Abstract
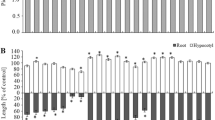
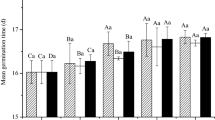
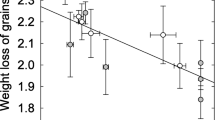
Phenylacetic acid (PAA), one of the phytotoxic compounds in corn (Zea mays) pollen, was identified by GC-MS and by direct comparison with a pure commercial sample of PAA. Bioassays were carried out by testing whole pollen, methylene chloride extract of the pollen, and pure PAA on germination and radical growth ofAmaranthus leucocarpus andEchinochloa crusgalli. The effect of corn pollen was compared with that ofZea mexicana (Teosinte), one of the wild relatives of cultivated maize.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, H., Uchiyama, M., andSato, R. 1974. Isolation of phenyl acetic acid and its phydroxy derivative as auxinlike substances fromUndaria pinnatifida.Agric. Biol. Chem. 38:897–898.
Anaya, A.L.,Ramos, L.,Hernandez, J., andCruz-Ortega, R. 1987. Allelopathy in Mexico, pp. 89–101,in G.R. Waller (ed.). Allelochemicals: Role in Agriculture and Forestry. ACS Symposium Series 330. Washington, D.C.
Anaya, A.L., Calera, M.R., Mata, R., andPereda-Miranda, R. 1990. Allelopathic potential of compounds isolated fromIpomoea tricolor Cav (Convolvulaceae).J. Chem. Ecol. 16:2145–2152.
Anaya, A.L., Cruz-Ortega, R., andNava, V. (1992). Impact of allelopathy in the traditional management of agroecosystems in Mexico,in S.J.H. Rizvi and V. Rizvi (eds.). Allelopathy: Basic and Applied Aspects. Chapman and Hall, London. In press.
Anderson, R.J. 1923. Composition of corn pollen.J. Biol. Chem. 5:611–628.
Ceska, O., andStyles, E.D. 1984. Flavonoids fromZea mays pollen.Phytochemistry 23:1822–1823.
Chou, Ch.H., andPatrick, Z.A. 1976. Identification and phytotoxic activity of compounds produced during decomposition of com and rye residues in soil.J. Chem. Ecol. 2:369–387.
Chuman, T., andNoguchi, M. 1977. Acidic aroma constituents of Turkish tobacco.Agric. Biol. Chem. 41: 1021–1030.
Cruz-Ortega, R., Anaya, A.L., andRamos, L. 1988. Effects of allelopathic compounds of corn pollen on respiration and cell division of watermelon.J. Chem. Ecol. 14:71–86.
Jimenez-Osornio, J.J., andSchultz, K. 1981. Relaciones cultivoarvenses en una “chinampa.” Thesis, Science Faculty, Mexico, UNAM.
Jimenez-Osornio, J.J., Schultz, K., Anaya, A.L., Hernandez, J., andEspejo, O. 1983. Allelopathic potential of corn pollen(Zea mays “Chalquinocónico”).J. Chem. Ecol. 9:1011–1026.
Kanchan, S.D. 1975. Allelopathic effects ofParthenium pollen, pp. 72–73,in Proceedings of the 62nd Session of Indian Science Congress, Section of Botany, ISCAP, New Delhi.
Kanchan, S., andJayachandra. 1980. Pollen allelopathy, a new phenomenon.New Phytol. 84:739–746.
Katsumata, T., Nakamura, S., andTogasawa, Y. 1974. Biochemical studies on pollen (part 12): Flavonoid compounds from pollen.J. Fac. Agric. Iwate Univ. 12:21–32.
Kimland, B., Aasen, A.J., Almqvist, S.O., Arpino, P., andEnzell, C.R. 1973. Volatile acids of suncured GreekNicotiana tabacum.Phytochemistry 12:835–847.
Kvanta, E. 1968. Sterols in pollen.Acta Chem. Scand. 22:2161–2165.
Maugh, T.H. II 1981. New chemical promise larger crops.Science 212:33.
Murphy, S.D., andAarssen, L.W. 1989. Pollen allelopathy among sympatric grassland species: In vitro evidence inPhleum pratense L. New Phytol. 112:295–306.
Nair, M.G., andBurke, B.A. 1988. A new fatty acid methyl ester and other biologically active compounds fromAspergillus niger.Phytochemistry 27:3169–3173.
Nilsson, M., Ryhage, R., andSydow, E. Von. 1957. Constituents of pollen.Acta Chem. Scand. 11:634–639.
Ostle, B. 1963. Statistics in Research. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa. XV + 585 pp.
Rasmussen, L.E.L., Hess, D.L., andHaight, J.D. 1990. Chemical analysis of temporal gland secretions collected from an Asian bull elephant during a fourmonth musth episode.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:2167–2181.
Schildknecht, H., andKoob, K. 1971. Myrmicacin, the first insect herbicide.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10:124–125.
Stanley, R.G., andLinskens, H.R. 1974. Pollen: Biology, Biochemistry, Management. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Suzuki, Y., Yamaguchi, I., Yokota, T., andTakahashi, N. 1986. Identification of castasterone, typhasterol, and teasterone from pollen ofZea mays.Agric. Biol. Chem. 50:3133–3138.
Thomson, J.D., Andrews, B.J., andPlowright, R.C. 1982. The effect of a foreign pollen on ovule development inDiervilla lonicera (Caprifoliaceae).New Phytol. 90:777–783.
Wightman, F., andLighty, D.L. 1982. Identification of phenylacetic acid as a natural auxin in the shoots of higher plants.Physiol. Plant. 55:17.
Yasuhara, A., andFuwa, K. 1983. Isolation and analysis of odorous components in swine manure.J. Chromatogr. 281:225–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anaya, A.L., Hernandez-Bautista, B.E., Jimenez-Estrada, M. et al. Phenylacetic acid as a phytotoxic compound of corn pollen. J Chem Ecol 18, 897–905 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988330
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988330