Abstract
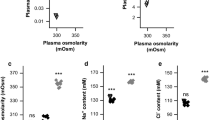
We studied the effect of mannitol-induced hyperosmolality on brain interstitial fluid (ISF) by autoradiography. Adult cats underwent intracerebral infusion of the extracellular marker,14C-sucrose. Nine animals were given 2 g/kg of mannitol intravenously, and another nine animals without mannitol were controls. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) osmolalities were measured. After 2 hr the brains were removed for determination of water and electrolyte content and for preparation of the autoradiograms. Diffusion coefficients were calculated for intracerebral transport with equations for radial diffusion. We found that mannitol increased the plasma osmolality but did not affect that of the CSF. Water and potassium contents were significantly lower in the white matter of mannitol-treated animals than in controls. Diffusion was reduced in the direction of gray matter into the white matter. We conclude that lower doses of mannitol control CSF pressure by selectively removing water from white matter, reducing the CSF volume, and affecting molecular transport at the gray/white interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bering, E. A., Jr., and Avman, N. (1960). The use of hypertonic urea solutions in hypothermia.J. Neurosurg. 17: 1073–1082.
Blasberg, R. G., Gazendam, J., Patlak, C. S., and Fenstermacher, J. D. (1980). Quantitative autoradiographic studies of brain edema and a comparison of multi-isotope autoradiographic techniques.Adv. Neurol. 28: 255–270.
Chan, P. H., Pollack, E., and Fishman, R. A. (1981). Differential effects of hypertonic mannitol and glycerol on rat brain metabolism and amino acids.Brain Res. 225: 143–153.
Cserr, H. F., DePasquale, M., and Patlak, C. S. (1987a). Regulation of brain water and electrolytes during acute hyperosmolality in rats.Am. J. Physiol. 253: F522-F529.
Cserr, H. F., DePasquale, M., and Patlak, C. S. (1987b). Volume regulatory influx of electrolytes from plasma to brain during acute hyperosmolality.Am. J. Physiol. 253: F530-F537.
Dimattio, J., Hochwald, G. M., Malhan, C., and Wald, A. (1975). Effects of changes in serum osmolarity on bulk flow of fluid into cerebral ventricles and on brain water content.Pflugers Arch. 359: 253–264.
Finberg, L., Luttrell, C., and Malhan, C. (1959). Pathogenesis of lesions in the nervous system in hypernatremic states.Pediatrics 23: 46–53.
Guisado, R., Arieff, A. I., and Massry, S. G. (1974). Effects of glycerol infusions on brain water and electrolytes.Am. J. Physiol. 227: 865–872.
Hochwald, G. M., Wald, A., Dimattio, J., and Malhan, C. (1974). The effects of serum osmolarity on cerebrospinal fluid volume flow.Life Sci. 15: 1309–1316.
Johnston, I. H., and Harper, A. M. (1973). The effect of mannitol on cerebral blood flow: An experimental study.J. Neurosurg. 38: 461–471.
Marshall, L. F., Smith, R. W., Rauscher, L. A., and Shapiro, H. M. (1978). Mannitol dose requirements in brain-injured patients.J. Neurosurg. 48: 169–172.
Nicholson, C. (1985). Diffusion from an injected volume of a substance in brain tissue with arbitrary volume fraction and tortuosity.Brain Res. 333: 325–329.
Pape, L., and Katzman, R. (1970). Effects of hydration on blood and cerebrospinal fluid osmolalities.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 134: 430–433.
Pappius, H. M., and Dayes, L. A. (1965). Hyptertonic urea: Its effect on the distribution of water and electrolytes in normal and edematous brain tissues.Arch. Neurol. 13: 395–402.
Pollock, A. S., and Arieff, A. J. (1980). Abnormalities of cell volume regulation and their functional consequences.Am. J. Physiol. 239: F195-F205.
Pullen, R. G. L., DePasquale, M., and Cserr, H. F. (1987). Bulk flow of cerebrospinal fluid into brain in response to acute hyperosmolality.Am. J. Physiol. 253: F538-F545.
Rosenberg, G. A., and Kyner, W. T. (1983). Effect of mannitol-induced hyperosrriolarity on transport between brain interstitial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid. In Wood, J. H. (ed.),Neurobiology of Cerebrospinal Fluid 2, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 765–775.
Rosenberg, G. A., Kyner, W. T., and Estrada, E. (1980). Bulk flow of brain interstitial fluid under normal and hyperosmolar conditions.Am. J. Physiol. 238: F42-F49.
Rottenberg, D. A., Hurwitz, B. J., and Posner, J. B. (1977). The effect of oral glycerol on intraventricular pressure in man.Neurology (Minn.) 27: 600–608.
Sahar, A., and Tsipstein, E. (1978). Effects of mannitol and furosemide on the rate of formation of cerebrospinal fluid.Exp. Neurol. 60: 584–591.
Snider, R. S., and Niemer, W. T. (1961).A Stereotactic Atlas of the Cat Brain, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Stern, W. E., and Coxon, R. V. (1964). Osmolality of brain tissue and its relation to brain bulk.Am. J. Physiol. 206: 1–7.
Thurston, J. H., Hauhard, R. E., and Dirgo, J. A. (1981). Effects of a single therapeutic dose of glycerol on cerebral metabolism in the brains of young mice: Possible increase in brain glucose transport and glucose utilization.J. Neurochem. 36: 830–838.
Weed, L. H., and McKibben, P. S. (1919). Experimental alteration of brain bulk.Am. J. Physiol. 48: 531–555.
Wise, B. L., and Chater, N. (1962). The value of hypertonic mannitol solution in decreasing brain mass and lowering cerebrospinal-fluid pressure.J. Neurosurg. 19: 1038–1043.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenberg, G.A., Barrett, J., Estrada, E. et al. Selective effect of mannitol-induced hyperosmolality on brain interstitial fluid and water content in white matter. Metab Brain Dis 3, 217–227 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999238
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999238