Abstract
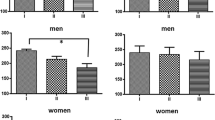
In order to assess the effectiveness of verbal relaxation instructions and EMG relaxation training on the relief of tension headaches, 18 medically documented tension-headache sufferers were randomly assigned to one of three conditions:(1) Jacobson-Wolpe autogenic-relaxation training,(2) EMG relaxation training, or(3) EMG relaxation training combined with Jacobson-Wolpe autogenic instructions. The two EMG-assisted groups showed significantly better results, compared to the verbal group, in terms of reduction of headache activity and the rate at which reduction took place. Thus, EMG-assisted relaxation procedures seem the treatment method of choice for relief of tension headaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budzynski, T. H., Stoyva, J. M., & Adler, C. S. Feedback-induced muscle relaxation: Application to tension headache.Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry 1970,1 205–211.
Budzynski, T. H., Stoyva, J. M., Adler, C. S., & Mullaney, D. T. EMG biofeedback and tension headache: A controlled outcome study.Psychosomatic Medicine 1973,35 484–496.
DiCara, L. Learning in the autonomic nervous system.Scientific American 1970,222 30–39.
Jacobson, E.Progressive relaxation (2nd ed.) Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1938.
Miller, N. E. Learning of visceral and glandular responses.Science 1969,163 434–445.
Miller, N. E. Introduction: Current issues and key problems. In D. Shapiro (Ed.),Biofeedback and self-control: 1973. Chicago: Aldine Press, 1974, XI–XX.
Mitchell, K. R. The treatment of migraine: An exploratory application of time limited behavior therapy.Technology 1969,14 50–55.
Raskin, M., Johnson, G., & Rondestvedt, J. W. Chronic anxiety treated by feedback-induced muscle relaxation: A pilot study.Archives of General Psychiatry 1973,28 263–266.
Reinking, R. H., Morgret, M. M., Tamayo, F., & Hutchings, D. F. Effects of various forms of relaxation training on physiological and self-report measures of relaxation. Paper presented at the 5th Annual Convention of the Biofeedback Research Society, Monterey, California, February 4, 1975.
Sargent, J., Green, E., & Walters, E. D. Preliminary report on the use of autogenic feedback training in the treatment of migraine and tension headaches.Psychosomatic Medicine 1973,35 129–135.
Schultz, J., & Luthe, W.Autogenic training: A psychophysiological approach to psychotherapy. New York: Grune and Stratton, 1959.
Wickramasekera, I. Electromyographic feedback training and tension headaches: Preliminary observations.The American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 1972,15 83–85.
Winer, B.Statistical procedures in experimental design. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1962.
Wolpe, J., & Lazarus, A.Behavior therapy techniques. New York: Pergamon Press, 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchings, D.F., Reinking, R.H. Tension headaches. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation 1, 183–190 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998585
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998585