Abstract
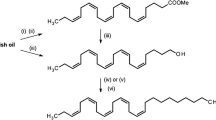
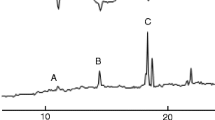
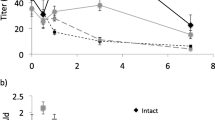
Tritium-labeled components of the red-banded leaf-roller female sex pheromone, (Z)- and (E)-[11,12-3H2]-11-tetradecenyl acetate (57 Ci/mmol), applied to antennae of males and females were degraded causing formation of tritiated 11-tetradecenol, 11-tetradecenoic acid, and water. Results indicate that the catabolic pathway involves acetate hydrolysis, oxidation of alcohol to fatty acid, and degradation of the acid viaβ-oxidation. Both geometric isomers were degraded equally well by males but degradation proceeded comparatively less rapidly with female antennae. It is surmised that under natural conditions of olfactory sensing, sex pheromone impinging upon the moth's antennae is probably subject to a similar catabolic fate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjostad, L., Linn, C., Roelofs, W., andDu, J.W. 1985. Identification of new sex pheromone components inTrichoplusia ni andArgyrotaenia velutinana, predicted from biosynthetic precursors, pp. 224–237,in Semiochemistry: Flavors and Pheromones. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin.
Ferkovich, S.M. 1982. Enzymatic alteration of insect pheromones, pp. 165–186,in D.M. Norris (ed.). Perception of Behavioral Chemicals. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam.
Ferkovich, S.M., Mayer, M.S., andRutter, R.R. 1972. Conversion of the sex pheromone of the cabbage looper.Nature 242:53–55.
Hansson, B.S., Ljungberg, H., Hallberg, E., andLöfstedt, C. 1992. Functional specialization of olfactory glomeruli in a moth.Science 256:1313–1315.
Kasang, G. 1971. Bombykol reception and metabolism on the antennae of the silkwormBombyx mori, pp. 245–250,in G. Ohloff and A.F. Thomas (eds.). Gustation and Olfaction. Academic Press, New York.
Kasang, G., Knauer, B., andBeroza, M. 1974. Uptake of the sex attractant3H-disparlure by male gypsy moth antennae (Lymantria dispar) (Ponhetria dispar).Experientia 30:147–148.
Kasang, G., Nicholls, M., andVon Proff, L. 1989. Sex pheromone conversion and degradation in antennae of the silkworm mothBombyx moriL.Experientia 45:81–87.
Klun, J.A., Schwarz, M., andUebel, E.C. 1991. European corn borer: Pheromonal catabolism and behavioral response to sex pheromone.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:317–334.
Klun, J.A., Schwarz, M., andUebel, E.C. 1992. Biological activity and in vivo degradation of tritiated female sex pheromone in the male European corn borer.J. Chem. Ecol. 18:283–298.
Lehninger, A.L. 1975. Biochemistry. Worth Publishers, New York, pp. 544–553.
Prestwich, G.D. 1987. Chemical studies of pheromone reception and catabolism, pp. 473–527,in G.D. Prestwich and G.J. Blomquist (eds.). Pheromone Biochemistry. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida.
Prestwich, G.D., Graham, S.M., andKoenig, W.A. 1989. Enantioselective opening of the (+)- and (−)-disparlure by epoxide hydrolase in gypsy moth antennae.J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1989:575–577.
Prestwich, G.D., Graham, S.M., Kuo, J.-W., andVogt, R.G. 1990. Tritium-labeled enantiomers of disparlure. Synthesis and in vitro metabolism.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111:636–642.
Raming, K., andBreer, H. 1990. Comparative studies on G-proteins in the nervous tissue of invertebrates.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 956:861–864.
Tasayco, M.L., andPrestwich, G.D. 1990. Aldehyde-oxidizing enzymes in an adult moth: in vitro study of aldehyde metabolism inHeliothis virescens.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 278:444–451.
Vogt, R.G., Prestwich, G.D., andRiddiford, L.M. 1988. Sex pheromone receptor proteins. Visualization using a radiolabeled photoaffinity analog.J. Biol. Chem. 263:3952–3957.
Voot, R.G., Prestwich, G.D., andLerner, M.R. 1991. Odorant-binding-protein subfamilies associate with distinct classes of olfactory receptor neurons in insects.J. Neurobiol. 22:74–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klun, J.A., Schwarz, M. Sex pheromone catabolism in the redbanded leafroller moth. J Chem Ecol 19, 751–762 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985006
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00985006