Abstract
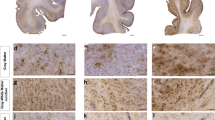
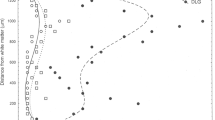
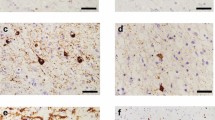
Two patients with acute Wemicke's encephalopathy, with the diagnosis confirmed pathologically at autopsy, showed substantial vacuolation and neuronal degeneration in discrete nuclei of the thalamus. Thalamic vacuolation has not been described previously in acute Wernicke's encephalopathy. The use of frozen sections to minimize processing artifact was fundamental in demonstrating this pathology. The pathogenic mechanism underlying this change appears to be different to that seen in the more typical periventricular, mamillary body and brainstem lesions. We hypothesize that a specific neural pathway may be involved and suggest that this pathway could be the ascending nitric oxide-containing cholinergic pathway from the brainstem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt, T., Bigl, V., Arendt, A. and Tenntedt, A. (1983). Loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease, paralysis agitans and Korsakoff's disease,Acta Neuropathol.,61: 101–108.
Butterworth, R. (1989). Effects of thiamin deficiency on brain metabolism: implications for the pathogenesis of the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome,Alcohol Alcohol.,24: 271–79.
Cravioto, H., Korein, J. and Silberman, J. (1961). Wernicke's encephalopathy — a clinical and pathological study of 28 cases,Arch. Neurol.,4: 510–519.
Ellison, D.W., Kowall, N.W. and Martin, J.B. (1987). Subset of neurons characterized by the presence of NADPH-diphorase in human substantia innominata,J. Comp. Neurol.,260: 233–245.
Harper, C. (1979). Wernicke's encephalopathy: a more common disease than realised,J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry,42: 226–231.
Harper, C. (1980) Sudden, unexpected death and Wernicke's encephalopathy: A complication of prolonged intravenous feeding,Aust. N. Z. J. Med.,10: 230.
Harper, C. (1981). Confusion, coma, and death from a preventable disease,Med. J. Aust.,2: 219–221.
Harper, C. (1983). The incidence of Wemicke's encephalopathy in Australia — a neuropathological study of 131 cases,J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry,46: 593–598.
Hazell, A.S. and Hakim, A.M. (1992). Development of glutamate induced excitotoxicity in experimental thiamin deficiency,Soc. Neurosci. Abstr.,18: 440.
Heckers, S., Geula, C. and Mesulam, M.-M. (1992). Cholinergic innervation of the human thalamus: Dual origin and differential nuclear distribution,J. Comp. Neurol.,325: 68–82.
Jones, E. and Thomas-Smith, W. (1971). Hypoglycaemic brain damage in the neonatal rat. In Brierley, J. and Meldrum, B. (eds.),Brain Hypoxia, William-Heinemann Medical Books, London, pp. 231–241.
Lancaster, F. (1992). Alcohol, nitric oxide, and neurotoxicity: Is there a connection?- A review,Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res.,16: 539–541.
Langlais, P.J. and Mair, R.G. (1990). Protective effects of the glutamate anatagonist MK-801 on pyrithiamine-induced lesions and amino acid changes in rat brain,J. Neurosci.,10: 1664–1674.
Meldrum, B. and Garthwaite, J. (1991). Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease,Trends Pharmacol. Sci.,11, Suppl.: 54–62.
Olney, J. (1990). Excitotoxin-mediated neuron death in youth and old age,Prog. Brain Res.,86:37–51.
Schroth, G., Wichmann, W. and Valavanis, A. (1991). Blood-brain-barrier disruption in acute Wernicke encephalopathy: MR findings,J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr.,15: 1059–1061.
Tanaka, K., Gotoh, F., Gomeh, S., Takashima, S., Mihara, B., Shirai, T., Nogawa, S. and Nagata, E. (1991). Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis induces a significant reduction in local cerebral blood flow in the rat,Neurosci. Lett.,127: 129–132.
Torvik, A. (1985). Two types of brain lesions in Wernicke's encephalopthy,Neuropath. Appl. Neurobiol.,11: 179–190.
Victor, M., Adams, R. and Collins, G. (1989).The Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome and Related Neurologic Disorders Due to Alcoholism and Malnutrition, 2nd ed., P.A. Davis & Co., Philadelphia.
Vincent, S., Satoh, K., Armstrong, D., Panula, P., Vales, W. and Fibiger, H. (1986). Neuropeptides and NADPH-diaphorase activity in the ascending cholinergic reticular system of the rat,Neuroscience,17: 167–182.
Vincent, S.R. and Hope, B.T. (1992). Neurons that say NO,Trends Neurosci.,15: 108–113.
Watanabe, I., Tomita, T., Hung, K. and Iwasaki, Y. (1981). Edematous necrosis in thiamine-deficient encephalopathy of the mouse,J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.,40: 454–471.
Zimitat, C., Kril, J., Harper, C.G. and Nixon, P.P. (1990). Progression of neurological disease in thiamin-deficient rats is enhanced by ethanol,Alcohol,7: 493–501.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byrne, C., Halliday, G., Ellis, J. et al. Thalmic vaciuation in acute Wernicke's encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 8, 107–113 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00996893
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00996893