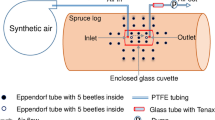
Abstract
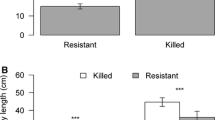
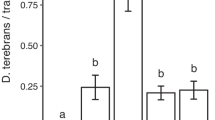
exo-brevicomin, a multifunctional pheromone of the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae, was tested at release rates of 0.5 and 2.5 mg/day alone and in combination with the antiaggregation pheromone verbenone against unbaited controls. Significantly more lodgepole pinePinus contorta var.latifolia trees were attacked, and at higher densities, with both release rates ofexo-brevicomin than with all other treatments. Verbenone significantly reduced the response of mountain pine beetles toexo-brevicomin. Verbenone alone did not reduce the number of trees attacked by mountain pine beetle or the attack density when compared to the unbaited controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amman, G.D., Thier, R.W., McGregor, M.D., andSchmitz, R.F. 1989. Efficacy of verbenone in reducing lodgepole pine infestation by mountain pine beetles in Idaho.Can. J. For. Res. 19:60–64.
Bakke, A. 1981. Inhibition of the response inIps typographus to the aggregation pheromone; field evaluation of verbenone and ipsenol.X. Angew. Entomol. 92:172–177.
Bedard, W.D., Tilden, P.E., Lindahl, K.Q., Wood, D.L., andRauch, P.A. 1980. Effects of verbenone andtrans-verbenol on the response ofDendroctonus brevicomis to natural and synthetic attractant in the field.J. Chem. Ecol. 6: 997–1013.
Bentz, B.,Lister, C.K.,Schmid, J.M.,Mata, S.A.,Rasmussen, L.A., andHaneman, D. 1989. Does verbenone reduce mountain pine beetle attacks in susceptible stands of ponderosa pine? U.S.D.A., Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest Range Experiment Station, Research Note RM-495.
Billings, R.F., Gara, R.I., andHrutfiord, B.F. 1976. Influence of ponderosa pine resin volatiles on the response ofDendroctonus ponderosae to synthetictrans-verbenol.Environ. Entomol. 5:171–179.
Borden, J.H., andLacey, T.E. 1985. Semiochemical-based manipulation of the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins: A component of lodgepole pine silviculture in the Merritt Timber Supply area of British Columbia.Z. Angew. Entomol. 99:139–145.
Borden, J.H., Conn, J.E., Friskie, L.M., Scott, B.E., Chong, L.J., Pierce, H.D., Jr., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1983. Semiochemicals for the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), in British Columbia: Baited-tree studies.Can. J. For. Res. 13:325–333.
Borden, J.H., Ryker, L.C., Chong, L.J., Pierce, H.D., Jr., Johnston, B.D., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1987. Response of the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), to five semiochemicals in British Columbia lodgepole forests.Can. J. For. Res. 17:118–128.
Borden, J.H., Chong, L.J., andLindgren, B.S. 1990. Redundancy in the semiochemical message required to induce attack on lodgepole pines by the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Scolytidae).Can. Entomol. 122:769–777.
Byers, J.A., andWood, D.L. 1980. Interspecific inhibitions of the response of the bark beetles.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:149–164.
Byers, J.A., Lanne, B.S., andLofqvist, J. 1989. Host tree unsuitability recognized by pine shoot beetles in flight.Experientia 45:489–492.
Conn, J.E., Borden, J.H., Scott, B.E., Friskie, L.M., Pierce, H.D., Jr., andOehlschlager, A.C. 1983. Semiochemicals for the mountain pine beetle,Dendroctonus ponderosae (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), in British Columbia: Field trapping studies.Can. J. For. Res. 13:320–324.
Gibson, K.E. 1989. Mountain pine beetle status-western United States, pp. 4–5,in G.D. Amman (ed.). Proceedings-Symposium on the Management of Lodgepole Pine to Minimize Losses to the Mountain Pine Beetle. U.S.D.A. Forest Service, International Research Station, General Technical Report INT-262.
Hughes, P.R., andPitman, G.B. 1970. A method for observing and recording the flight behaviour of tethered bark beetles in response to chemical messengers.Boyce Thompson Inst. 24:329–336.
Libbey, L.M., Ryker, L.C., andYandell, K.L. 1985. Laboratory and field studies of volatiles released byDendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera, Scolytidae).Z. Angew. Entomol. 100:381–392.
Lindgren, B.S., Borden, J.H., Cushon, L.J., andHiggins, C.J. 1989. Reduction of mountain pine beetle (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) attacks by verbenone in lodgepole pine stands in British Columbia.Can. J. For. Res. 19:65–68.
Livingston, W.H., Bedard, W.D., Mangini, A.C., andKinzer, H.G. 1983. Verbenone interrupts attraction of roundheaded pine beetle,Dendroctonus adjunctus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), to sources of its natural attractant.J. Econ. Entomol. 76:1041–1043.
McKnight, R.C. 1979. Differences in response among populations ofDendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins to its pheromone complex. MSc thesis. University of Washington.
McMullen, L.H.,Safranyik, L., andLinton, D.A. 1986. Suppression of mountain pine beetle infestations in lodgepole pine forests. Canadian Forest Service, Pacific Forest Research Centre, Information Report BC-X-276.
Payne, T.L., Coster, J.E., Richerson, J.V., Edson, L.J., andHart, E.R. 1978. Field response of the southern pine beetle to behavioral chemicals.Environ. Entomol. 7:578–582.
Pitman, G.B. 1971.trans-Verbenol and alpha-pinene: Their utility in manipulation of the mountain pine beetle.J. Econ. Entomol. 64:426–430.
Pitman, G.B., Vité, J.P., Kinzer, G.W., andFentiman, A.F., Jr. 1968. Bark beetle attractants:trans-Verbenol isolated fromDendroctonus.Nature 218:168–169.
Pitman, G.B., Vité, J.P., Kinzer, G.W., andFentiman, A.F., Jr. 1969. Specificity of populationaggregating pheromones inDendroctonus.J. Insect. Physiol. 15:363–366.
Renwick, J.A.A. 1967. Identification of two oxygenated terpenes from the bark beetlesDendroctonus frontalis andDendroctonus brevicomis.Boyce Thompson Inst. 23:355–360.
Renwick, J.A.A., andVite, J.P. 1970. Systems of chemical communication inDendroctonus.Boyce Thompson Inst. 24:283–292.
Richerson, J.V., andPayne, T.L. 1979. Effects of bark beetle inhibitors on landing and attack behavior of the southern pine beetle and beetle associates.Environ. Entomol. 8:360–364.
Rudinsky, J.A., Morgan, M.E., Libby, L.M., andPutnam, T.B. 1974. Antiaggregative rivalry pheromone of the mountain pine beetle, and a new arrestant of the southern pine beetle.Environ. Entomol. 3:90–98.
Ryker, L.C., andRudinsky, J.A. 1982. Field bioassay ofexo-andendo-brevicomin withDendroctonus ponderosae in lodgepole pine.J. Chem. Ecol. 8:701–707.
Ryker, L.C., andYandell, K.L. 1983. Effects of verbenone on aggregation ofDendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera, Scolytidae) to synthetic attractant.Z. Angew. Entomol. 96:452–459.
Safranyik, L. 1988. Estimating attack and brood totals and densities of the mountain pine beetle in individual lodgepole pine trees.Can. Entomol. 120:323–331.
Safranyik, L.,Shrimpton, D.M., andWhitney, H.S. 1974. Management of lodgepole pine to reduce losses from the mountain pine beetle. Environment Canada, Canadian Forest Service, Forest Technical Report 1.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1985. SAS Users Guide: Statistics, Version 5 Edition. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, North Carolina.
Schlyter, R., Byers, J.A., Lofqvist, J., Leufven, A., andBirgersson, G. 1988. Reduction of attack density of the bark beetlesIps typographus andTomicus on host bark by verbenone inhibition of attraction to pheromone and host kairomone, pp. 53–63in T.L. Payne and H. Saarenmaa (eds.). Proceedings of the IUFRO Working Party and XVIII International Congress of Entomological Symposium, “Integrated Control of Scolytid Bark Beetles.” Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
Schmitz, R.F., andMcGregor, M.D. 1990. Antiaggregative effects of verbenone on response of the mountain pine beetle to baited traps. U.S.D.A. Forest Service, International Research Station, Research Paper INT-423.
Silverstein, R.M., Brownlee, R.G., Bellas, T.E., Wood, D.L., andBrown, L.E. 1968. Brevicomin: principal sex attractant in the frass of the female western pine beetle.Science 159:889–891.
Van Sickle, G.A. 1989. Status of mountain pine beetle in western Canada, (1988), pp. 6–8,in G.D. Amman (ed.). Proceedings-Symposium on the Management of Lodgepole Pine to Minimize Losses to the Mountain Pine Beetle. U.S.D.A. Forest Service, International Research Station, General Technical Report INT-262.
Watterson, G.P., Payne, T.L., andRicherson, J.V. 1981. The effects of verbenone and brevicomin on the within-tree populations ofDendroctonus frontalis.J. Ga. Entomol. Soc. 17:119–126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shore, T.L., Safranyak, L. & Lindgren, B.S. The response of mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) to lodgepole pine trees baited with verbenone and exo-brevicomin. J Chem Ecol 18, 533–541 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00987817
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00987817