Abstract
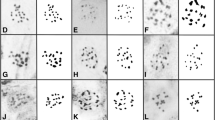
Basic chromosome number inGalaxia is believed to be x = 9, and this number, or multiples, occurs in all species of subgenusGalaxia. In subgenusEurystigma, G. barnardii has n = 8,G. versicolor n = 8 and 7,G. citrina n = 8, 7 and 17 whileG. variabilis has n = 7 exclusively. Karyotypes in forms ofG. versicolor with n = 7 and inG. variabilis are quite different and clearly originated independently. Karyotypic features provide evidence for the hypothesis that changes in chromosome number were accomplished through chromosome fusion either by classical Robertsonian translocation, or unequal reciprocal translocation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose, S., Flory, W. S., 1963: A study of phylogeny and of karyotype evolution inLycoris. — Nucleus (Calcutta)6, 141–156.
Goldblatt, P., 1971: Cytological and morphological studies in the southern AfricanIridaceae. — J. S. Afr. Bot.37, 317–460.
, 1976: A revision ofMoraea (Iridaceae) in the winter rainfall region of southern Africa. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gdn.63, 657–786.
- 1979: Biology and systematics ofGalaxia (Iridaceae). — J. S. Afr. Bot.45. (In press.)
Hair, T. B., Beuzenberg, E. J., 1958: Chromosomal evolution in thePodocarpoceae. — Nature (Lond.)181, 1584–1586.
Jackson, R. C., 1962: Interspecific hybridication inHaplopappus and its bearing in chromosome evolution in theBlepharodon section. — Am. J. Bot.49, 119–132.
John, B., Freeman, M., 1975: Causes and consequences of Robertsonian exchange. — Chromosoma52, 123–136.
Jones, K., 1974: Chromosome evolution by Robertsonian translocation inGibasis (Commelinaceae). — Chromosoma45, 353–368.
, 1977: The role of Robertsonian change in karyotype evolution in higher plants. — Chromosomes Today6, 121–129.
Kyhos, D., 1965: The independent aneuploid origin of two species ofChaenactis (Compositae) from a common ancestor. — Evolution19, 26–43.
Sherman, M., 1946: Karyotype evolution: A cytogenetic study of seven species and six interspecific hybrids ofCrepis. — Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot.18, 369–408.
Small, E., 1971: The evolution of reproductive isolation inClarkia sectionMyxocarpa. — Evolution25, 330–346.
Tobgy, H. A., 1943: A cytological study ofCrepis fuliginosa andC. neglecta and their F1 hybrid, and its bearing on the mechanism of phylogenetic reduction in chromosome number. — J. Genet.45, 67–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldblatt, P. Chromosome cytology and karyotype change inGalaxia (Iridaceae). Pl Syst Evol 133, 61–69 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985879
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985879