Summary
Two anaphylatoxin-forming agents have been investigated with respect to possible pyrogenic effects: the AT forming fraction of cobra venom and agar.
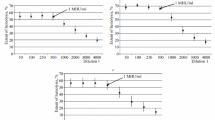
The cobra venom fraction produced fever in rabbits. The pyrogenic principle is, however, not identical with the AT forming enzyme. Unlike the latter the pyrogenic principle is stable in acidic solution and destroyed by periodate. It may be a lipopolysaccharide.
Rabbit plasma, incubated with agar caused fever in rabbits. Agar also induced pyrogenic activity in saline after it had been incubated in that medium. The active principle proved to be agaropectin, the water-soluble acidic fraction of agar. Agarose was inert. In contrast, anaphylatoxin formation is induced by agarose, not by agaropectin.
In rabbit plasma, agaropectin induces the formation of an endogenous pyrogen. This principle can be separated from the agaropectin by DEAE cellulose chromatography. It is further distinguished from the latter by being heat-labile.
Besides being activated by different agents the processes of pyrogen and AT formation differ in their requirement for cations. AT formation is blocked by EDTA but pyrogen formation is not. It is concluded that in spite of similarities and common activation by endotoxins the processes of AT and pyrogen formation are different and independent events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkinson, N. F., L. M. Lichtenstein, H. Gewurz, andS. E. Mergenhagen: The generation of anaphylatoxin by interaction of endotoxin and guinea-pig serum. Fed. Proc.27, 316 (1968).
Dyer, J. R.: Use of periodate oxidations in biochemical analysis. Meth. biochem. Anal.3, 111–152 (1956).
Friedberger, E., u.S. Mita: Über Anaphylaxie. XVIII: Die anaphylaktische Fieberreaktion. Z. Immun.-Forsch.10, 216–281 (1911).
Giertz, H., u.F. Hahn: Makromolekulare Histaminliberatoren. C. Das Anaphylatoxin. In: Heffters Handbuch der Pharmakologie, Erg.-Band18/1, S.521. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1966.
Grant, R., andW. J. Whalen: Latency of pyrogen fever. Appearance of a fastacting pyrogen in the blood of febrile animals and in plasma incubated with bacterial pyrogen. Amer. J. Physiol.173, 47–54 (1953).
Greisman, S. E.: Activation of histamine-releasing factor in normal rat plasma by E. coli endotoxin. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)103, 628–632 (1960).
Haining, C. G.: Activation of rabbit serum protease by dextran sulphate. Brit. J. Pharmacol.11, 107–110 (1956).
Hinshaw, L. B., J. A. Vick, C. H. Carlson, andY.-L. Fan: Role of histamine in endotoxin shock. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)104, 379–381 (1960).
Netzer, W., u.W. Vogt: Anaphylatoxinbildung durch pyrogenes Lipopolysaccharid. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.248, 261–268 (1964).
Osler, A. G., H. G. Randall, andZ. Ovary: Studies on the mechanism of hypersensitivity phenomena. III. The participation of complement in the formation of anaphylatoxin. J. exp. Med.110, 311–339 (1959).
Rothschild, A. M., andL. A. Gascon: Sulphuric esters of polysaccharides as activators of a bradykinin-forming system in plasma. Nature (Lond.)212, 1364 (1966).
Schwoerer, D.: Untersuchungen über das Vorkommen des anaphylatoxinbildenden Systems im Plasma verschiedener Tierarten. Thesis, Göttingen 1966.
Ungar, G., andS. H. Mist: Release of serum fibrinolysin by specific antigen, peptone, and certain polysaccharides. J. exp. Med.90, 39–51 (1949).
,T. Yamura, J. B. Isola, andS. Kobrin: Further studies on the role of proteases in the allergic reaction. J. exp. Med.113, 359–380 (1961).
Vogt, W.: Preparation and some properties of anaphylatoxin from hog serum. Biochem. Pharmacol.17, 727–733 (1968).
, u.G. Schmidt: Abtrennung des anaphylatoxinbildenden Prinzips aus Cobragift von anderen Giftkomponenten. Experientia (Basel)20, 207–208 (1964).
: Formation of anaphylatoxin in rat plasma, a specific enzymic process. Biochem. Pharmacol.15, 905–914 (1966).
Weil, M. H., andW. W. Spink: A comparison of shock due to endotoxin with anaphylactic shock. J. Lab. clin. Med.50, 501–515 (1957).
White, L. R., andR. G. Petersdorf: Species-specificity of endogenous pyrogen in serum. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)114, 567–571 (1963).
Wiedersheim, M., W. Hertlein, E. Husemann u.R. Lötterle: Über die Pharmakologie von wasserlöslichen Polysacchariden und Polysaccharidderivaten. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.217, 107–129 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogt, W., Lyncker, J. Differentiation between formation, in plasma, of anaphylatoxin and of endogenous pyrogen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 264, 23–31 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00997746
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00997746