Abstract
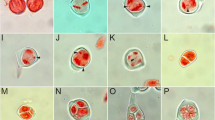
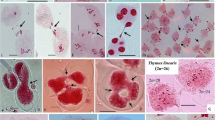
Meiosis was studied in aT. turgidum ×Ae. longissima hybrid (ABS1, 2n = 21) and in backcrosses of its amphidiploid toT. turgidum. Analysis of PMCs of the hybrid showed that non-reductional meiosis led to the production of a large number of non-reduced male gametes. The hybrid showed high seed set. All progeny had 2n = 42. The BC1 plants (2n = 35, AABBS1) showed the expected meiotic pairing of 14II + 7I. At anaphase I, univalents behaved in a non-reductional way. The possible role of meiotic non-reduction is discussed in terms of the evolution of theTriticum-Aegilops complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benavente, E., Orellana, J., 1986: Differential anaphase I behaviour between wheat and rye univalents inTriticale-wheat hybrid plants. — Genetica (NL)96: 161–166.
Blanco, A., Simeone, R., Orecchia, C., 1983: Cytology, morphology, and fertility of the amphiploidTriticum durum Desf. ×Haynaldia villosa (L.)Schur. — Proc. 6th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp. 1983. — Kyoto: University of Kyoto.
Croston, R. P., Williams, J. T., 1981: A world survey of wheat genetic resources. — Rome: IBPGR.
Giraldez, R., Lacadena, J. R., 1976: Univalents behaviour at anaphase I in desynaptic rye. — Chromosoma59: 63–72.
Golubovskaya, I. N., 1979: Genetic control of meiosis. — Int. Rev. Genet.58: 247–290.
Grant, V., 1971: Factors promoting polyploidy. — InGrant, V., (Ed.): Plant speciation, pp. 245–261. — New York, London: Columbia University Press.
Harlan, J. R., De Wet, J. M. J., 1975: OnÖ. Winge and a prayer: the origin of polyploidy. — Bot. Rev.41: 361–390.
Islam, A. K. M. R., Shepherd, K. W., 1980: Meiotic restitution in wheat-barley hybrids. — Chromosoma79: 363–372.
Koduru, P. R. K., 1980: Chromosome pairing and meiotic behaviour of univalents in the synaptic mutant of pearl millet,Pennisetum americanum (L.)Lekee (Gramineae). — Genetica (Tokyo)54: 191–195.
Maan, S. S., Sasakuma, T., 1977: Fertility of amphihaploids inTriticinae. — J. Heredity68: 87–94.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F., 1962: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. — Physiol. Plant.15: 473–497.
Nakajima, G., 1959: Cytogenetical studies on intergeneric hybrid betweenHaynaldia andSecale. III. External characteristics and meiosis in PMC's of F1 plants ofSecale fragile ×Haynaldia villosa. — Japan. J. Genet.34: 373–380.
Naranjo, T., Lacadena, J. R., 1982: Wheat univalents orientation at anaphase I in wheatrye derivates. — Chromosoma84: 653–661.
Padilla, J. A., Martin, A., 1987: Cytology, fertility, and morphology of amphiploidsHordeum chilense × tetraploid wheat (Tritordeum). — Pl. Breed.99: 295–302.
Rhoades, M. M., Dempsey, E., 1966: Induction of chromosome doubling at meiosis by the elongate gene in maize. — Genetics54: 505–522.
Satina, S., Blakeslee, A. F., 1935: Cytological effect of a gene inDatura which causes dyad formation in sporogenesis. — Bot. Gaz.96: 521–523.
Sears, E. R., Okamoto, M., 1958: Intergenomic chromosome relationships in hexaploid wheat. — Proc. X. Int. Congr. Genetics 2, pp. 258–259. — Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Stefani, A., 1986: Unreduced gametes in the F1 hybrid ofTriticum durum Desf. ×Haynaldia villosa Schur. — Z. Pfanzenzücht.96: 8–14.
Zohary, D., Feldman, M., 1962: Hybridization between amphidiploids and the evolution of polyploids in the wheat (Aegilops-Triticum) group. — Evolution16: 44–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pignone, D. Non-reductional meiosis in aTriticum turgidum ×Aegilops longissima hybrid and in backcrosses of its amphidiploid withT. turgidum (Poaceae). Pl Syst Evol 187, 127–134 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994095
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994095