removal ofO-acylated sialic acids from rat colonic epithelial glycoproteins by cell-free extracts of rat faeces.Can. J. Biochem. 61, 868–74.
Quintarelli, G. &Dellovo, M. C. (1965) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. IV. Further studies on the methods for the identification of acid glycosaminoglycans.Histochemie 5, 196–209.
Quintarelli, G., Scott, J. E. &Dellovo, M. C. (1964a) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue II. Dye binding of tissue polyanions.Histochemie 4, 86–98.
Quintarelli, G., Scott, J. E. &Dellovo, M. C. (1964b) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. III. Chemical blocking and unblocking.Histochemie 4, 99–112.
Reid, P. E. &Culling, C. F. A. (1980) The periodate oxidation of carbohydrates in relation to the PAS reaction.J. Histotechnol. 3, 82–90.
Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1973) Saponification-induced increase in the periodic acid-Schiff reaction in the gastrointestinal tract: mechanism and distribution of the reactive substance.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 21, 473–82.
Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1974) The histochemical interpretation of the complex results of methylation upon gastrointestinal mucins with special reference to their periodic acid-Schiff reactivity.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 22, 986–91.
Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A., Dunn, W. L., Ramey, C. W., Magil, A. B. &Clay, M. G. (1980) Differences between theO-acetylated sialic acids of the epithelial mucins of human colonic tumours and normal controls.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 217–22.
Reid, P. E., Dunn, W. L., Ramey, C. W., Coret, E., Trueman, L. &Clay, M. G. (1984) Histochemical identification of side chain substitutedO-acylated sialic acids. The PAT-KOH-Bh-PAS and the PAPT-KOH-Bh-PAS procedure.Histochem. J. 16, 623–39.
Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Ramey, C. W., Dunn, W. L., Clay, M. G. &Jones, E. A. (1985a) Histochemical procedures for the simultaneous visualization of sialic acid, its side chainO-acyl variants andO-sulphate ester.Histochem. J. 17, 113–7.
Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Ramey, C. W., Dunn, W. L., Jones, E. A., Lazosky, D. A., Allen, E. (neeAtkins),Park, C. M. &Clay, M. G. (1985b) Chemical and histochemical studies of normal and diseased gastrointestinal tract. V. A. differential diagnostic method for the histochemical classification of glycoproteins.Histochem. J. 17, 891–903.
Reid, P. E., Volz, D., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987) Methods for the identification of side chainO-acyl substituted sialic acids and for the simultaneous visualization of sialic acid, itsO-acyl variants andO-sulphate ester.Histochem. J. 19, 396–8.
Scott, J. E. &Dorling, J. (1965) Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by Alcian Blue in salt solutions.Histochemie 5, 221–33.
Scott, J. E., Quintarelli, G. &Dellovo, M. C. (1964) The chemical and histochemical properties of Alcian Blue. I. The mechanism of Alcian Blue staining.Histochemie 4, 73–85.
Shamsuddin, A. K. M. &Trump, B. F. (1981) Colon epithelium I. Light microscopic, histochemical and ultrastructural features of normal colon epithelium of Male Fischer 344 rats.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 66, 375–88.
Sheahan, D. G. &Jervis, H. R. (1976) Comparative histochemistry of gastrointestinal mucosubstances.Amer. J. Anat. 146, 103–32.
Spicer, S. S. (1960) A correlative study of the histochemical properties of rodent acid mucopolysaccharides.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 8,18–34.
Spicer, S. S. (1965) Diamine methods for differentiating mucopolysaccharides histochemically.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 211–34.
Spicer, S. S., Horn, R. G. &Leppi, J. T. (1967) Histochemistry of connective tissue mucopolysaccharides. InThe Connective Tissue (edited byWagnEr, B. M. &Smith, D. E., Chapter 17, pp. 251–303. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Thomopoulos, G. N., Schulte, B. A. &Spicer, S. S. (1983) Light and electron microscopic cytochemistry of glycoconjugates in the recto-sigmoid colonic epithelium of the mouse and rat.Amer. J. Anat. 168, 239–56.
Volz, D., Reid, P. E., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987a) Histochemical procedures for the simultaneous visualization of neutral sugars and either sialic acid and its side chainO-acyl variants orO-sulphate ester. I. Methods based upon the selective periodate oxidation of sialic acids.Histochem. J. 19, 249–56.
Volz, D., Reid, P. E., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987b) A new method for the selective periodate oxidation of total tissue sialic acids.Histochem. J. 19, 311–18.
Wetzel, M. G., Wetzel, B. K. &Spicer, S. S. (1966) Ultrastructural localization of acid mucosubstances in the mouse colon with iron containing stains.J. Cell Biol. 30, 299–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reid, P.E., Walker, D.C., Terpin, T. et al. Histochemical studies of the colonic epithelial glycoproteins of the normal rabbit. Histochem J 20, 533–550 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01002608
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01002608